12
Risks and benefits of orthodontic treatment
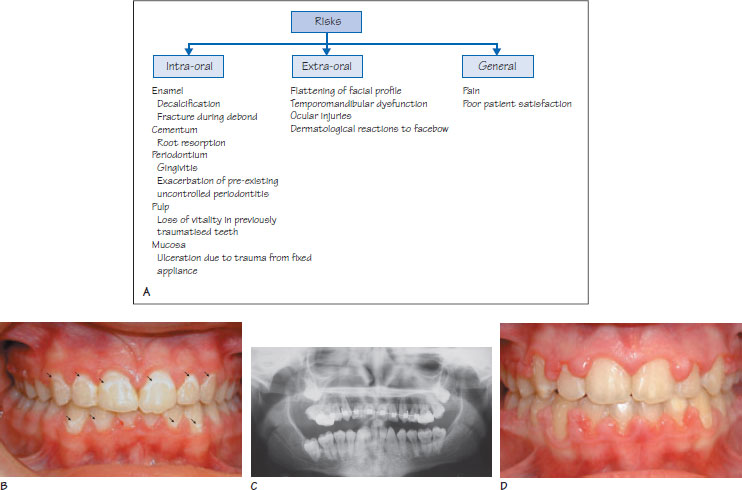
Figure 12.1 (A) The risks of orthodontic treatment. (B) Enamel decalcification associated with orthodontic treatment. This commonly occurs located adjacent to the gingival margin where plaque readily accumulates. (C) A rare example of severe root resorption following fixed appliance therapy: it can be seen that the maxillary incisor roots are resorbed. (D) Gingival hyperplasia during orthodontic treatment.
The decision to undergo orthodontic treatment should be based upon an evaluation of the risks and benefits of the procedure (risk–benefit analysis). The aim of this chapter is to give an overview of the factors that require consideration during the treatment planning stage.
Benefits of orthodontic treatment
The benefits of orthodontic treatment can be considered under the following headings:
- Psychological;
- Dental health;
- Functional.
Psychological benefits
The smile is an important component of an attractive facial appearance. Malocclusion may affect self-esteem and social interaction, and can be a focus of teasing. Individuals with similar degrees of malocclusion can be affected differently depending on their self-esteem. Therefore, it should not always be assumed that any given dental irregularity will require treatment from the point of psychological benefits. There is evidence to suggest that orthodontic treatment can lead to an improvement in self-esteem and psychological health in those whose malocclusion is affecting them psychologically.
Dental health benefits
Dental health benefits of orthodontic treatment include:
- A reduction in the risk of sustaining traumatic dental injuries. An increased overjet and lip incompetence increases the susceptibility of the upper incisors to traumatic dental injuries. The risk of traumatic injury is proportional to the size of the overjet as shown in Table 12.1.
- A reduction in complications associated with mandibular displacement. A posterior crossbite associated with a lateral mandibular displacement may predispose to temporomandibular joint dysfunction within a susceptible patient. An anterior crossbite associated with a mandibular displacement can exacerbate toothwear of the incisal edges and compromise the periodontal health of the lower incisors.
- A reduction in complications associated with deep traumatic overbite. A traumatic overbite may aggravate periodontal destruction of the upper palatal and lower labial gingivae if oral hygiene is poor. A deep overbite can also potentiate toothwear at the site where the incisors shear past each other.
- A reduction in complications associated with impacted teeth. Impacted teeth may resorb the roots of adjacent teeth and their dental follicle may undergo cystic change in rare circumstances.
- A reduction in caries and improvement of periodontal health? There is no evidence />
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


