CHAPTER 8 Oral Health Promotion
Dental recall guidelines
The following issues need to be discussed or reinforced with the patient where relevant:
The oral health message
Most oral diseases, including not only the more common problems (such as tooth surface loss due to caries, trauma, abrasion, erosion and periodontal disease) but also potentially fatal diseases (such as cancer), are largely related to people’s lifestyle and habits (Table 8.1). Thus these diseases are often preventable by careful attention to lifestyle. For example, oral health can be improved by:
| Disease | Risk Factor |
|---|---|
| Abrasion | Incorrect toothbrushing |
| Cancer | Tobacco, alcohol, betel nut use |
| Candidosis | Dry mouth, antibiotic use, HIV and other immunity problems |
| Caries | High sugar diet, low fluoride |
| Erosion | Soft drinks, fruit juices, alcohol |
| Gingivitis | Plaque accumulation |
| Halitosis | Plaque accumulation, tobacco use, alcohol use |
| Periodontitis | Plaque and calculus accumulation, tobacco use |
| Trauma | Alcohol use; some contact sports |
This chapter is based on the toolkit ‘Delivering better oral health: An evidence-based toolkit for prevention’ by the Department of Health and British Association for the Study of Community Dentistry. See the Department of Health website for the full toolkit (http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_078742)
Diet
General advice
Refined carbohydrates and sugars, particularly non-milk extrinsic sugars in items other than fresh fruits and vegetables, are the major causes of dental caries (Chapter 5). The frequency of intake is more important than the amount. Thus to lessen the chances of accumulating dental plaque, and developing caries, it is important to limit and reduce the frequency of consumption of sugary foods, such as restricting them to meal times.
Older children and adults
Fluoride
Fluoride can protect teeth against caries by:
Water fluoridation
Fluoride supplements
TABLE 8.2 Sodium Fluoride Supplement Doses (Tablets) to Reduce Caries in Children in Relation to Water Fluoride Content

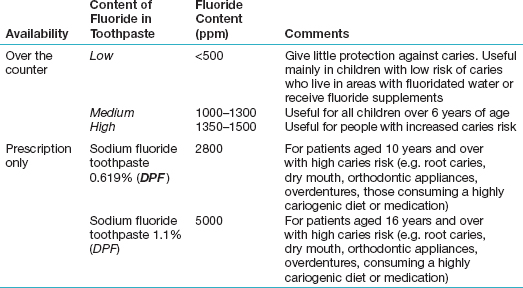
Fluoride toothpastes
Fluoride varnishes
Prophylaxis: In the dental context prophylaxis refers to cleaning the surface of teeth with a rotary brush (see Figure 8.8 below) to remove all plaque and fine deposits before treatment.
There is a small risk of allergy to the colophony component of Duraphat. Therefore varnish application is contraindicated for children who have a history of allergies, including asthma. Duraphat is also contraindicated in patients with ulcerative gingivitis and stomatitis (see Chapter 5).
Fluoride mouthwashes and gels
Fluoride mouthwashes or rinses can be prescribed for patients aged 8 years and above, for daily or weekly use, in addition to twice-daily brushing with toothpaste containing at least 1350 ppm fluoride. They should be used at a different time to toothbrushing to maximise the topical effect. Fluoride mouthwashes and gels are particularly recommended for people with a dry mouth (hyposalivation; see Chapter 5), who are otherwise particularly at risk of caries.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses