Chapter 33 Microbiology of periodontal disease
Classification of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can be broadly categorized into gingivitis and periodontitis. These are yet again subdivided into numerous categories; a recent classification of periodontal diseases is given in Table 33.1. It should be noted that there is no universally acknowledged classification of periodontal disease and the clinical descriptors used relate to:
| Gingival diseases |
|
A Dental plaque-induced gingival diseases
|
Aetiological factors
Host tissues
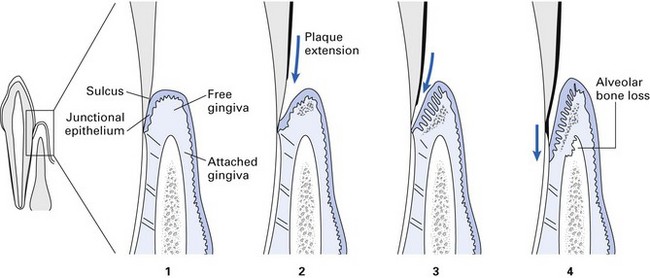
The periodontium comprises the gingivae, periodontal ligament, cementum and alveolar bone (Fig. 33.1). Although the dentogingival junction is perhaps the most vulnerable site for microbial attack, it is not breached as long as oral hygiene is satisfactory. However, when plaque accumulates close to the gingival margin, the host defences are overcome, and gingival inflammation (gingivitis) and subsequent periodontal inflammation with loss of attachment ensue (periodontitis).
Host defence factors
Both the specific and non-specific immune responses of the host to subgingival plaque are considered to play critical roles in the initiation, progression and recovery from periodontal diseases. One of the most important components of the host response is the GCF, which contains both specific and non-specific defence factors (Table 33.2).
Table 33.2 Specific and non-specific defence factors in gingival crevicular fluid
| Specific | Non-specific |
|---|---|
| B and T lymphocytes | Polymorphs |
| Macrophages | |
| Antibodies: IgG, IgA, IgM | Complement system |
| Proteases | |
| Lysozyme | |
| Lactoferrin |
IgG, immunoglobulin G.
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Microorganisms in subgingival plaque biofilm
Microbiological studies of periodontal plaque flora
Specific and non-specific plaque hypotheses
The ecological plaque hypothesis
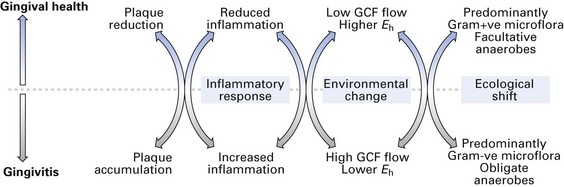
This simple yet elegant hypothesis implies that periodontal disease is an endogenous or an opportunistic infection, caused by an imbalance in the composition of the resident microflora at a site, owing to an alteration in the ecology of the local habitat (Fig. 33.2).
Periodontal health and disease
Healthy gingival sulcus has a scant flora dominated by almost equal proportions of Gram-positive and facultative anaerobic organisms; spirochaetes and motile rods make up less than 5% of the organisms (Table 33.3). With increasing severity of disease, the proportions of strict anaerobic, Gram-negative and motile organisms increase significantly (Fig. 33.3).
Table 33.3 Microorganisms associated with various types of periodontal disease
| Condition | Predominant microorganisms | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Health | Streptococcus sanguinis (previously Streptococcus sanguis) | Mainly Gram-positive cocci with few spirochaetes or motile rods |
| Streptococcus oralis |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses