Chapter 10 The Lower Limb
The Lower Limb
1 Skeleton
PELVIC GIRDLE
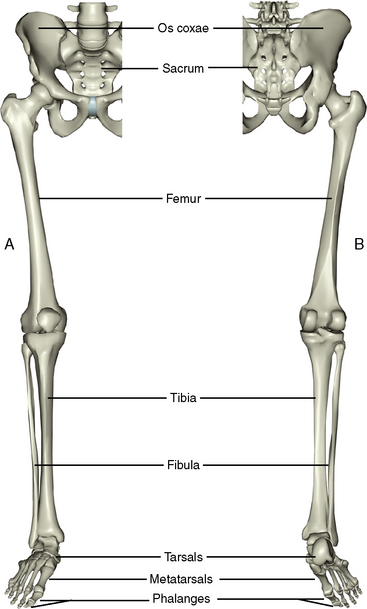
The lower limb girdle consists of the right and left os coxae, the sacrum, and the coccyx (Figure 10-1). The bones of the pelvis were considered in Chapter 4, Section 1.
THIGH
Femur
Description
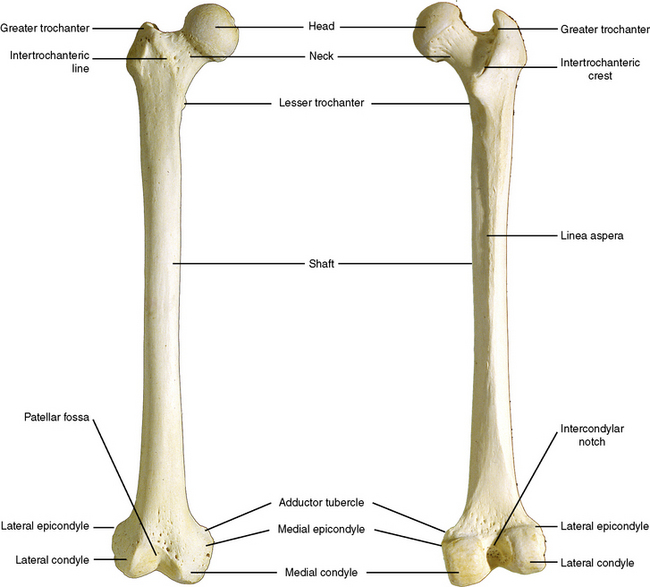
The femur is the only bone of the thigh (Figure 10-2). It is a large, long bone with a rounded head superiorly that articulates with the os coxae and two large knuckles, or condyles, that articulate inferiorly with the tibia.
Features
Patella
The patella is a sesamoid bone embedded within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle (Figure 10-3). The anterior surface is roughened for the tendinous attachments to the quadriceps femoris muscle. The medial and lateral borders converge inferiorly as the apex. The posterior aspect of the patella is lined with articular cartilage that articulates with the trochlea of the femur. The articular surface is divided into several facets.
LEG
There are two long bones of the leg, the tibia on the medial aspect and the fibula on the lateral.
Tibia
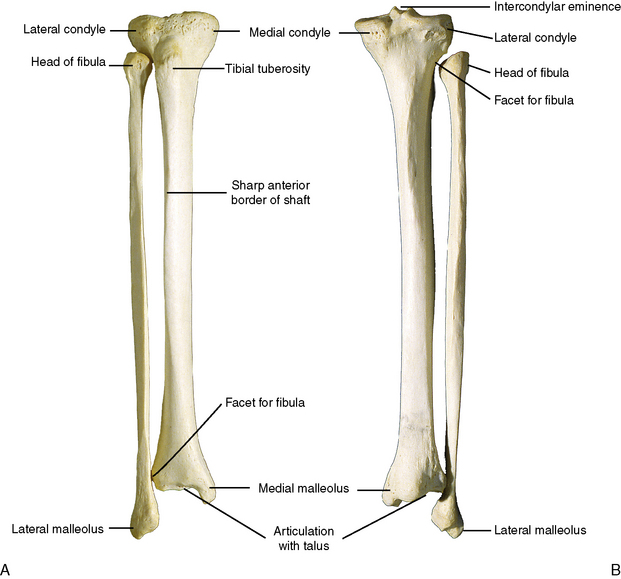
Description
The tibia is relatively strong and massive because it bears all of the weight transmitted inferiorly from the femur and, in turn, transfers the weight to the ankle below (Figure 10-4).
