6
Dental hard tissues
Figure 6.1 Scanning electron micrograph (×1000) of etched enamel.
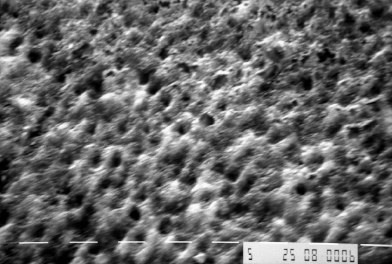
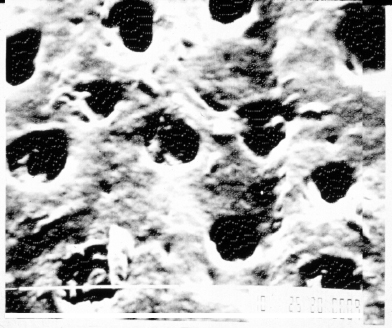
Figure 6.2 Scanning electron micrograph (×1000) of dentin tubules with smear layer present.
Box 6.1 Changes in dental enamel with patient age
Permeability decreases.
Water content decreases.
Surface composition changes through ion exchange with oral environment (e.g., fluoridation of enamel surface).
Color darkens, in part through addition of organic matter to the enamel and sclerosis and staining of underlying dentin.
Wear facets occur in areas of heavy function.
Box 6.2 Proteinaceous components of dentin
Collagenous proteins
(mainly Type I collagen with smaller amounts of Type V and Type I trimer collagens)
Noncollagenous dentin-specific proteins
(phosphophoryns, dentin sialoprotein, and dentin matrix protein-1)
Nonspecific proteins associated with mineralized tissues
(e.g., osteocalcin and osteopontin)
Table 6.1 Characteristics of dental hard tissues
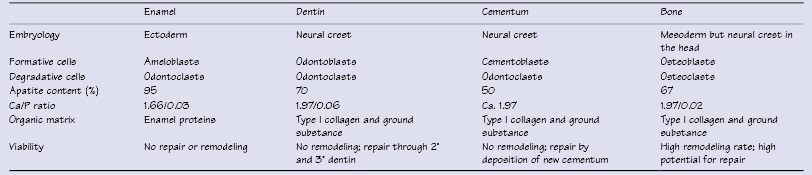
Table 6.2 Average inorganic constituents content (wt.%) of mineralized tissue
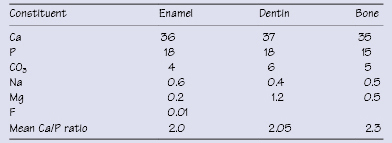
Table 6.3 Inorganic and organic content (wt.%) of enamel and dentin
| Enamel | Dentin | |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral (hydroxyapatite) content | 96 | 70 |
| Organic matter | 1 | 20 |
| Water | 3 | 10 |
Table 6.4 Characteristics of dentinal tubules
| Near DEJ | Near pulp | |
|---|---|---|
| Dens/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


