3
Physical properties of materials
Figure 3.1 Effect of temperature rise on a restoration and tooth with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
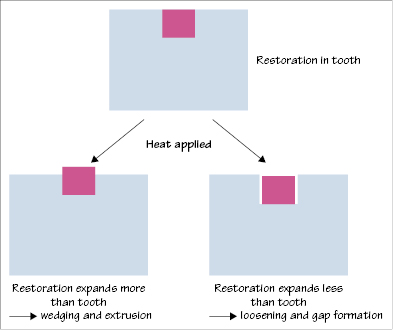
Table 3.1 Thermal properties of various dental materials
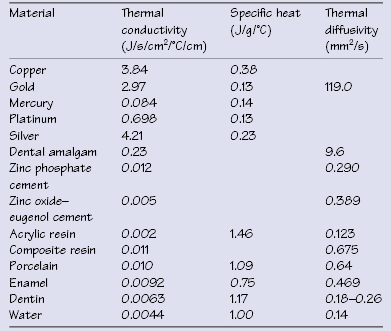
Table 3.2 Coefficients of thermal expansion
| Material | Coefficient of thermal expansion (×10−6/°C) |
|---|---|
| Tooth (crown portion) | 11.4 |
| Amalgam | 22.1–28.0 |
| Gold | 14.4 |
| Composite resin | 17–50 |
| Acrylic resin | 76.0 |
| Porcelain | 12.0 |
| Glass ionomer | 10.2–11.4 |
| Inlay wax | 350–450 |
| Silicone impression material | 210 |
| Polysulfide impression material | 140 |
Table 3.3 Electrical constants for dental materials and teeth
| Material | Resistivity (Ω·cm) | Dielectric constant |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth enamel | 2.6–6.9 × 106 | |
| Dentin | 1.1–5.2 × 104 | 8.6 |
| Glass ionomer | 0.8–2.5 × 104 | 2–7 × 105 |
| Zinc oxide–eugenol | 109–1010 | 10 |
| Zinc polyacrylate | 0.4–4 × 105 | 4 × 103–2 × 105 |
| Zinc phosphate | 2 × 105 |
Table 3.4 Wavelengths of visible light
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


