29
Resin-modified and resin cements
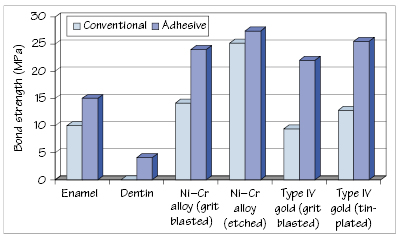
Figure 29.1 Bond strengths for conventional and adhesive resin cements.
Box 29.1 Requirements of resin-modified and resin cements
Consistency and handling
Working and setting time
Film thickness
Radiopacity
Strength and wear resistance
Retention (bond strength)
Shade availability
Fluoride release
Table 29.1 Types of RMGI and their applications
| Resin-modified glass ionomer | Application |
|---|---|
| Type I | Luting agents |
| Type II | Filling materials |
| Type III | Base/liner |
| Type IV | Core buildup |
Table 29.2 Components of liquid portion of RMGI cements
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Methacrylate resin | Permits setting by polymerization |
| Polyacid | Reacts with the glass causing setting by an acid–base reaction |
| Hydroxyethylmethacrylate (HEMA) | Facilitates coexistence of resin and acid in aqueous solution and participation in polymerization |
| Water | Essential for ionization of acid required for acid–base reaction |
Table 29.3 Components of several RMGI cements
| Product | Powder–paste | Liquid–paste |
|---|---|---|
| A | Fluoroaluminosilicate glass + redox catalyst (encapsulated potassium persulfate + ascorbic acid) | Aqueous solution of methacrylate-modified polycarboxylic acid + HEMA + tartaric acid + activator + water |
| B | Fluoroaluminosilicate + borosilicate glasses | Complex monomer with carboxylic acid groups + vinyl groups + water |
| C | Fluoroal/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


