28 Root Canal Filling Pastes
Sealers containing zinc oxide eugenol set via the formation of a comparatively highly soluble zinc-eugenolate complex, which also has poor compressive strength. Free eugenol is cytotoxic, but with proper mixing it is bound to the eugenolate as well as the zinc oxide.
Eugenol can act as an allergen, causing contact urticaria or even an anaphylactic reaction (Grade, 1995). In patients with a known allergy to eugenol or Peruvian balsam, the use of these sealers is contraindicated. During the setting procedure, these compounds exhibit shrinkage of about 0.3–1%.
Due to a condensation reaction, epoxy resin AH 26 releases very little formaldehyde during its rapid setting process (Spangberg et al., 1993). For this reason, AH 26 has low cytotoxicity initially (Leonardo et al., 1999), and is virtually undetectable after several weeks. AH Plus (Dentsply International, PA, USA), the improved version of the AH 26 sealer, releases virtually no formaldehyde, due to an addition reaction. For this reason it exhibits improved biocompatibility in comparison with the original AH 26 (Rödig et al., 2005a). AH Plus is identical to 2Seal paste (VDW, Munich, Germany). Overall, sealers with an epoxy resin base have very good physical characteristics with regard to viscosity, solubility, and radiopacity. AH Plus, in particular, is virtually insoluble (Schäfer and Zandbiglari, 2003). In general, these types of sealers have excellent sealing ability and good volume stability.
28.1 Biocompatibility of root canal filling pastes/sealers
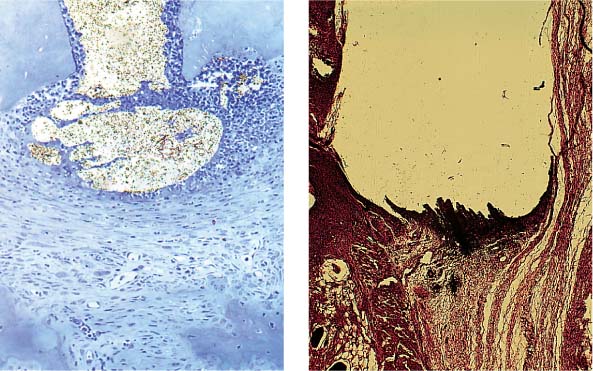
Left: Animal studies indicated that the epoxide resin 2Seal is associated with a good tissue reaction despite slight overfilling of the canal.
Right: Extensive undesirable tissue reaction following subcutaneous implantation of a sealer based on zinc oxide eugenol.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses