13
Elastic impression materials
Figure 13.1 Compression of impression material at the bulbosity of the tooth as tray is withdrawn from the mouth.
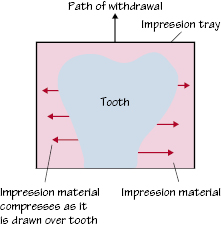
Figure 13.2 Approximate permissible distortions for 100% recovery of elastomerics.
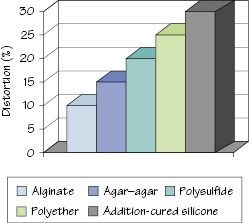
Figure 13.3 Contact angle of water and castability of dental gypsum into impression materials.
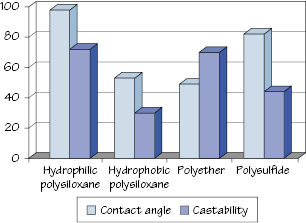
Table 13.1 Approximate composition of alginate impression material
| Component | Amount (%) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium/potassium alginate | 15 | Water soluble, reacts with Ca2+ |
| Calcium sulfate | 14 | Reacts with potassium alginate to form insoluble gel |
| K2SO4, silicates, borates | 10 | Counterbalance gel effect on gypsum |
| Sodium phosphate | 2 | Retarder for Ca2+/alginate reaction |
| Diatomaceous earth | 70 | Filler |
| Colorant, flavoring, disinfectant | Minor/trace |
Table 13.2 Problems with alginate impressions
| Grainy material Improper mixing Prolonged mixing Excessive gelation Incorrect W/P ratio Tearing Inadequate bulk Moisture contamination Premature tray removal Prolonged mixing |
Irregular voids Moisture/debris Poor mixing Rough/chalky cast Impression not clean Impression too wet Premature cast removal Delayed cast removal Incorrect mix of gypsum material |
Distortion Delayed pouring Tray movement during set Premature tray removal Incorrect tray removal Excessive gelation Bubbles Overmixing of material Poor mixing technique |
Table 13.3 Polysulfide elastomeric impression material
| Base paste | Catalyst |
|---|---|
| Polysulfide polymer, 80–85% Filler (TiO2, ZnSO4, CuCO3, or silica), 16–18% |
Lead dioxide, 60–68% Dibutyl phthalate, 30–35% Sulfur, 3% Minor ingredients, 2% |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


