35
Endodontic filling materials
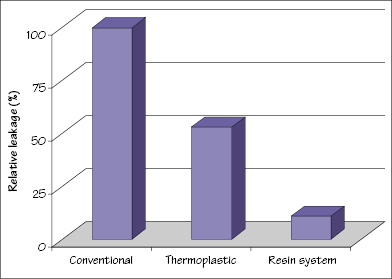
Figure 35.1 Relative leakage behavior of endodontic obturation techniques.
Box 35.1 Factors in successful root canal therapy
1 Effective biomechanical instrumentation of the root canal to produce a debris-free surface
2 Disinfection and dissolution of organic matter from within the canal to eliminate bacterial pathogens
3 Hermetic sealing of the obturated canal
Box 35.2 Ideal characteristics of endodontic irrigants
Nontoxic
Dissolve/disrupt tissue and debris in the canal
Low surface tension for good penetration
Lubricating action on cutting instruments
Sterilizing/disinfecting action
Ability to remove smear layer
Box 35.3 Requirements of endodontic sealer cements
Biocompatibility
Radiopacity equivalent to 3 mm of aluminum
Resistance to dissolution
Nonstaining
Long working time
Bacteriostatic/bacteriocidal characteristics
Good adhesion to cementum
Capability of forming a seal at tooth apex
Sealing action along canals walls
Table 35.1 Components of traditional endodontic sealer cements
| Sealer cement formulation | Powder | Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| Grossman’s sealer | Zinc oxide Staybellite resin Bismuth subcarbonate Barium sulfate Sodium borate |
Eugenol |
| Rickert’s sealer | Zinc oxide Silver Rosin Thymol iodide |
Eugenol Canada balsam |
Table 35.2 Potential proble/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


