G
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) protein See: Osteocalcin.
Gamma ray Part of electromagnetic radiation with the smallest wavelengths and thus the most energy of any wave in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Gap See: Edentulous space.
GBR Abbreviation for Guided bone regeneration.
GCF Abbreviation for Gingival crevicular fluid.
Gene therapy Treatment of human disease by the transfer of genetic material into specific cells.1
Nonviral g. t. Method of gene therapy that uses nonviral vectors to deliver genetic material into target cells, ie, plasmid DNA and synthetic vectors (eg, lipoplexes, polyplexes).
Viral g. t. Method of gene therapy that uses viruses as gene-delivery vectors; viruses have a portion of their genome replaced by a therapeutic gene. The most widely used viruses are adenovirus, adeno-associated virus, lentivirus, and retrovirus.
Gene transfer Introduction of genes into cells. The viral particle binds to specific cellular receptors and is taken up by endocytosis. Acidification of the endosome results in release to the cytoplasm and partial disassembly of the viral particle. Transport through the nuclear pore is by viral proteins. Once in the nucleus the DNA remains extrachromosomal, and transcription and translation are by the host cell’s own protein synthetic machinery. See also: Gene therapy.
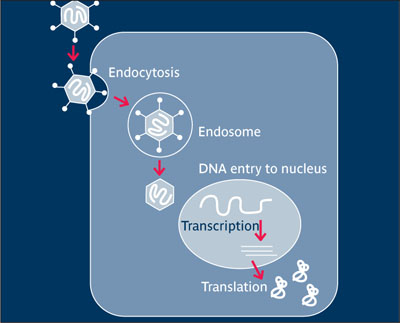
Gene transfer by an adenovirus vector.
(Redrawn from Partridge and Oreffo2 with permission.)
Gingiva (pl: gingivae) That part of the masticatory mucosa covering the alveolar process and surrounding cervical portion of teeth. This fibrous connective tissue, covered by keratinized epithelium, is contiguous with periodontal ligament and mucosal tissues of the mouth.3 See also: Attached gingiva; Keratinized gingiva; Marginal gingiva.
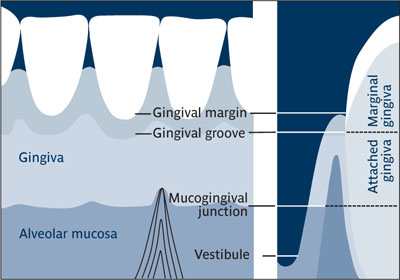
Gingiva.
(Redrawn from Genco et al4 with permission.)
Free g. See: Marginal gingiva.
Gingival abscess Localized purulent infection involving the marginal gingivae or interdental papillae.5
Gingival cleft Vertical fissure in gingiva occurring over a dehiscence of bone covering a root.
Gingival crater Saucer-shaped defect of interproximal gingiva.5
Gingival crevice See: Gingival sulcus.
Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) Serum ultrafiltrate tissue fluid that seeps into the gingival sulcus from gingival connective tissue and vasculature through thin sulcular epithelia. GCF is increased in the presence of inflammation and contains multiple mediators involved in inflammation, connective tissue homeostasis, and host response.
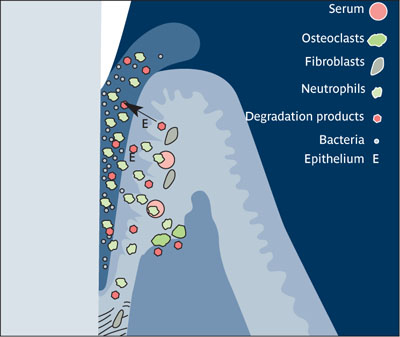
Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF).
(Reprinted from Uitto6 with permission.)
Gingival curettage Process of debriding the soft tissue wall of a periodontal pocket.5
Gingival disease See: Gingivitis; Periodontal disease; Periodontitis.
Gingival enlargement Increase in size of the gingiva. Gingival enlargement may result from systemic drug use. Drugs commonly associated with this condition include calcium channel blockers, cyclosporin, and dilantin. Called also gingival overgrowth.7
Gingival epithelium See: Epithelium.
Gingival graft Autogenous graft of masticatory mucosa or collagenous tissue completely or partially detached from its original site and placed in a prepared recipient bed. See also: Free gingival graft.
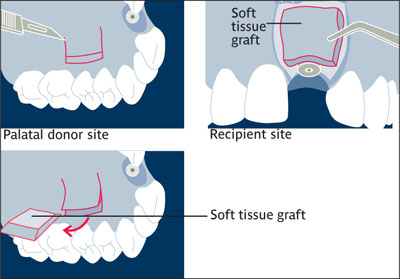
Gingival graft.
(Redrawn from Langer8 with permission.)
Gingival hyperplasia
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


