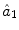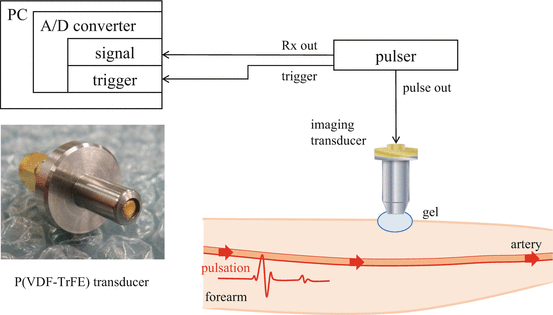
21.2.2 Subject
21.2.3 Velocity Measurement
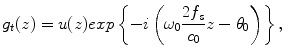
![$$ {g}_{t+\Delta \mathrm{T}}(z)=u(z) exp\left[-i\left\{{\omega}_0\frac{2{f}_s}{c_0}\left(z-{z}_{\tau}\right)-{\theta}_0\right\}\right], $$](/wp-content/uploads/1008/A322452_1_En_21_Chapter_Equ2.gif)
where u(z) was the envelope of the analytical signal, f s was the sampling frequency, c 0 was the sound speed, θ 0 was the initial phase, and z τ was the true displacement induced by the pulsation. The complex cross-correlation function γ(z lag ) at lag z lag was defined as
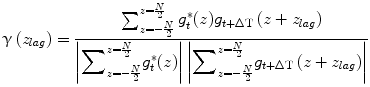
where N was 1-D cross correlation window of 256 pixels, corresponding to 195 μm depth window with 91 % overlap using hamming window. An index at maximum value of the real part of the Eq. (21.3) corresponded to the index of 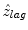 . In this paper, f s was 1 GHz, and the temporal resolution was enough high to observe the deformation with HFUS of 100 MHz. Additionally, the received RF signal was up-sampled to 4 GHz before implementing the 1-D cross-correlation. Because of these reasons, the estimated displacement
. In this paper, f s was 1 GHz, and the temporal resolution was enough high to observe the deformation with HFUS of 100 MHz. Additionally, the received RF signal was up-sampled to 4 GHz before implementing the 1-D cross-correlation. Because of these reasons, the estimated displacement 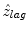 was almost equal to the true displacement z lag . The velocity, denoted by v t + ΔT/2(z), of the skin in his forearm between the interval was given as follows:
was almost equal to the true displacement z lag . The velocity, denoted by v t + ΔT/2(z), of the skin in his forearm between the interval was given as follows:
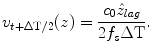
The acceleration was calculated from the measured velocity. The acceleration was calculated by differentiating the measured velocity as
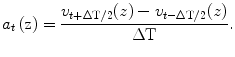
21.2.4 Shear Wave Measurement
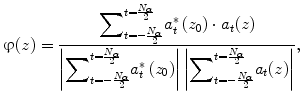
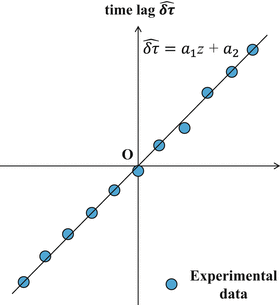
where N α was an estimation window of 50 pixels, corresponding to a 50 ms time. A hamming window was used for the estimation. A variable z 0 was a reference depth, and a variable z was an interest depth. A time lag between the reference depth and the interest depth was expressed as follows:
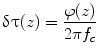
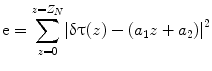
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses