NOSE AND NASAL CAVITY
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
Nose
The prominent anatomic structure located inferior and medial to the eyes
Helps in breathing and olfaction
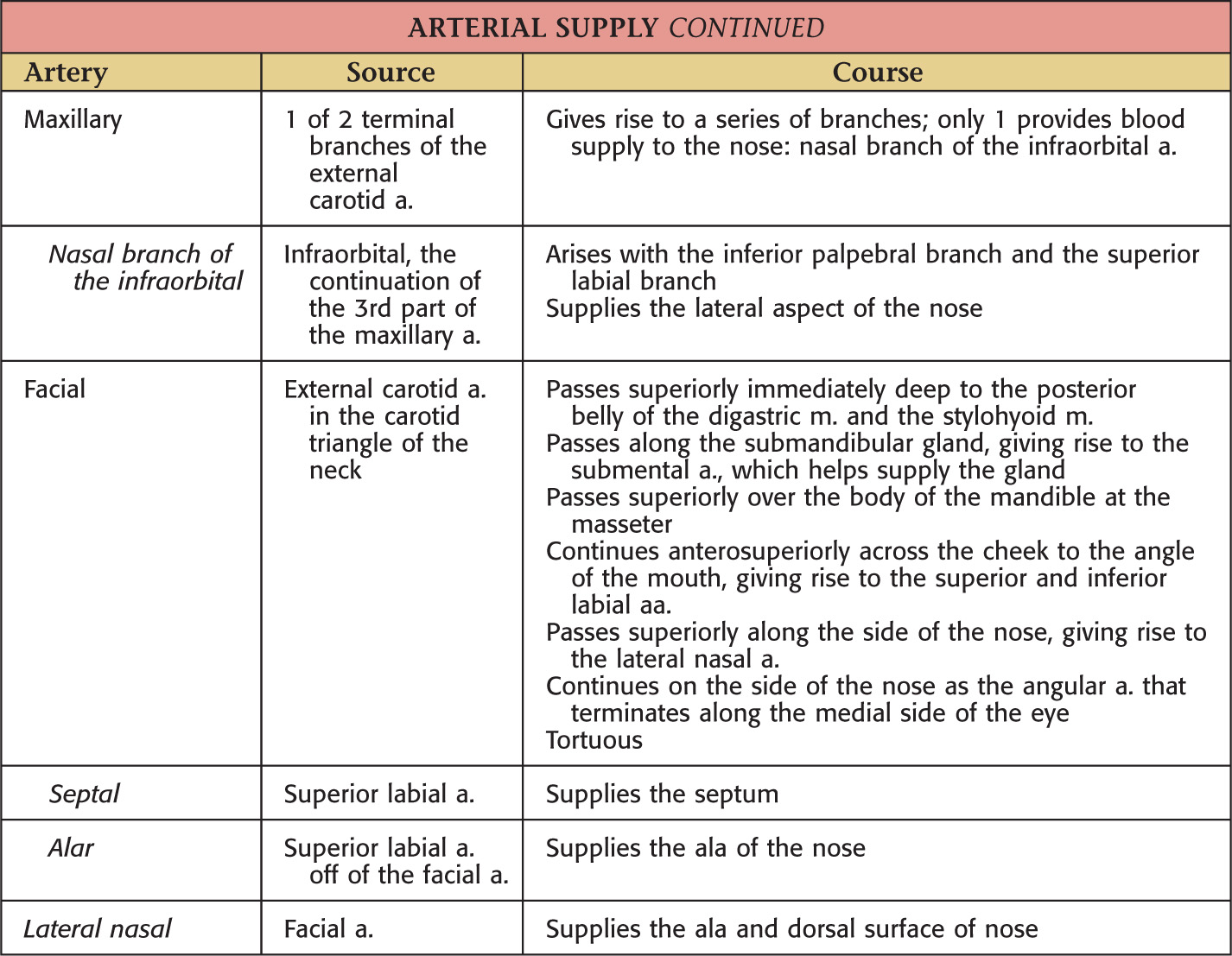
