CHAPTER 8
CARCINOMA EX PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA
Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma is a malignant epithelial tumor of salivary glands arising in preexisting pleomorphic adenoma and accounts for approximately 12% of all malignant salivary gland tumors. It occurs equally in men and women, and it is found mainly in the parotid gland.
Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma (ca-ex-PA) involves mostly the parotid gland (the most common place of pleomorphic adenoma), followed by minor salivary glands and submandibular gland with equal sex distribution. It comprises approximately 3.6% of all salivary gland tumors, and it is estimated that approximately 10% of PAs become malignant. The patients commonly present in the sixth or seventh decade with a long history of a slowly growing mass in parotid or other site of the neck, and with recent rapid increase in size, pain, or facial paralysis. Sometimes, there is a history of previous surgery or radiotherapy. The malignant transformation might be confined to the gland or might extend beyond the gland to invade surrounding structures.
Occasionally, patients present with a rapidly growing mass without a history of a preexisting mass (de novo ca-ex-PA). This mass has been called by some authors as true malignant mixed tumor or carcinosarcoma, and often it shows ductal carcinoma mixed with chondrosarcoma.
8.3 CYTOLOGICAL FEATURES AND HISTOLOGICAL CORRELATION
The aspirate smears of ca-ex-PA usually are cellular and contain dual populations of malignant cells and benign residual PA cells (Figure 8.1). Perhaps because of low cohesion of the tumor cells in the malignant part, the aspirate is dominated usually by malignant cells (Table 8.1). These malignant cells are arranged frequently in loose, irregular clusters or single cells (Figures 8.2 and 8.3). An epithelial component is almost always present and includes discohesive groups or single malignant cells, with glandular or squamous differentiation or undifferentiated cells. Usually, the cells are large and pleomorphic with atypical nuclei featuring an irregular membrane, hyperchromasia, and macronucleoli (Figure 8.4). A malignant stromal cell component may be observed rarely, but it is more difficult to identify than the carcinoma component on cytology aspirates (Figures 8.5 and 8.6). Cell block sections can be helpful in demonstrating microfragments of malignant tumor with both malignant epithelial cells and benign PA cell components (Figure 8.7). A clear presence of benign PA components (uniform small cells and spindle cells in chondromyxoid fibrillary stroma) should be identified microscopically to make this diagnosis, although this is frequently overrun, obscured, or dominated by the malignant component of the tumor.
FIGURE 8.1. Ca-ex-PA. Group of atypical cells with overlapping discohesive arrangement and pleomorphic nuclei. An adjacent fragment of fibrillary myxoid stromal tissue of preexisting PA is present (Diff-Quik stain, 400×).
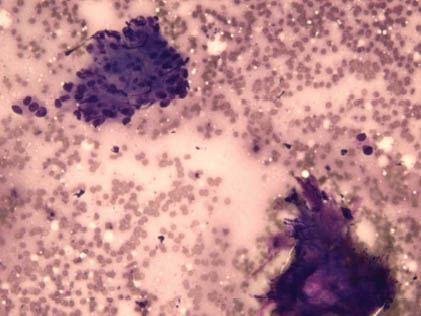
TABLE 8.1. Key Diagnostic Features of Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma
|
FIGURE 8.2. Ca-ex-PA. A cluster of atypical dispolarized pleomorphic cells with irregular pleomorphic nuclei (Diff-Quik stain, 600×).
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


