R
Radiation Process of emission of energy in the form of waves or particles. When radiation impinges on matter, it is absorbed (ie, transformed), transmitted, or reflected.
Radiation-damaged bone and soft tissues See: Osteoradionecrosis (ORN).
Radiograph Portrayal of hard tissue structures on film sensitive to x-rays and light. See also: Panoramic radiograph.
Radiographic guide See: Radiographic template.
Radiographic marker See: Radiopaque marker.
Radiographic prosthesis Prosthesis that represents the position of missing teeth and dentoalveolar tissues for radiographic imaging. Structure or marking that directs the motion or positioning of something. It is used to transfer the intended position of the implant from the diagnostic cast to the patient and to record its relationship to the underlying bone. Compare: Radiographic template; Surgical template.
Radiographic template Acrylic resin guide used by the surgeon to direct placement of an implant into its proper position. It is based on the information from two-dimensional panoramic radiographs or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) or digital volume tomography (DVT) images to achieve optimal implant body placement within the available bone and to preserve vital structures.
Radiology Medical specialty directing medical imaging technologies for the diagnosis and possible treatment of diseases.
Radionecrosis Osteonecrosis induced by radiation. It can occur in patients who have undergone radiotherapy because of a malignant process in the ear, nose, and throat (ENT) or other maxillofacial region.
Radiopaque marker Marker made of metal, or any radiopaque material (eg, radiopaque filling material) that is placed into the mouth before taking radiographs. Detected in the radiograph, the markers help to interpret the image mostly for length, angulation, or localization assessment.
Ramus Bilateral posterior vertical extensions of the mandibular body. At the superior border, each ramus ends in two processes: the coronoid, which is anterior, and the condyle, which is separated posteriorly by a deep concavity.
Ramus frame implant One-piece implant of tripodal design consisting of a horizontal supragingival connecting bar with right and left posterior extensions that extend into bilateral ascending rami and one area that extends from the U-shaped frame into the anterior symphysis area. Later design changes incorporated multi-pieces for the same U-shaped frame.1-3 (See figure next page.)
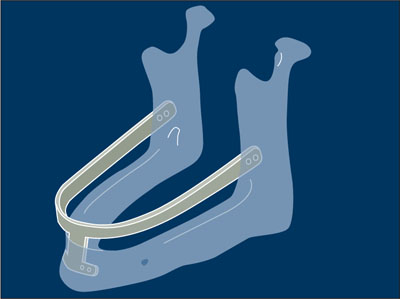
Ramus frame implant.
Ramus graft See: Alveolar ridge augmentation; Bone graft, Donor site for; Mandibular block graft, from the ramus.
Ramus implant “A type of endosseous blade implant placed into the anterior border of the mandibular ramus.”3 See also: Implant type.
Random assignment Process of assigning study participants to experimental or control groups at random, such that each participant has an equal probability of being assigned to any given group. This method of assignment helps to prevent bias in a study.4
Random controlled trial Experimental study in which participants are randomly assigned to a treatment or a control group.4 See also: Random assignment.
Range Distance between the highest and the lowest values of distribution.
Rank sum test Comparison of two groups on the median values of the response variable. Called also Wilcoxon rank sum test.4
RAP Abbreviation for Regional acceleration phenomenon.
Ratchet Instrument with “a mechanism consisting of a metal wheel operating with a catch that permits motion in only one direction.”5
RBM Abbreviation for Resorbable blast media.
Reactive bone See: Wolff Law.
Reattachment To attach again; the reunion of epithelial and connective tissue with root surfaces and bone such as occurs after an incision or injury. It should not be confused with new attachment.6
Recall appointment after implantation Scheduled dental visits after endosseous implants have been placed in a patient.
Recall maintenance See: Periodontal maintenance.
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) A 317-aminoacid peptide, member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily that stimulates osteoclast differentiation and activity as well as inhibits osteoclast apoptosis. It is expressed by osteoblast-stromal cells, fibroblasts, and activated T cells. In the bone tissue, RANKL binds directly to its receptor (ie, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B [RANK]) on the surface of osteoclasts or preosteoclasts, stimulating both the differentiation of osteoclast progenitorcells and the activity of mature osteoclasts. It exists as either a 40- to 45-kd cellular, membrane-bound form or a 31-kd soluble form derived by cleavage of the full-length form at position 140 or 145. It also has a number of effects on immune cells, including activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in T cells, inhibition of apoptosis of dendritic cells, induction of cluster formation by dendritic cells, and proliferation of cytokine-activated T cells.7
Recipient site Position or site in the alveolar bone crest that is to receive a graft and/or implant.
Reconstruction Restoration of an anatomic organ or structure to its original appearance and function. In dentistry, it is the restoration or replacement of a tooth, teeth, or portion of a jaw or craniofacial structure using an artificial prosthesis. See also: Alveolar reconstruction; Prosthesis.
Record Information or data recorded in any medium (eg, handwriting, print, tapes, film, microfilm, microfiche, any electronic form). It provides evidence of what was planned, the treatment provided, and the results.
Record base Temporary prosthesis base used to carry registration materials to the mouth for the recording of maxillomandibular positional relationships.8,9 See also: Maxillomandibular relationship.
Records, legal requirements for maintaining Laws that specify the length of time that records must be kept.
Re-entry Second surgical procedure to place an implant in a staged approach, such as alveolar ridge augmentation or sinus grafting procedures. It can be combined with the removal of an inert biomaterial (eg, nonresorbable membranes or bone graft fixation screws). Can also be performed to improve, enhance, or evaluate results obtained from the initial operation.
Regenerate See: Alveolar distraction osteogenesis.
Regenerate maturation See: Consolidation period.
Regeneration
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


