16
Periodontal history, examination and diagnosis
Figure 16.1 Steps in taking a periodontal history, examination and diagnosis.
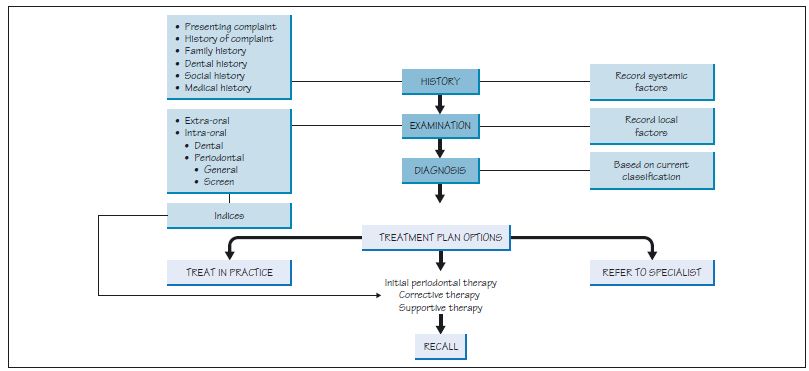
Figure 16.2 Points a general description of a periodontal condition should cover.
Figure 16.3 A detailed examination of periodontal tissues and recording of periodontal indices.

Figure 16.4 Diagram of probing pocket depth, recession and clinical attachment loss.
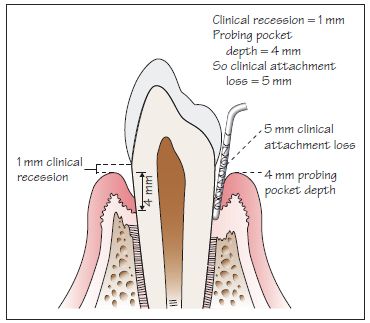
Figure 16.5 Suppuration.
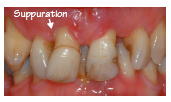
Figure 16.6 Classification of furcation involvement.
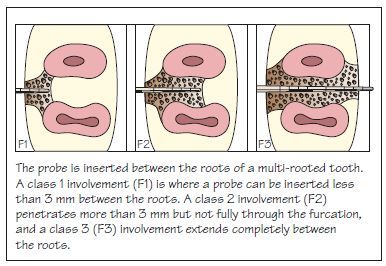
Figure 16.7 Mobility.

Figure 16.8 Radiographic assessment.
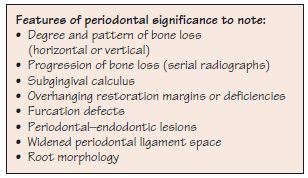
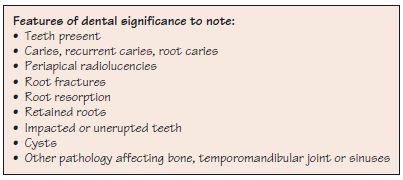
The history and examination should provide relevant information to enable the clinician to formulate a clinical diagnosis and treatment plan (Fig. 16.1).
Eliciting a good history requires a structured approach, good communication skills and building up a rapport with the patient. The history for a patient presenting for a periodontal assessment should include details of:
1 Presenting complaint:
2 History of complaint/reason for attendance: the onset, duration, severity and any triggers of the presenting complaint should be noted.
3 Family history of periodontal p/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


