46
Dental erosion
Figure 46.1 Enamel dissolution caused by excessive consumption of citrus soft drinks. (Courtesy of Dr. Howard Strassler.)
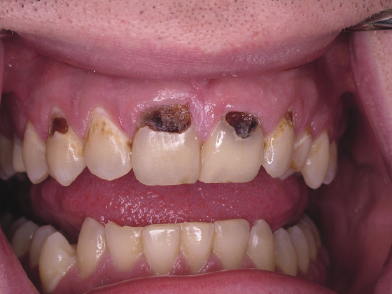
Figure 46.2 Enamel dissolution caused by consumption of a sports drink. (Courtesy of Dr. Howard Strassler.)
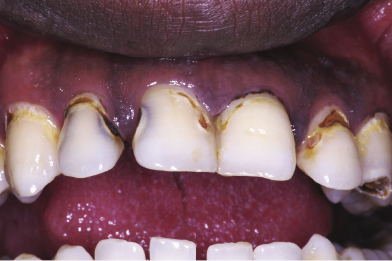
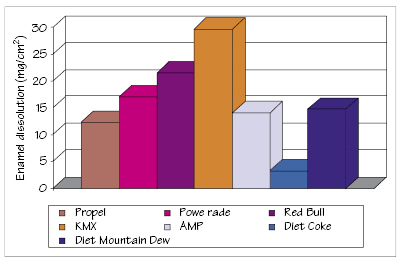
Figure 46.3 Enamel dissolution in soft drinks (14 days).
Dental erosion is irreversible hard tissue loss that does not involve bacterial, mechanical, or traumatic factors (Figure 46.1 and Figure 46.2). Erosion is associated with intrinsic and extrinsic acids.
Intrinsic acids are gastric acids present in the mouth due to induced vomiting, e.g. in bulimics and alcoholics, and reflux acids caused by GERD. Erosion of lingual surfaces is often diagnostic of bulimia and GERD.
Extrinsic acids derive from an acidic diet, commonly wines and low-pH beverages with a high organic acid content. Low-pH foods, e.g. pickles, fresh fruits, and yogurt, can contribute to dental erosion.
46.1 Soft drink consumption
Soft drink consumption is increasing by 2–3% per year. It has risen sevenfold over the past 50+ years in the United States and by 56% in the United Kingdom in the past 10 years, with similar trends likely in other countries.
Sugary beverage intake is higher in adolescents and children than adults, diet drinks possibly being more popular with the latter. The consumption of noncola (citrus-flavored) beverages is growing rapidly.
Dental erosion rates are the same for regular and diet />
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


