Peri-implantitis is the destructive inflammatory process affecting the bone and gum tissues around dental implants. It is caused by similar bacteria involved in gum disease (periodontitis) that leads to bone loss around natural teeth.
Joan had to have her lower right tooth extracted because of a fracture and wanted it replaced as soon as possible. She saw her general dentist who performed the extraction with immediate placement of a single implant and restored it with a single crown. Soon after, Joan noticed increasing pain around her dental implant and receding gum tissue. She was reassured that it would gradually improve, but the gum recession and her pain continued to worsen over the next four months. She also became concerned about the grayish color from her gum tissue (Fig 1). Realizing her condition was worsening, she finally decided to seek a second opinion from a specialist. When she came to see us, her gum tissue was noted to be inflamed and painful to touch. A CBCT (cone beam CT scan) was obtained to assess the condition of the implant, supporting bone, and source of her pain. It was immediately noted that the implant had been placed too far from its proper path with an excessive outward tilt (Fig 2). This, in turn, resulted in loss of bone and recession of her gum and subsequent exposure of the implant surface. Inadequate tissue support, plaque retention on the implant surface, and continued inflammation led to peri-implantitis and her symptoms of pain.
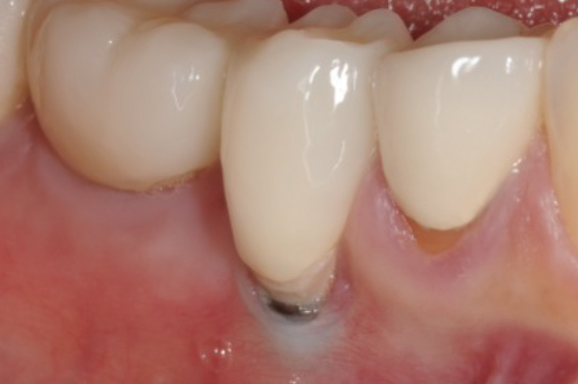
Fig 1 Peri-implantitis in a patient with gum recession, inflammation, pain, and grayish appearance
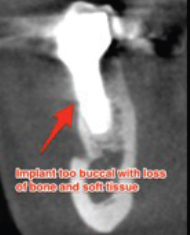
Fig 2 CBCT demonstrating excessive tilting of dental implant with loss of bone and soft tissue
What led to this problem:
 Poorly-placed implant by an inexperienced dentist
Poorly-placed implant by an inexperienced dentist
 No diagnostic CT imaging
No diagnostic CT imaging
 Poor planning
Poor planning
 Improper implant placement technique
Improper implant placement technique
 Failure to use a surgical guide for proper alignment
Failure to use a surgical guide for proper alignment
 Failure to recognize thin tissue biotype with high susceptibility to recession
Failure to recognize thin tissue biotype with high susceptibility to recession
“Over 95% of dental implant complications may be preventable”
How this could have been avoided:
 Knowledge base – Critical to selecting patient- and site-specific treatments
Knowledge base – Critical to selecting patient- and site-specific treatments
 Proper diagnosis – Use of CBCT to assess bone density and availability
Proper diagnosis – Use of CBCT to assess bone density and availability
 Computer-assisted planning – Precision planning for placement of dental implant
Computer-assisted planning – Precision planning for placement of dental implant
 Team approach – Treatment by a team of dentists: surgical placement of the implant by a trained surgeon and restoration by an experienced restorative dentist
Team approach – Treatment by a team of dentists: surgical placement of the implant by a trained surgeon and restoration by an experienced restorative dentist
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


