History of the Procedure
Thyroglossal duct cysts are among the most common congenital neck masses. The thyroglossal duct is a remnant epithelial tract that forms as the thyroid gland migrates from its origin at the foramen cecum to its final position in the anterior neck.
Simple excision of the thyroglossal duct is associated with a high recurrence rate. In 1893, Schlange described excision of the thyroglossal duct en bloc with the central portion of the hyoid bone. Schlange’s approach was associated with a lower recurrence rate compared to simple excision. In 1920, Sistrunk extended Schlange’s approach to include excision of a cuff of tissue between the hyoid bone and the foramen cecum. Sistrunk’s procedure reduced the recurrence rate from about 50% to 5%. Today, the Sistrunk procedure is considered the standard management approach for thyroglossal duct cysts.
History of the Procedure
Thyroglossal duct cysts are among the most common congenital neck masses. The thyroglossal duct is a remnant epithelial tract that forms as the thyroid gland migrates from its origin at the foramen cecum to its final position in the anterior neck.
Simple excision of the thyroglossal duct is associated with a high recurrence rate. In 1893, Schlange described excision of the thyroglossal duct en bloc with the central portion of the hyoid bone. Schlange’s approach was associated with a lower recurrence rate compared to simple excision. In 1920, Sistrunk extended Schlange’s approach to include excision of a cuff of tissue between the hyoid bone and the foramen cecum. Sistrunk’s procedure reduced the recurrence rate from about 50% to 5%. Today, the Sistrunk procedure is considered the standard management approach for thyroglossal duct cysts.
Indications for the Use of the Procedure
A thyroglossal duct cyst (TGDC) commonly presents as a midline neck mass below the hyoid bone that moves with swallowing and tongue protrusion. In a few cases, the cyst may present above the level of the hyoid bone. The diagnosis of TGDC is mostly based on history and physical examination. Ultrasonography may be obtained to confirm the cystic lesion and the presence of a normal thyroid gland. Surgical excision of the TGDC is indicated in the setting of recurrent infection, recurrent drainage, cosmesis, and to rule out the presence of malignancy.
Limitations and Contraindications
In some cases, the TGDC may represent the only functioning thyroid tissue. Excision of the TGDC results in permanent hypothyroidism requiring thyroid hormone replacement. Surgical excision is also contraindicated in the setting of active infection, as this is associated with a higher rate of recurrence. The infection should be treated prior to excision of the TGDC.
Technique: Sistrunk Procedure
Step 1:
Position and Incision
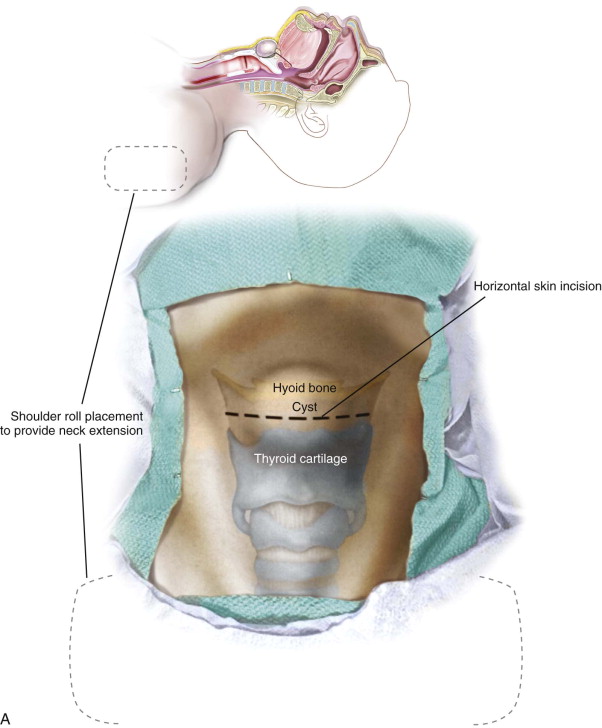
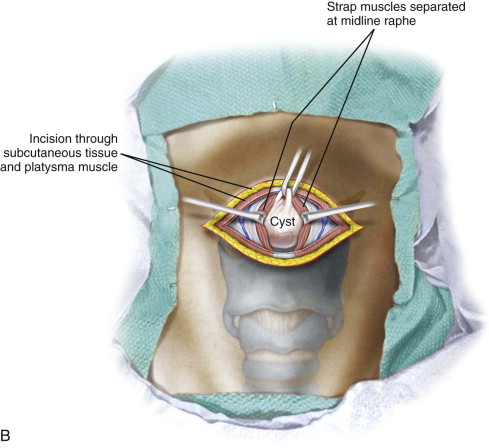
The patient is placed in the supine position, and a shoulder roll is used to extend the neck. A transverse incision is marked in the midline through a skin crease in the upper neck slightly below the level of the hyoid bone. The patient is draped in a manner that provides access to the oral cavity ( Figure 91-1, A ).
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses