43
Orthodontic materials
Figure 43.1 Schematic diagram of orthodontic elastomeric chains (A, closed loop; B, short open loop; C, long open loop).
Figure 43.2 Force required to distract three- and four-loop segments of elastomeric chain in the dry (as-received) condition and after immersion in water and a citrate-containing power drink.
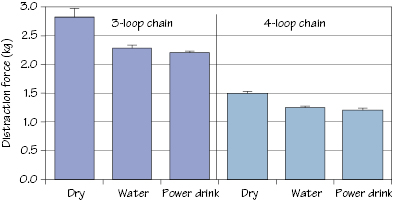
Table 43.1 Appliances for jaw orthopedics
| Device | Application |
|---|---|
| Headgear | Exerts a specified amount of pressure on the maxilla to ensure proper eruption of upper teeth and guide maxillary growth direction. |
| Bionator | Assists both jaws to grow in proportion to one another, usually keeping the mandible forward and promoting proper tooth eruption. |
| Herbst | Semipermanently affixed to both sets of molars to prevent recessive mandibular movement and protruding maxillary teeth. |
| Frankel | Combines functional orthodontic therapy of the mandible while correcting tooth positioning in the maxilla. |
| Expansion devices | A palatal expansion device is applied to the maxillary teeth to help expand the maxillary width and reduce or eliminate crossbite. |
Table 43.2 Characteristics of common orthodontic arch wires
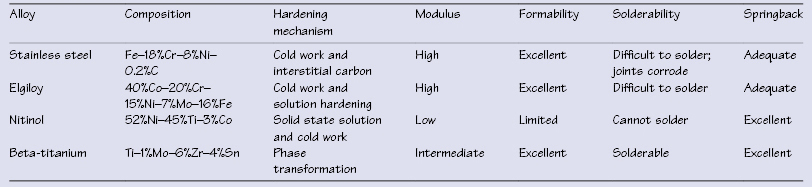
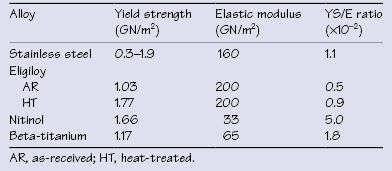
Table 43.3 Yield strength, elastic modulus, and YS/E ratio for orthodontic arch wires
43.1 Intraoral appliances
Orthodontic appliances, used to correct malocclusions through tooth and jaw movement, fall into two broad classifications. Fixed appliances use brackets bonded/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


