45
Adverse effects of dental biomaterials
Figure 45.1 Prevalence of adverse reactions in dental specialties.
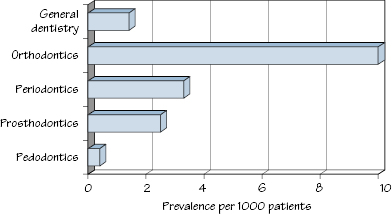
Figure 45.2 Potential adverse reactions.
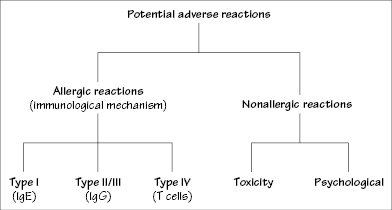
Figure 45.3 Corrosion of metal by reaction with sweat or saliva.
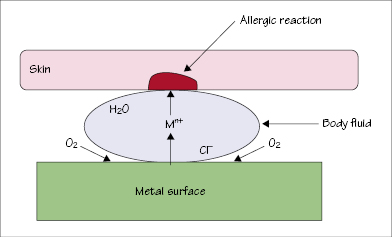
Figure 45.4 Mechanism of mercury release from amalgam restorations.
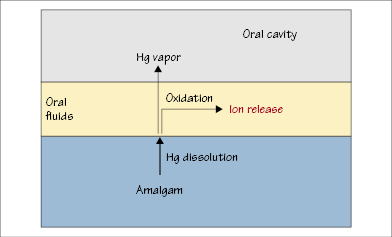
Table 45.1 Carcinogenic and toxic substances used in dentistry
| Carcinogens | Toxic substances |
|---|---|
| Formaldehyde Cadmium Beryllium |
Methyl methacrylate Formaldehyde Mercury vapor Metals: Arsenic Barium Cadmium Chromium Lead Mercury Selenium Silver |
Table 45.2 Principal allergic reactions
| Allergy | Reaction type | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Anaphylactic reactions—antibody (IgE) mediated | Immunoglobulin antibodies (IgE) bind to receptors on mast cells. Pharmacologically active compounds may be released. Clinical effect may be respiratory system obstruction and cardiovascular collapse. |
| Type II | Cytolytic or cytotoxic | Immunoglobulins (IgM or IgG) bind to antigens on surface of cells and activate complement. Activation may result in cytolysis, phagocytosis, and chemotactic reactions. |
| Type III | Immune-complex | Occur when complexes made of IgM and IgG antibodies accumulate in blood vessels or tissue and activate the complement system |
| Type IV | Delayed-type hypersensitivity (T-cell mediated) |
Immune response is mediated by T cells, usually CD4+. Cytokines are released, leading to macrophage activation and resulting in local damage. |
Ig, immunoglobulin; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IgM, immunoglobulin M.
Table 45.3 Type I and Type IV allergic reactions
| Type I | Type IV | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of reaction | IgE-mediated anaphylactic | T-cell mediated, delayed-type hypersensitivity |
| Characteristic | Immediate/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