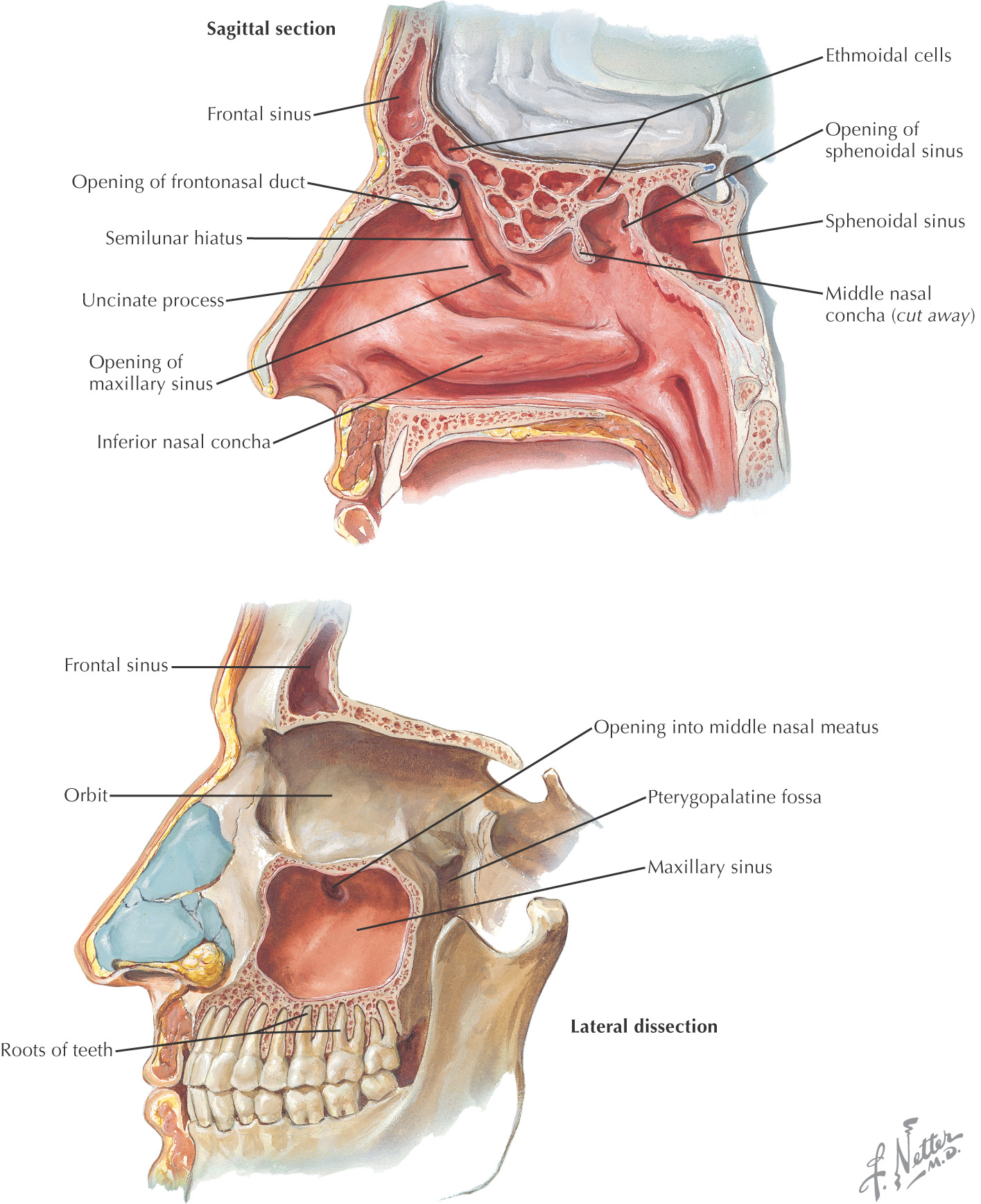
Nasal Cavity
The complex chamber located posterior to the vestibule and atrium of the nose
Respiratory Epithelium
Highly vascular and easily congested
When this tissue is irritated, its blood vessels reflexively dilate and the