25
Types of periodontal surgery
Figure 25.1 Gingivectomy.
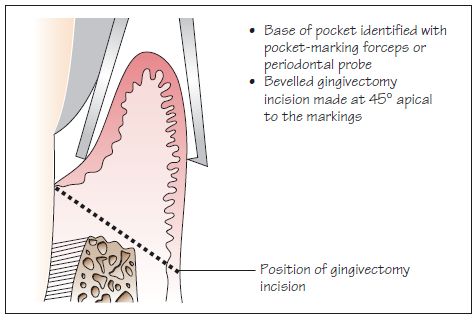
Figure 25.2 (a–c) Apically repositioned flap. (a) inverse bevel incision to alveolar crest (dashed line), (b) flap moved apically (arrow), (c) flap sutured just above the alveolar crest.
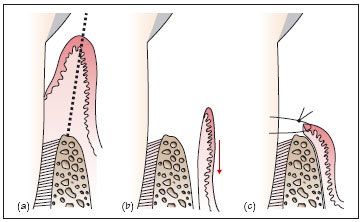
Figure 25.3 (a–c) Modified Widman flap. (a) inverse bevel incision to alveolar crest (dashed line), (b) following removal of inner lining of pocket the root surface can be accessed for cleaning, (c) flap is replaced at or close to its presurgical position.
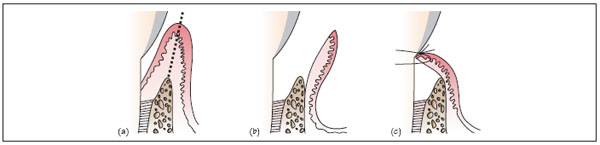
Figure 25.4 Distal wedge procedure: (a) occlusal view. The incision is made around the last standing molar and the wedge of tissue is removed. (b) vertical section. The tissue wedge is removed and the flaps thinned and approximated over the underlying bone. (c) clinical image. Incisions for distal wedge procedure. Photograph courtesy of Mr P J Nixon.
The techniques used can be divided as follows:
1 Surgery to eliminate disease and produce conditions to minimise its recurrence (outlined in this chapter):
2 Surgery to eliminate disease and regenerate lost periodontal structures (Chapter 26):
• Guided tissue regeneration.
3 Surgery for root coverage (mucogingival surgery) (Chapter 32):
This can be used for:
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


