31
Dental amalgam
Figure 31.1 Setting reaction of conventional amalgam alloy.
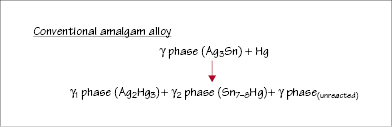
Figure 31.2 Setting reaction of dispersion-modified (admixed) amalgam alloy.
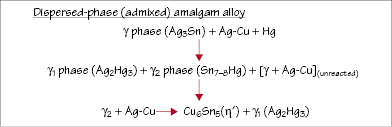
Figure 31.3 Setting reaction of single-phase amalgam alloy.
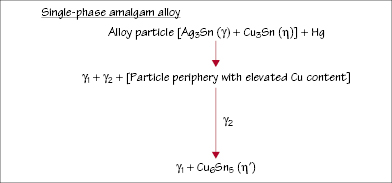
Figure 31.4 Increase in amalgam compressive strength with time.
Figure 31.5 Corrosion process with a conventional dental amalgam.
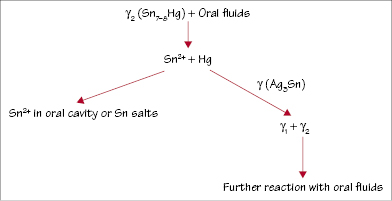
Table 31.1 Specification composition limits (wt.%) of amalgam alloys
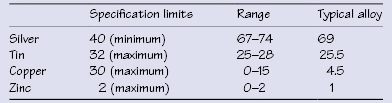
Table 31.2 Compositions (wt.%) of amalgam alloys
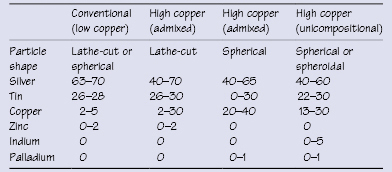
Table 31.3 Average properties of dental amalgams
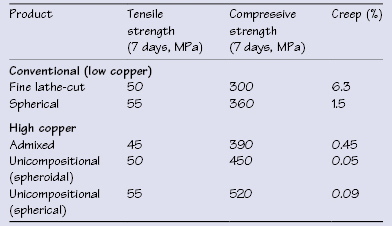
Dental amalgam is produced by reaction (trituration) of mercury with silver–tin alloy particles. However, clinical use of amalgam is decreasing due to concern over its mercury content as well as environmental issues associated with waste amalgam disposal.
31.1 Dental amalgam alloy
Alloys are supplied as irregular (lathe-cut) particles, spherical/spheroidal particles, or a mixture of both, and they consist of silver and tin with lesser contents of copper and zinc (Table 31.1). Zinc-containing alloys have ≥0.01% zinc content whereas nonzinc alloys have <0.01% zinc.
Alloy type and the alloy-to-mercury ratio affect the properties of the set amalgam. The mix contains insufficient mercury for complete reaction and set amalgam contains 11–13% unreacted Ag3Sn particles.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


