SECTION 5
LOCAL ANAESTHESIA
Local anaesthetics provide temporary loss of sensation to a particular area of the mouth, so that the patient will not feel pain.
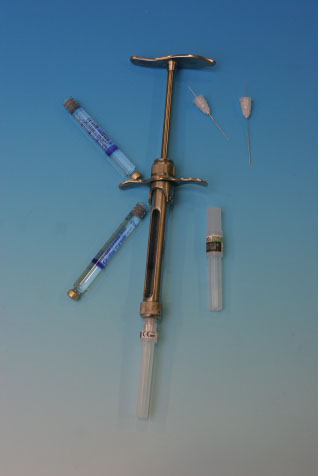
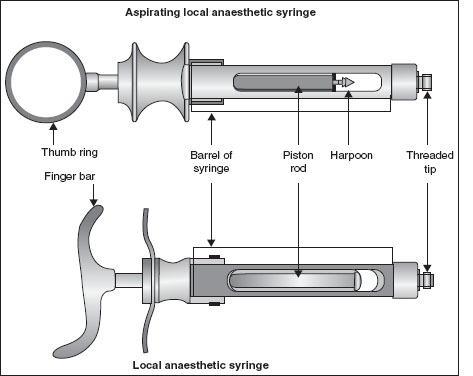
SYRINGES, NEEDLES AND CARTRIDGES
FIGURE 5.1
Name
Self-aspirating local anaesthetic syringe, Local anaesthetic syringe
Function and features
- A self-aspirating local anaesthetic syringe allows the operator to aspirate or draw back to see if they have injected into a blood vessel prior to injecting local anaesthetic, it is the harpoon or extension on the plunger which allows this. If the operator pulls towards themselves with the thumb ring, the ‘draw back’ action happens and if they depress the thumb ring it injects the local anaesthetic. If the operator ‘draws back’ and blood can be seen in the local anaesthetic carpule, they have injected into a blood vessel and will reposition prior to administering the local anaesthetic.
- Used to administer local anaesthetic with a disposable anaesthetic cartridge and a disposable needle
- The finger bar of the syringe controls the piston rod, which depresses the rubber stopper of the anaesthetic cartridge during aspiration
- When the piston rod is depressed, the local anaesthetic solution is forced out through the disposable needle, which is screwed onto the threaded tip
- The barrel of the syringe is open on both sides to facilitate loading the anaesthetic cartridge and check for blood cells during aspiration
Variations
Non-self-aspirating type, disposable type (assembled), top loading type, intraligamentary syringe
False friends
Irrigation syringe, endodontic syringe
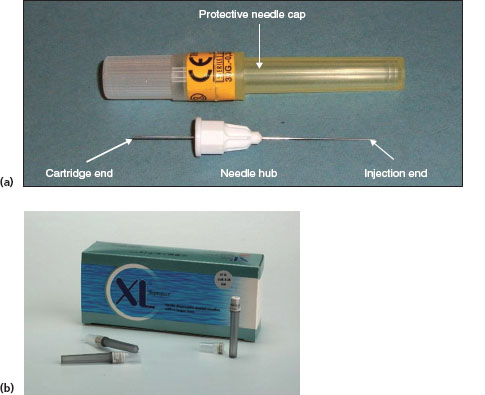
FIGURE 5.2a, b
Name
Disposable needle
Function, features and precautions
- Used in conjun/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


