37
Materials in periodontics
Figure 37.1 Water solubilities of periodontal dressing materials at room and mouth temperature. (Adapted from: J.A. von Fraunhofer and D.C. Argyropoulos, Properties of periodontal dressings, Dental Materials (1990) 6:51–55.)
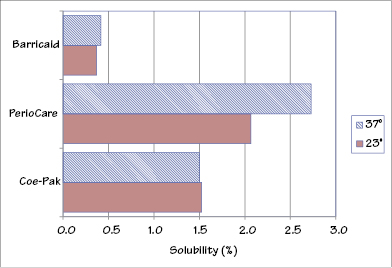
Figure 37.2 Water sorption behavior at 37°C. (Adapted from: J.A. von Fraunhofer and D.C. Argyropoulos, Properties of periodontal dressings, Dental Materials (1990) 6:51–55.)
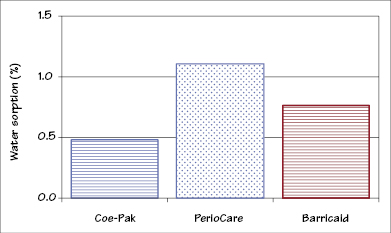
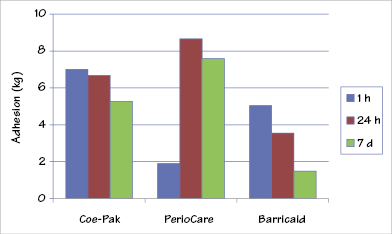
Figure 37.3 Adhesion (separating force) of periodontal dressing materials to hard tissue. (Adapted from: J.A. von Fraunhofer and D.C. Argyropoulos, Properties of periodontal dressings, Dental Materials (1990) 6:51–55.)
Box 37.1 Properties of an ideal periodontal dressing material
Slow setting
Smooth, nonirritant surface
Flexibility
Good adhesion
Bacterial growth inhibition
Dimensional stability
Nonallergenic
Resistant to plaque accumulation
Acceptable taste
Table 37.1 Components of modern periodontal dressing materials
| Coe-Pak | Base | Accelerator |
|---|---|---|
| Rosin Fatty acids Chlorothymol Zinc acetate Alcohol Cellulose |
Zinc oxide Vegetable oils Chlorothymol Magnesium oxide Silica Synthetic resin Coumarin |
|
| PerioCare | Paste | Gel |
| /> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


