12
Inelastic impression materials
Figure 12.1 Structure of eugenol.
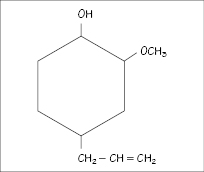
Figure 12.2 Structure of zinc eugenolate.
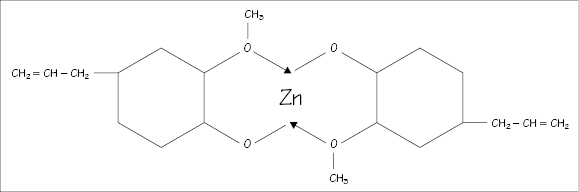
Table 12.1 Impression compound
| Component | Addition level (%) |
|---|---|
| Thermoplastic (rosin, copal resin, carnauba wax) | 47 |
| Lubricant (stearic acid) | 3 |
| Filler (talc) | 50 |
Table 12.2 Flow properties of impression and tray compound
| Material | Flow at 37°C | Flow at 45°C |
|---|---|---|
| Type I (impression compound) | <6% | >85% |
| Type II (tray compound) | <2% | 70–85% |
Table 12.3 Zinc oxide–eugenol impression material
| Base paste | Reactant |
|---|---|
| Zinc oxide, 85% Inert oil, 15% |
Eugenol, 15% Rosin, gum, oil, 65% Filler (talc, kaolin), 16% |
Impression materials, central to fabricating all fixed and removable prostheses, fall into two broad categories, inelastic and elastic. The former are used for edentulous patients and for interocclusal records whereas the latter (Chapter 13) are for dentate patients.
12.1 Factors in impression-making
An impression material must wet the hard a/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


