44
Grinding, polishing, and finishing
Figure 44.1 Effect of external temperature on internal (pulpal) temperature of teeth.
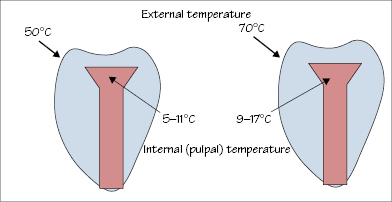
Figure 44.2 Effect of coolant flow rate on dental cutting rates.
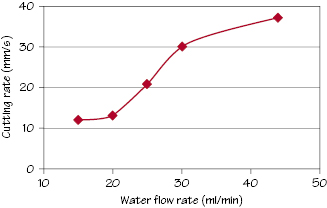
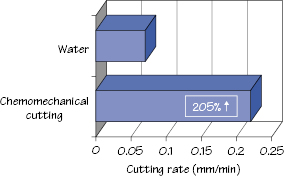
Figure 44.3 Chemomechanically enhanced dental cutting.
Box 44.1 Effects of cutting, grinding, and polishing on surfaces
Surface material is removed.
Subsurface layers are affected.
Microcracks are generated.
There is a nonuniform stress distribution.
An anisotropic surface layer is created.
Table 44.1 Common abrasives
| Abrasive | Composition | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Aluminum oxide | Finishing of metals, resins, and ceramics |
| Arkansas stone | Microcrystalline quartz | Fine grinding of enamel and metals |
| Chalk | Mineral form of calcite | Polishing of enamel, amalgam, and resins |
| Corundum | Alumina | Grinding of metals |
| Diamond | Natural | Finishing and polishing of ceramics and resins |
| Synthetic | Cutting, finishing, and polishing of tooth structure, ceramics, metals, and resins | |
| Emery | Fine-grain alumina | Finishing of metals and resins |
| Garnet | Silicate-based mineral | Grinding of metals and resins |
| Pumice | Volcanic material | Polishing of enamel, amalgam, and resins |
| Quartz | Silica | Finishing of metals |
| Rouge | Iron oxide | Polishing noble metals |
| Sand | Silica minerals | Air blasting to clean castings |
| Silicon carbide | Synthetic material | Cutting of metals, ceramics, and resins |
| Tin oxide | Metal oxide | Polishing teeth and metals |
| Tripoli | Sedimentary rock | Polishing of metals and resins |
| Zircon | Zirconium silicate | Prophylaxis paste |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