glands secrete, normally leading to sneezing
Nose
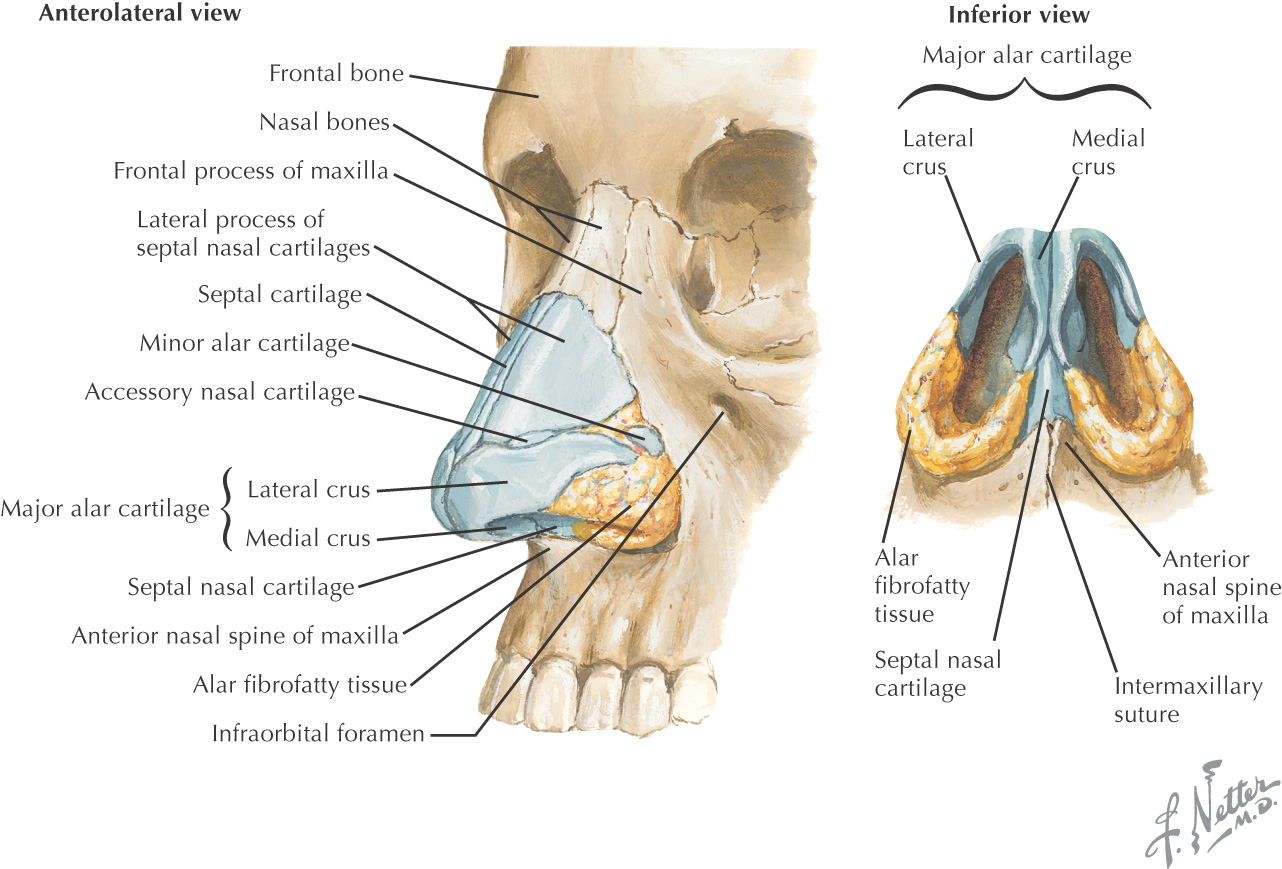
ANATOMY OF THE NOSE
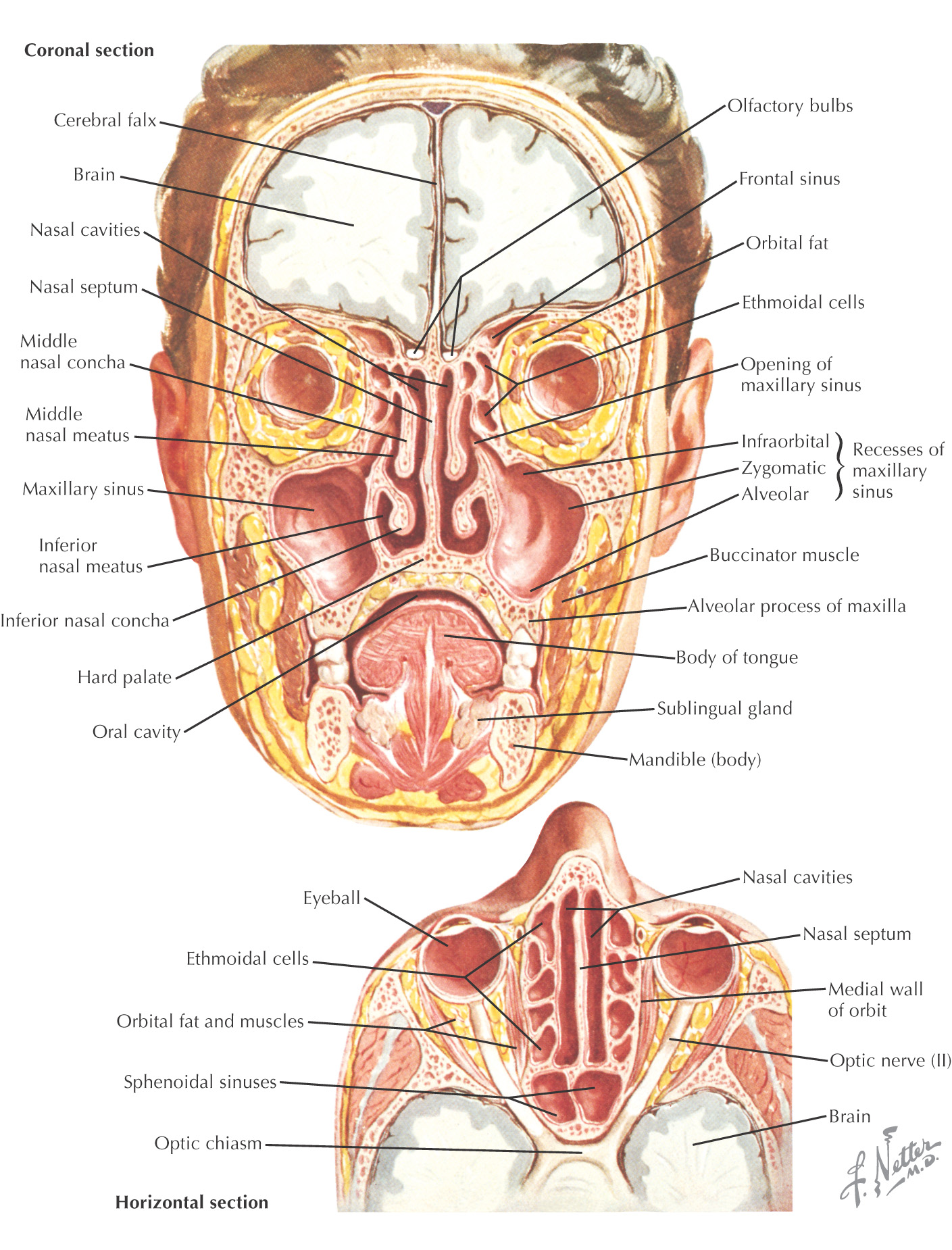
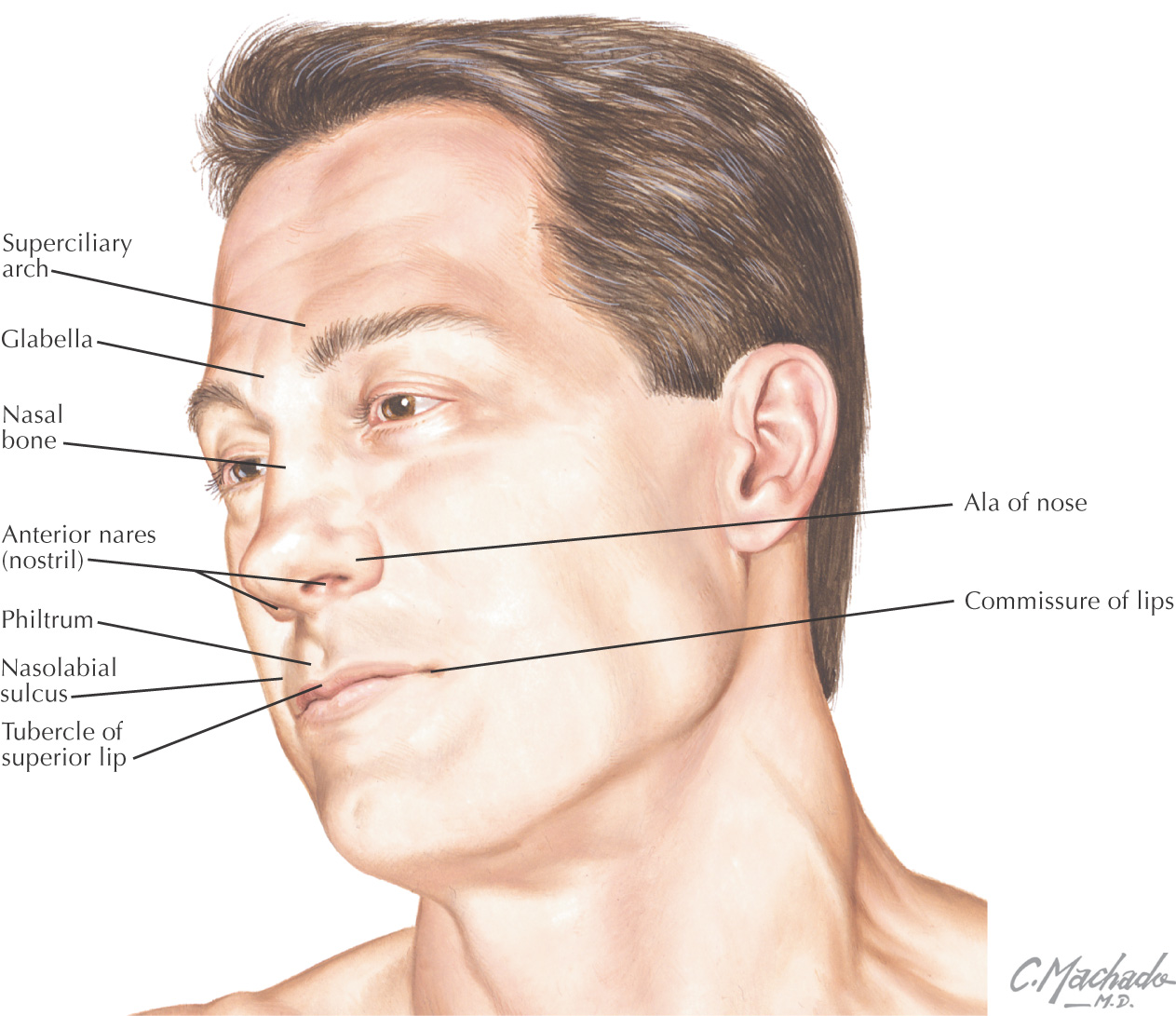
The nose is pyramidal in form
3 pairs of bones form the root of the nose:
• Nasal
Because the root of the nose is made of bone, it is fixed
3 different cartilages form the dorsum and apex of the nose:
• Septal
• Alar
Because the dorsum and apex are cartilaginous, the nose is quite mobile
The cavity of the nose opposite the alar cartilage is called the vestibule and is lined by many coarse hairs called vibrissae
The cavity superior to the vestibule is the atrium
At the apex are found the 2 nostrils, or anterior nares, which are separated by the septum connecting the apex to the philtrum of the upper lip
Fibrous tissue helps connect the cartilages together and posteriorly to the maxilla
The primary lymphatic drainage of the nose is into the submandibular lymph nodes
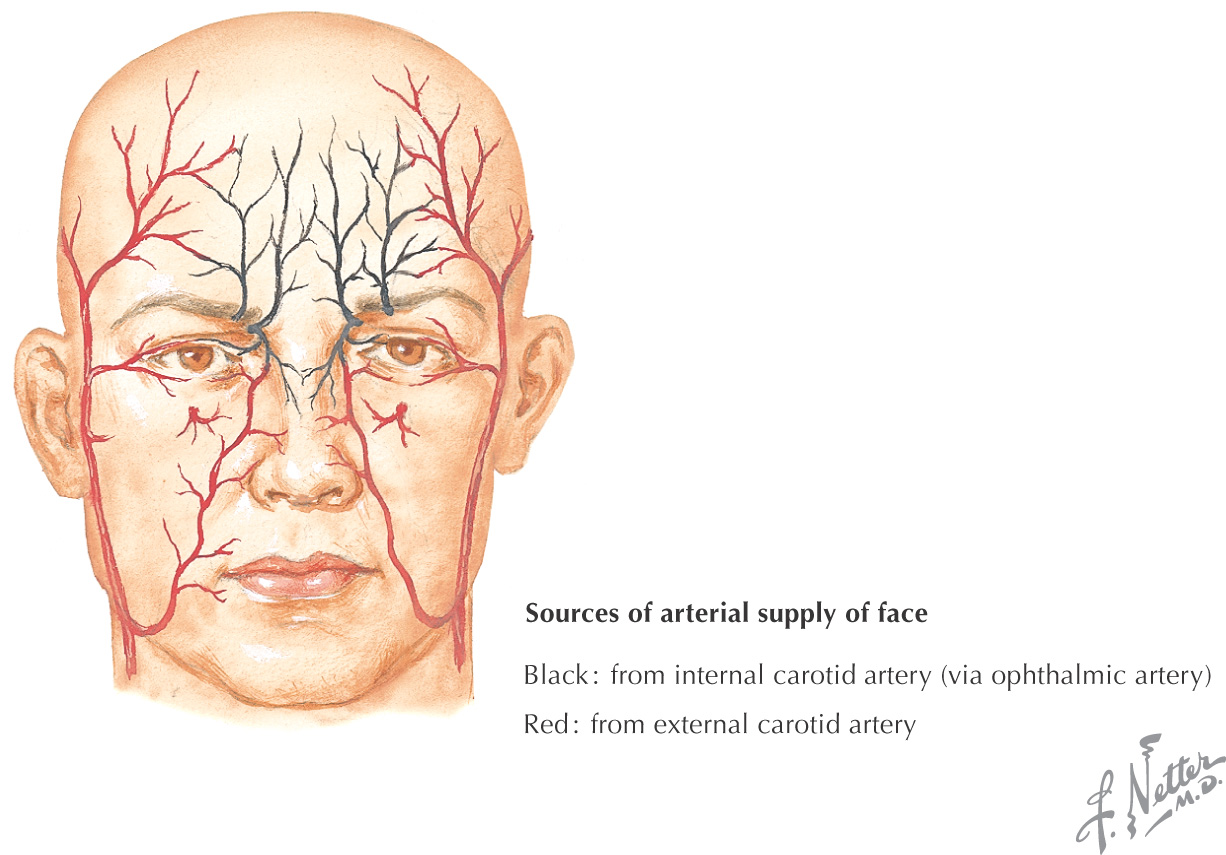