Features
ANKLE AND FOOT
Tarsal Bones
The tarsal bones in the ankle correspond to the carpal bones of the wrist, but there are seven tarsals in the ankle compared to eight carpals in the wrist (Figure 10-5). The tarsals occupy the posterior half of the foot. Two tarsals, the talus and calcaneus, are considerably larger, weight-bearing bones and comprise the entire posterior aspect of the foot.
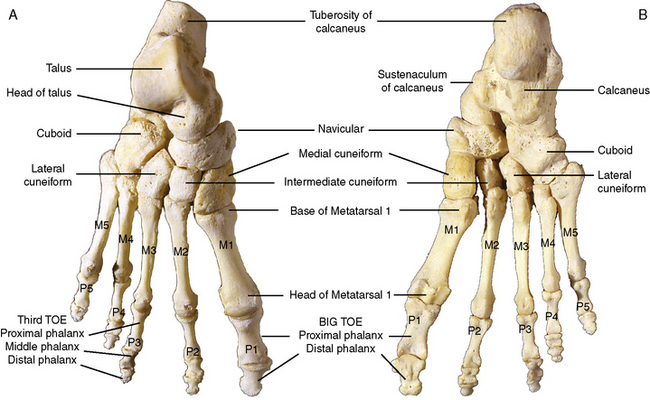
Figure 10-5 Bones of the right foot. A, Dorsal aspect. B, Plantar aspect. M, Metatarsal; P, phalanx.
2 Joints
THE PELVIC GIRDLE
Features
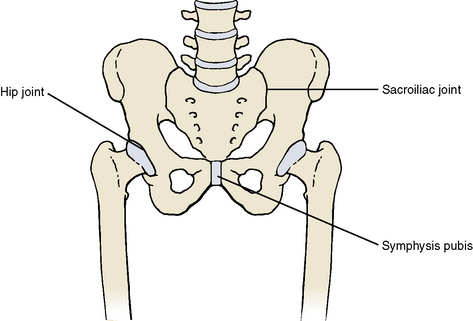
Two joints anchor the pelvic girdle to the axial skeleton: (1) the sacroiliac joint and (2) the hip joint (Figure 10-6).
HIP JOINT
Features
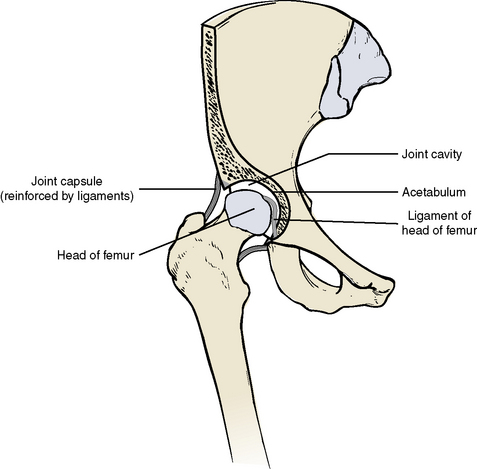
The hip joint is an extremely stable yet moveable ball-and-socket joint (Figure 10-7). It is an articulation between the spherical head of the femur (ball) and the cup-shaped acetabulum of the os coxae (socket). The articular surface of the acetabulum is horseshoe-shaped. The concavity of the acetabulum is further deepened by the acetabular labrum, a fibrocartilage ring that encircles the rim of the fossa. A joint capsule surrounds the joint, affording it a fair degree of movement. The capsule is thickened and reinforced by three strong ligaments running from each component of the os coxae to the neck of the femur to prevent dislocation of the joint. The ligaments include the iliofemoral ligament anteriorly, the ischiofemoral ligament posteriorly, and the pubofemoral ligament inferiorly and anteriorly. The ligament of the head of the femur is a rather weak ligament that runs from the lower end of the acetabulum to the fovea on the head of the femur. It may contain a small nutrient artery to the head of the femur.
