CHAPTER 17 Human Diseases and Health Promotion
17.1 Common human diseases
There are several reasons why diseases occur. These can be divided into (Box 17.1.1):
BOX 17.1.1 Causes of Human Diseases
Many diseases result from an interaction of several of these factors (Figure 17.1.1).
The severity of an illness
A commonly used system to classify the severity of illnesses is the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ (ASA) system, shown in Table 17.1.1.
| Class I | Normal healthy individual |
| Class II | Patient with mild systemic disease (not interfering with daily life) |
| Class III | Severe systemic disease (interferes with daily life) |
| Class IV | Incapacitating systemic disease (constant threat to life) |
| Class V | Moribund (very seriously ill) patient with life expectancy <24 hours |
Oral healthcare in ill patients
Alcoholism
Eventually alcoholism interferes with the working of the brain centres (e.g. respiratory) and can cause unconsciousness or even death (Table 17.1.2). The high rate of deaths among people with alcoholism is mainly as a result of road traffic accidents and assaults. Alcoholics can also drown in their own vomit.
Many other diseases can be caused or aggravated by alcohol including:
Allergy
Allergy is an abnormal response to an allergen (protein). Potential allergens in dentistry are:
Rare allergic reactions in dentistry occur in relation to:
| Allergen Source | Examples |
|---|---|
| Dental materials | Amalgam, gold, mercury, resins, plasters (e.g. Elastoplast) |
| Drugs | Aspirin, penicillins |
| Environment | Animal hair, dust mites, pollens |
| Foods | Milk, nuts (especially peanuts), eggs, shellfish |
| Latex | Gloves, dressings, elastic bands, condoms |
Allergies are responsible for some types of the following diseases and conditions:
As a dental professional, you must be familiar with the medical management of anaphylaxis within a dental setting (see Chapter 2).
Early Symptoms and Signs of an Allergic Reaction
Anaemia
A person is said to have anaemia when their haemoglobin (Hb) level is below the normal for their age, gender and ethnic background. Haemoglobin is required to carry oxygen to the brain and tissues (see Chapter 4). Anaemia has many causes as shown in Table 17.1.4.
| Nature of Anaemia | Cause |
|---|---|
| Increased loss of red blood cells (RBCs) | Menstrual blood loss |
| Gastro-intestinal blood loss | |
| Haemolysis (breakdown of the RBCs), such as in malaria or sickle disease | |
| Reduced RBC production | Dietary deficiency |
| Bone marrow disease, such as in leukaemia | |
| Increased tissue requirements | Puberty |
| Pregnancy | |
| Decreased tissue requirements | Hypothyroidism |
Anxiety and stress
Arthritis
Asthma
During an asthmatic attack a person may have difficulty breathing, cough and wheeziness.
There are two types of asthma (Table 17.1.5): extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic asthma is more common and is caused by exposure to allergens. Intrinsic asthma is much less common and is often not related to exposure to allergens.
| Extrinsic | Intrinsic | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Common | Less common |
| Associations | Allergic disease (hay fever, eczema, allergic rhinitis) | None |
| Main precipitating factors | Animal hairs | Air pollutants |
| House dust mite | Cold air | |
| Pollen and moulds | Drugs (NSAIDs) | |
| Stress | ||
| Exercise |
Atheroma (atherosclerosis)
Signs and Symptoms
Autism
Bell’s palsy
Bell’s palsy (Figure 17.1.5) is a type of facial paralysis that usually occurs on one side. It occurs mainly due to infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV). Most patients recover totally and spontaneously within a few weeks. Treatment includes:
Blood-borne viral infections
Blood-borne virus infections (e. g. hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), or HIV) are transmitted mainly by sharps injuries, but also via unscreened blood and sexual contact. Occasionally they are transmitted through the mucosa of the eye or mouth (see p. 379).
Cannabis (marijuana) use
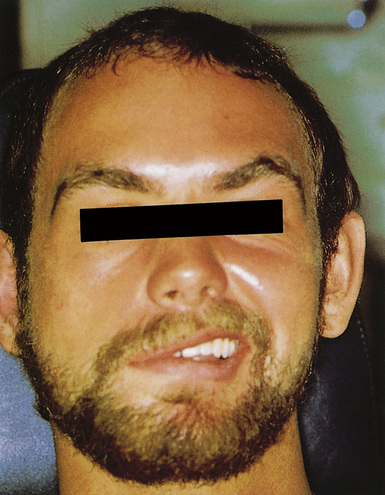
The long-term effects of using cannabis are not yet clear, but it may affect the lungs, heart, and immune system and mental health. Marijuana smokers may develop many of the breathing problems that tobacco smokers have, hypertension and increased heart rate and lowered oxygen-carrying capacity of blood. Because of this the risk of a heart attack is increased four-fold in the first hour after smoking marijuana. Long-term use of marijuana can trigger or worsen schizophrenia (see p. 389).
Cardiac disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Coronary (ischaemic) heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death in the UK.
It is caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
Signs and Symptoms (see also Box 17.1.2)
Creutzfeldt–jakob disease
To read more about prion disease and health and safety, see HTM 01-05 (Section 1; see Chapter 1) and Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy Agents: safe working and the prevention of infection produced by the Advisory Committee on Dangerous Pathogens (http://www.dh.gov.uk/ab/ACDP/TSEguidance/DH_098253).
Dementia and alzheimer disease
Depression
Drug abuse (substance dependence)
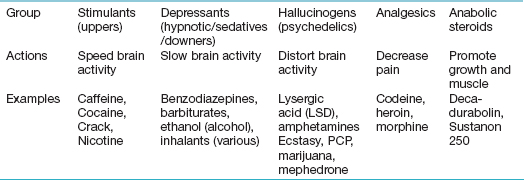
Drug abuse is self-administration of certain drugs without any medical indication for them, despite adverse medical and social consequences (Table 17.1.6). The use of some drugs is illegal and people found in possession of these or, particularly, if there is any intention of dealing (supplying), can be charged.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses