E
Ear prosthesis Fixed/removable artificial replacement for all or part of a human ear. Called also auricular prosthesis.
Early implant loss Loss of an implant that occurs prior to implant osseointegration.
Early implant placement Early implant placement takes place 4 to 8 weeks following tooth extraction, providing sufficient time for soft tissue healing. This approach is often used by clinicians in esthetic sites, where implant placement often requires a simultaneous guided bone regeneration (GBR) procedure and primary soft tissue closure is critical. It helps to reduce the risk of post-restorative soft tissue complications.1
Early loading Placing of an implant into function or a load-bearing situation following a reduced period of healing after the initial placement. It is generally considered to be loading more than 48 hours but less than 3 months after implant placement.2
Eccentric See: Maxillomandibular relationship, Eccentric.
ECM Abbreviation for Extracellular matrix.
Edentulism Oral condition of being without teeth, completely (ie, complete edentulism) or in segments of a dental arch (ie, partial edentulism).
Edentulous Without teeth.
Edentulous space Space interval between teeth that was previously occupied by a tooth or teeth.
EDM Abbreviation for Electric discharge method.
Effector cell Cell that becomes active in response to stimulation. In immunology, a differentiated lymphocyte capable of mounting a specific immune response, eg, antibody production; lymphokine production; or helper, suppressor, or killer function. Called also effector lymphocyte.
Effector lymphocyte See: Effector cell.
EGF Abbreviation for Epidermal growth factor.
Elastic modulus Measure of elasticity; relative stiffness of a material within the range of elastic deformation (below the point of plastic deformation). Called also modulus of elasticity or Young modulus.
Elastic modulus = Stress/Strain or E = σ/ε
Electric discharge method (EDM) Fabrication of components through use of electrically induced contact corrosion. Called also spark erosion.
Element Separate, identifiable part or a distinct group within a larger group; ie, any portion of an implant prosthesis. It can be identified by position or function as transmucosal, retentive, attachment, or dental.3,4
Elevator Surgical instrument. A luxating elevator is used to luxate teeth during extraction. A periosteal elevator is used to elevate a full-thickness or mucoperiosteal flap.
Buser e. See: Buser elevator.
EMD Abbreviation for Enamel matrix derivative.
Emergence angle Angle formed by the surface of the transmucosal element to the long axis of the implant.5 See also: Emergence profile. (See figure.)
Emergence profile Facial or buccal axial contour of a tooth or crown, extending from the base of the epithelial sulcus past the soft tissue margin to the height of contour. Control of this surface is important in achieving acceptable esthetics and maintaining soft tissue health.6,7 See also: Emergence angle.
Enamel matrix derivative (EMD) Extract of embryonic enamel matrix derived from six-month-old piglets. It is composed of several proteins, 90% of which are amelogenins, a family of hydrophobic proteins. EMD has been used as a periodontal regenerative treatment.
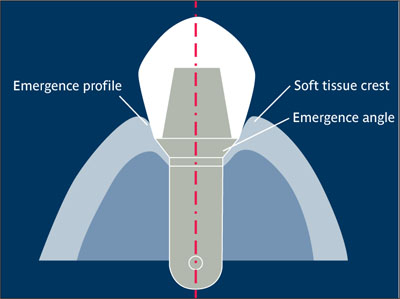
Emergence angle and emergence profile.
(Redrawn from Yanase and Preston7 with permission.)
Endochondral ossification Formation of long bones on the basis of a cartilaginous model. Longitudinal growth takes place both in growth plates and in the articular cartilage. At the growth plates, chondral ossification takes place. Cartilage cells calcify, serving as a basis for bone formation, and bone is deposited; cartilage is then replaced by bone.
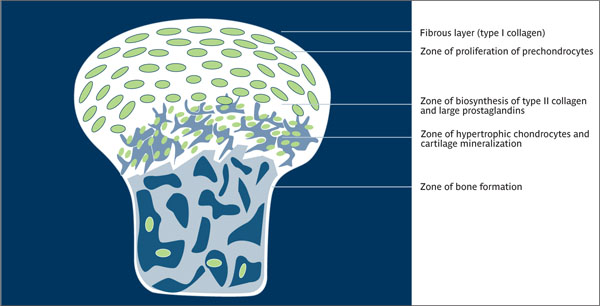
Endochondral ossification.
(Redrawn from Garant8 with permission.)
Endocrine Transfer of chemical compounds such as hormones and growth factors from secreting glands via blood to cells.
Endodontic pin See: Endodontic stabilizer.
Endodontic stabilizer Tapered post made of a biocompatible alloy that is cemented into a natural tooth, extending beyond the apex into the surrounding bone, on the assumption that it would stabilize the tooth.9 Called also endodontic pin.
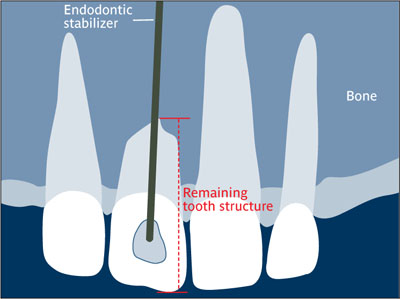
Endodontic stabilizer.
Endosseous distractor Distraction device designed to be placed within bone, between the bone base and transport segment. See also: Distraction osteogenesis (DO).
Endosseous implant Relative bony anatomic position of an implant placed into an osteotomy site. “A device placed into the alveolar and/or basal bone of the mandible or maxilla and transsecting only one cortical plate.” Classification term endosseous is interchangeable with the term endosteal.10
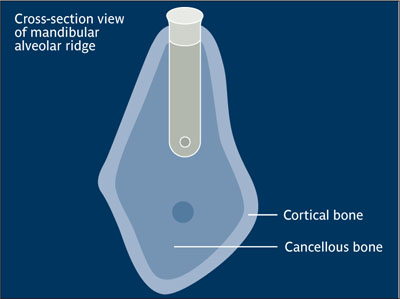
Endosseous implant.
Endosseous provisional implant See: Provisional implant.
Endosseous ramus implant Single- or multiple-piece implant in which the endosseous elements are placed in the symphysis area and into the anterior portion of bilateral mandibular rami. The transmucosal element extends from the endosseous portion that supports a mesostructure. The mesostructure can consist of a bar that follows the general outline of the residual mandibular bone. It is U-shaped as viewed from the occlusal.11-13
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


