34
Composite restorative resins
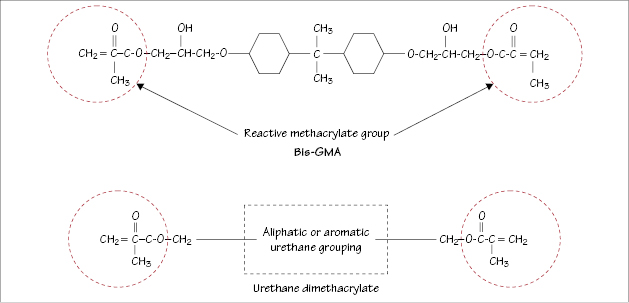
Figure 34.1 Molecular structure of bis-GMA (Bowen’s resin) and urethane dimethacrylate (UDMA).
Box 34.1 Clinical requirements of esthetic filling materials
High strength
Low solubility
Comparable elastic modulus to hard tissue
Customizable color
Rapid and controlled setting
Wear/abrasion resistance
Adhesive to tooth material
Box 34.2 Factors determining properties of composites
Monomer/oligomer
Filler type
Filler loading
Curing system
Additives
Shade/color
Table 34.1 Particle size of fillers in composite resins
| Type of composite | Filler particle size (μm) |
|---|---|
| Conventional | 5–30 |
| Fine particle | 0.5–3.0 |
| Microfine | 0.04–0.2 |
| Packable | 0.12–0.8 |
| Hybrid | 0.02–0.7 (mixture) |
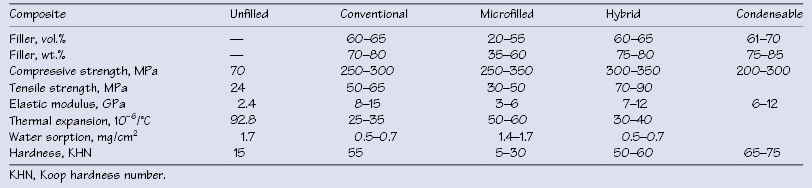
Table 34.2 Physical properties of composite restorative materials
Composites are tooth-colored resin-based materials whose properties approach those of tooth substance. They comprise a resin matrix, filler particles, and a polymerization initiator or catalyst.
34.1 Dental composites
Clinical requirements of composites (Box 34.1) are satisfied through selection of resin matrix, filler type, an/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