Movements
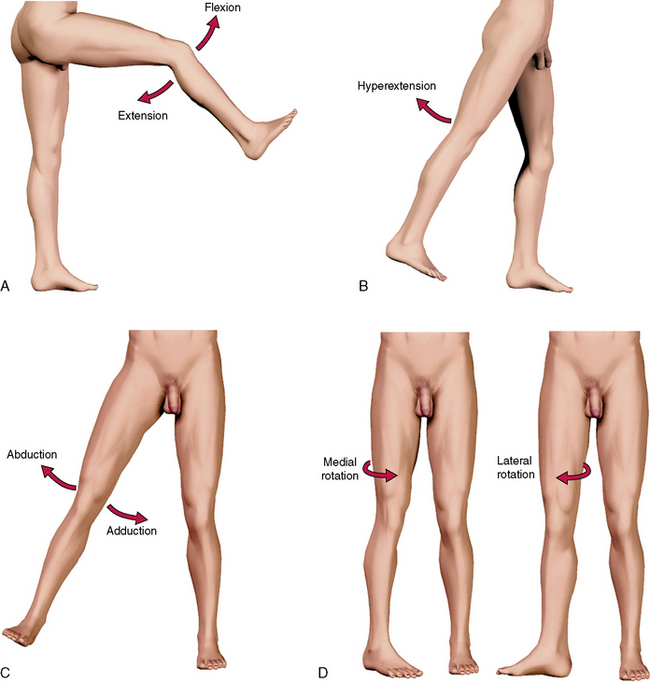
The following movements are described in relation to the anatomical position (Figure 10-8). This assumes that the foot is moved from the ground with resultant movement of the femur at the hip. If the foot remains on the ground, however, the os coxae moves in relation to the femur. The hip joint is capable of six movements:
THE KNEE JOINT
The knee joint is the largest and perhaps the most complicated joint in the body (Figure 10-9). It is classified as a synovial joint with interposing fibrocartilage discs, or menisci. The knee is really a complex of three joints: (1) between the lateral condyles of the femur and tibia, (2) between the medial condyles of the femur and the tibia, and (3) between the patella and the femur. The joints between the tibia and femur represent the weight-bearing portion of the knee. They are moveable, synovial joints that allow a combined hinge and sliding type movement and limited rotation. The joint between the patella and the femur allows a sliding type of movement.
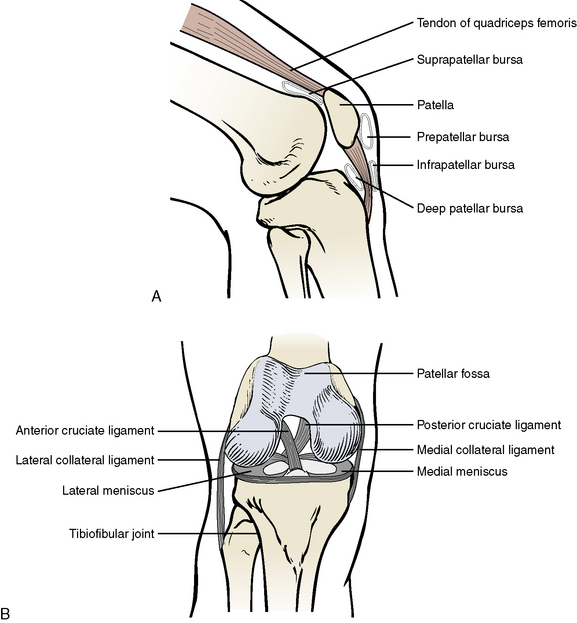
Figure 10-9 Internal features of the right knee. A, Lateral view. B, Anterior view with the knee flexed.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses