32
Adhesive dentistry
Figure 32.1 (a) Adhesive surface tension exceeds critical surface energy. (b) Critical surface energy greater than surface tension of adhesive.
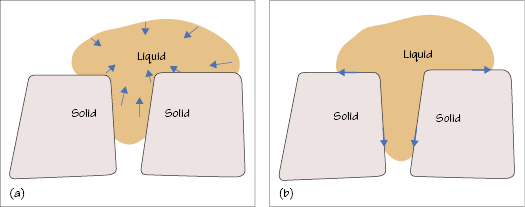
Figure 32.2 Compositions of enamel and dentin.
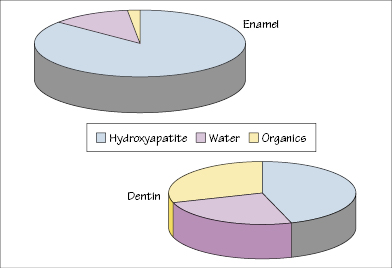
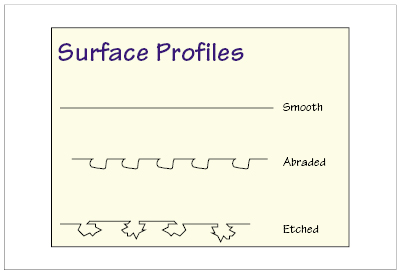
Figure 32.3 Schematic profiles of smooth, abraded, and etched surfaces.
Box 32.1 Factors in dental adhesion
Surface contamination
Surface conditioning
Surface irrigation
Dry/moist field
Adhesive used
Box 32.2 Causes of problems in enamel bonding
Poor surface preparation:
- inadequate etching
- overetching
- inadequate or excessive rinsing
Surface contamination
Improper manipulation of materials
Inadequate adaptation to cavity walls (poor wetting)
Thermal expansion differences
Dimensional change of adhesive on setting
Table 32.1 Common etch patterns of dental enamel
| Etch pattern | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Type I | Etching of matter between prisms (interprismatic) |
| Type II | Etching within prisms (intraprismatic) |
| Type III | Combination of Types I and II |
The introduction and proper application of adhesion science within dentistry has changed dental practice, and modern restorative procedures now conserve tooth structure and provide strengthening of the tooth. Adhesive dentistry involves the application and curing of an adhesive resin/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


