8
Gypsum materials
Figure 8.1 Effect of drying time on compressive strength of dental plaster.
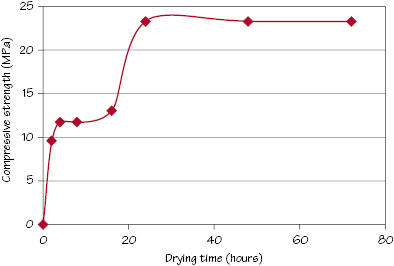
Figure 8.2 Effect of the W/P ratio (shown above the columns) on the strength of gypsum materials.
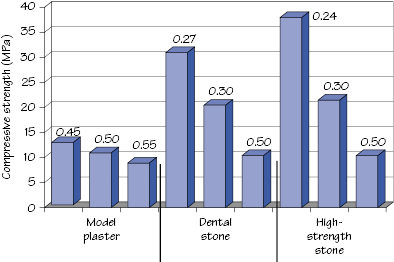
Figure 8.3 Wet and dry compressive strengths of gypsum materials.
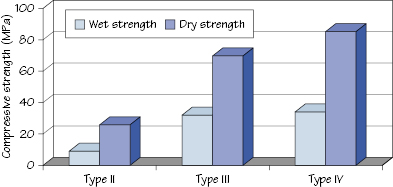
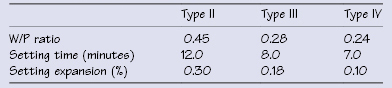
Table 8.1 Dental gypsum products
| ANSI/ADA specification nomenclature | Traditional nomenclature |
|---|---|
| Type I—Plaster, impression | Impression plaster |
| Type II—Plaster, model | Model or laboratory plaster |
| Type III—Dental stone | Class I stone; model stone |
| Type IV—Dental stone, high strength | Class II stone; die stone |
| Low expansion (ISO Type 4) | |
| High expansion (ISO Type 5) |
Table 8.2 Water-to-powder (W/P) ratios for gypsum materials
| Product | W/P ratio (g water/100 g powder) |
|---|---|
| Plaster | 40–50 |
| Dental stone | 25–30 |
| Die stone | 19–24 |
Table 8.3 Effect of W/P ratio on characteristics of mixed gypsum materials

Table 8.4 Comparative properties of dental gypsum products
8.1 Dental gypsum materials
Widely used in dentistry, gypsum materials are obtained from natural deposits of gypsum, CaSO4·2H2O, which when heated loses 1.5 g mol of water and converts to the hemihydra/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


