Ethical and Legal Considerations Regarding N2O/O2 Administration
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter, the reader should be able to:
1. Understand there are legal requirements for administering N2O/O2 sedation.
2. Recognize appropriate educational levels and training requirements for N2O/O2 administration.
3. Understand the importance of obtaining written informed consent before N2O/O2 sedation.
4. Recognize the components of appropriate informed consent for N2O/O2 sedation.
5. Identify the ethical principles associated with N2O/O2 sedation.
6. Identify ethical responsibilities associated with the administration of N2O/O2 sedation.
7. Identify appropriate practice guidelines for the administration of N2O/O2 sedation based on ethical and legal principles.
Healthcare professionals are ethically and legally responsible for providing the best care that is possible for each patient. Practitioners are also required to abide by the laws and rules governing their discipline in their area (e.g., state, province, or country). It is vitally important to be educated on all aspects of N2O/O2 sedation and be legally certified or licensed by a governing agency when necessary. As stated previously in this text, it is imperative to follow the ASA Practice Guidelines for Sedation and Analgesia by Non-Anesthesiologists, because these will be the standards to which your actions will be compared should there be legal and/or ethical concerns. Basic ethical principles such as nonmaleficence, beneficence, autonomy, and veracity all have implications associated with N2O/O2 sedation.
1 Legal Requirements Associated with N2O/O2 Administration
A. Depending on the discipline and the governing body regulating the requirements of practice within the discipline, there are rules by which to abide regarding the administration of N2O/O2 sedation.
1. Widespread variations exist among disciplines regarding who may administer and/or monitor the N2O/O2 sedation procedure; the licensing agency of the discipline will determine persons who are eligible to provide this type of service and under what conditions it may be administered. These parameters of practice are monitored by the appropriate governing agency, whose purpose is to protect the public.
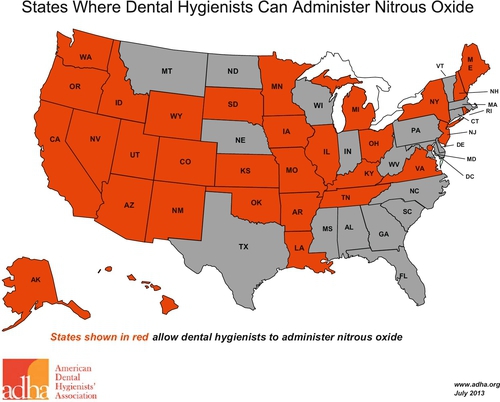
a. Depending on the discipline, a practitioner may only be legally allowed to monitor a patient under N2O/O2 sedation and not be allowed to administer the drug. This prohibits the individual from administering N2O to the patient. This may be the case for certain levels of auxiliaries within a discipline (Figure 18-1).*
b. Information regarding the legality of this procedure may be found within discipline-specific organizations. For example, the American Dental Hygienists’ Association maintains an updated map and corresponding document that identifies practice parameters for all U.S. states allowing dental hygienists to administer N2O/O2 sedation.1
2. In addition, the law outlines the level of supervision necessary for this procedure. In dentistry, states that allow auxiliaries such as dental hygienists to administer N2O may require that the procedure be under the direct supervision of a dentist.
B. Because so many legal variations of rules that are discipline specific exist, it is critical to be informed of the codified law and administrative rules applicable within each state and then it is imperative to practice within the scope of that law.
2 Informed Consent for N2O/O2 Sedation
A. It is also legally mandated that informed consent be obtained from the patient or parent or guardian before the administration of N2O/O2 sedation. The purpose of informed consent is to provide the appropriate information so that the patient can make an educated decision about his or her healthcare.2
1. Components of informed consent include patient identification, proposed treatment along with alternatives, and associated costs of that treatment. In addition, risks and potential adverse outcomes are included. State laws may dictate the inclusion of additional information. Therefore, again, it is strongly advised to be familiar with the appropriate statutes.
2. With N2O/O2 sedation, it is important that the patient or parent/guardian understand why this procedure is being recommended and what can be expected. All information that a reasonable, prudent individual would need or want to know about the procedure must be provided. The patient/parent/guardian must have the opportunity to ask questions, and it is even more important that all his or her questions have been answered.2
3. And from the practitioner’s perspective, it is considered standard of care to provide all the necessary information about the procedure to the patient/parent/guardian.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses