CHAPTER 5
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
Pleomorphic adenoma, which is also known as mixed tumor, is a benign tumor composed of a variable mixture of benign epithelial and myoepithelial cells with a stromal background composed of a mucoid, myxoid, or chondroid look.
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common neoplasm of all salivary glands in both adults and children. It represents approximately 65% of parotid tumors, 50% of submandibular tumors, and 40% of all minor salivary tumors. A wide age distribution has been observed with an average age in the fourth decade of life. Women are affected more than men, with a female-to-male ratio of approximately 2:1. The most common site is the parotid gland, and most tumors are located in the superficial lobe. The submandibular gland and palate are the second most common sites but are six to seven times less likely than the parotid gland. Clinically, it presents commonly as a slow-growing, firm, painless mass. A computed tomography (CT) scan usually shows a well-circumscribed tumor with lobulation. The radiological appearance of the cut surface of the tumor can be heterogeneous depending on the different proportions of its components. If the tumor is not well delineated on CT scan, then magnetic resonance imaging can be more helpful. A lobulated contour with a low signal capsule on T2-weighted images is able to characterize most PAs. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is often used for preoperative diagnosis.
Rarely, synchronous tumors besides PA on the same side or the other side with same or different histological type occur. PA, Warthin’s tumor, myoepithelioma, salivary duct carcinoma, and mucoepidermoid carcinoma have been reported. However, the most common tumor that can be present in association with PA is a Warthin’s tumor.
5.3 CYTOLOGIC FEATURES AND HISTOLOGIC CORRELATES
The aspirate smears of PA contain a mixture of epithelial cells, myoepithelial cells, and stromal matrix components. The epithelial cells are small to moderately sized cuboidal cells with distinct cell border and bland nuclear features arranged in cohesive sheets, clusters, or single cells (Figures 5.1 and 5.2). The myoepithelial cells may have a spindled, plasmacytoid, clear cell, or epithelioid appearance, and they are often found within the stromal myxoid matrix material, in loose clusters, or individually (Figures 5.3 and 5.4). One of the most characteristic features of PA is the fibrillary chondromyxoid matrix material, which appears as an intense magenta color on air-dried Diff-Quik stain (Figure 5.5) and as a pale green gray color on Papanicolaou stain (Figure 5.6). This matrix material has fibrillary ragged edges, often with embedded myoepithelial cells (Figure 5.7). Table 5.1 summarizes the key cytologic features. The proportion of each element can vary considerably from case to case. In some patients, the epithelial element predominates, whereas others are richer in chondromyxoid stroma. Crystalloids such as tyrosine-rich and oxalate crystals, squamous or oncocytic metaplasia, and mucin production can be observed in some cases.
FIGURE 5.1. Low-power view exhibiting the fibrillary myxoid background that appears magenta red on Diff-Quik stain. Embedded are scattered myoepithelial cells (Diff-Quik stain, 200×).
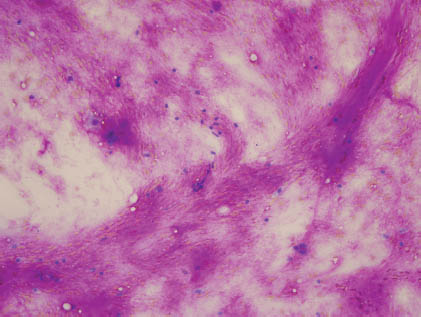
FIGURE 5.2. A high-power view of the fibrillary myxoid stroma with embedded myoepithelial cells (Papanicolaou stain, 400×).
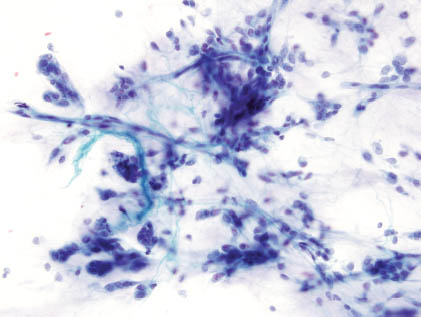
FIGURE 5.3. A high-power view on Diff-Quik stain with fibrillary stroma, few bland naked nuclei of myoepithelial cells, and few epithelial cells (left side of the image) with a suggestion of an acinus (Diff-Quik stain, 400×).
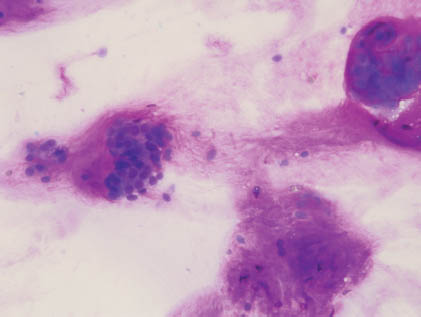
FIGURE 5.4. A high-power view with all three elements: fibrillary stroma, myoepithelial cells, and epithelial cells. The myoepithelial cells are embedded in the stroma, and their nuclei are slightly spindle. The epithelial cells form acini with basally located bland nuclei and small nucleoli (Papanicolaou stain, 600×).
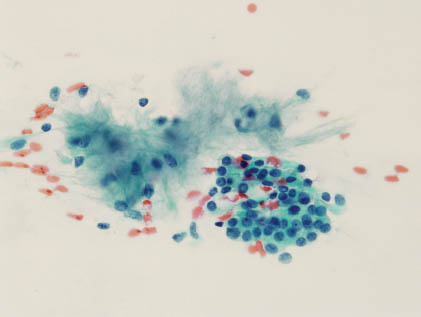
FIGURE 5.5. High-power view of epithelial cells forming acini with bland basally located nuclei (Diff-Quik stain, 1,000× oil).
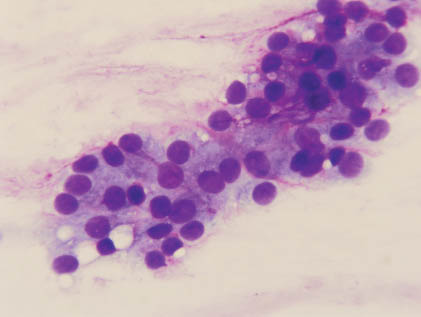
FIGURE 5.6. Another high-power view with all three elements exhibiting similar features (Papanicolaou stain, 1,000× oil).
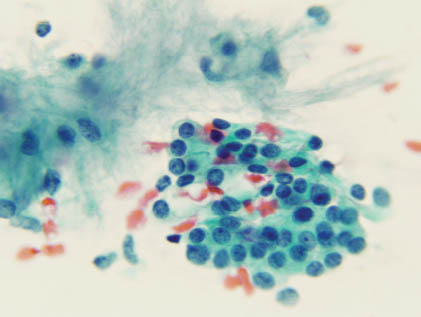
FIGURE 5.7. High-power view of myoepithelial cells. The cells are spindle with bland nuclei and inconspicuous nucleoli (Papan/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