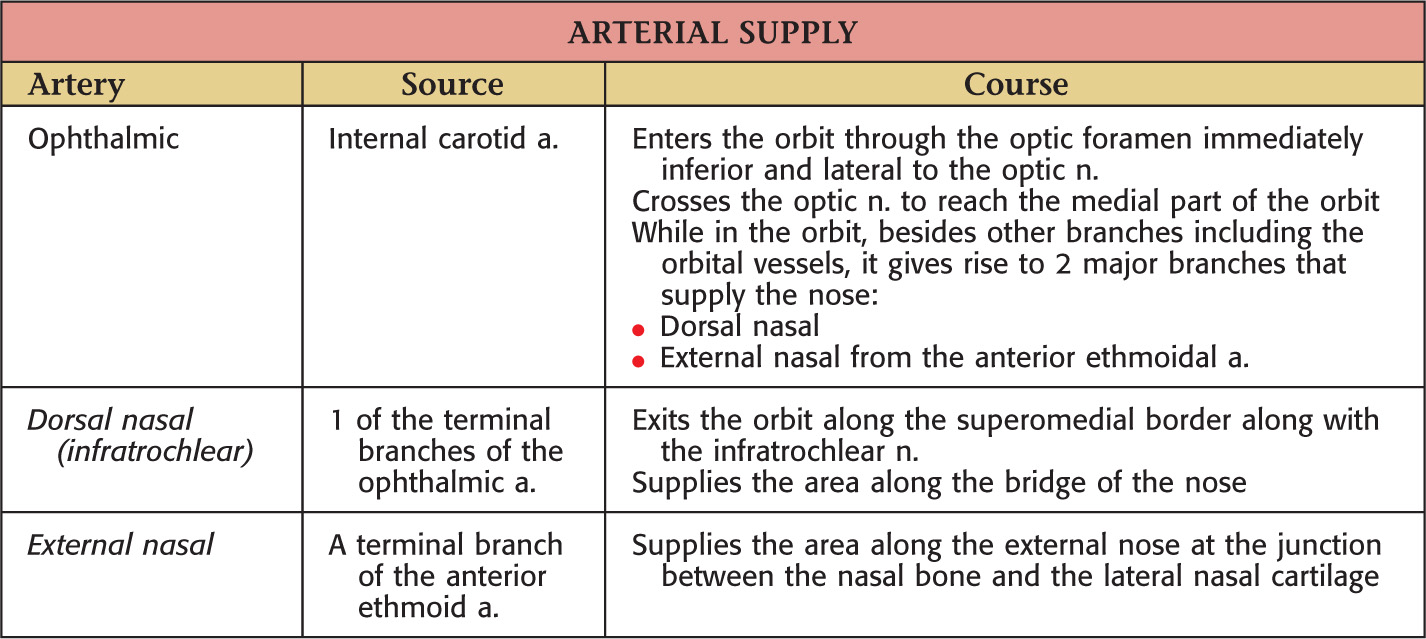
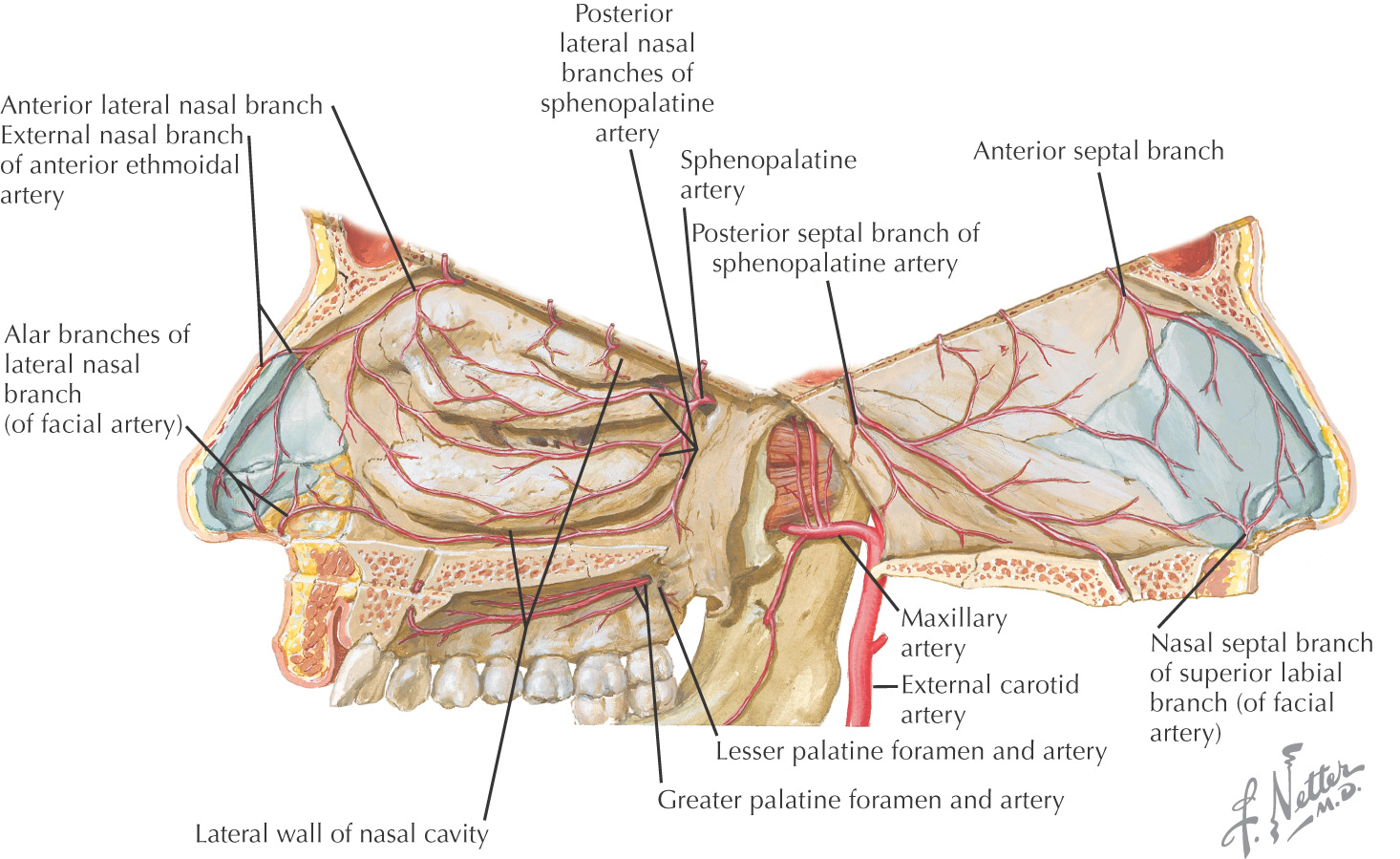
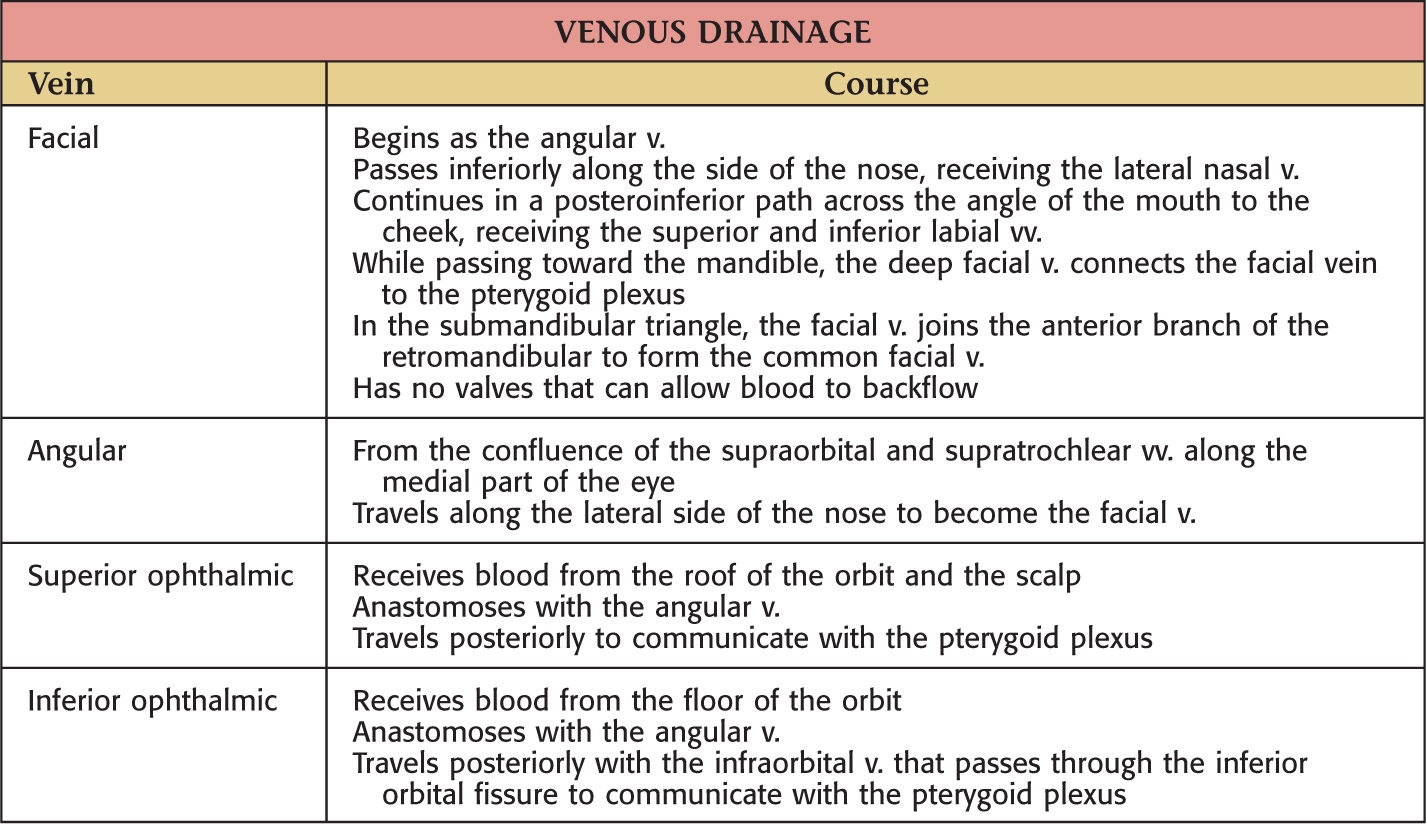
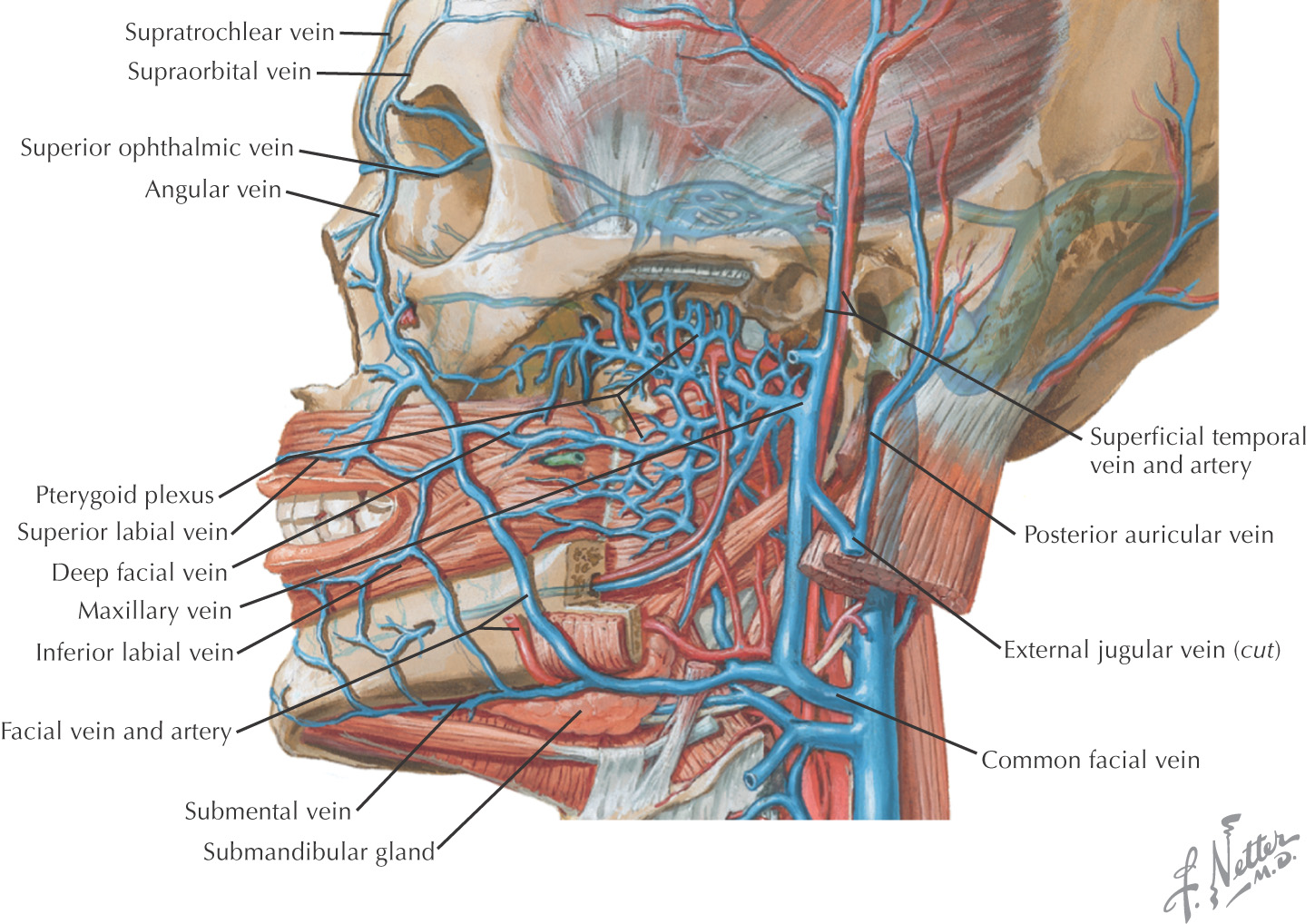
VASCULAR SUPPLY OF THE NOSE
The blood supply to the nose arises from 3 major arteries:
• Facial
These vessels are derived from the external and internal carotid arteries
These arteries anastomose along the nose
Many nosebleeds are due to trauma to the septal branch of the superior labial artery from the facial artery
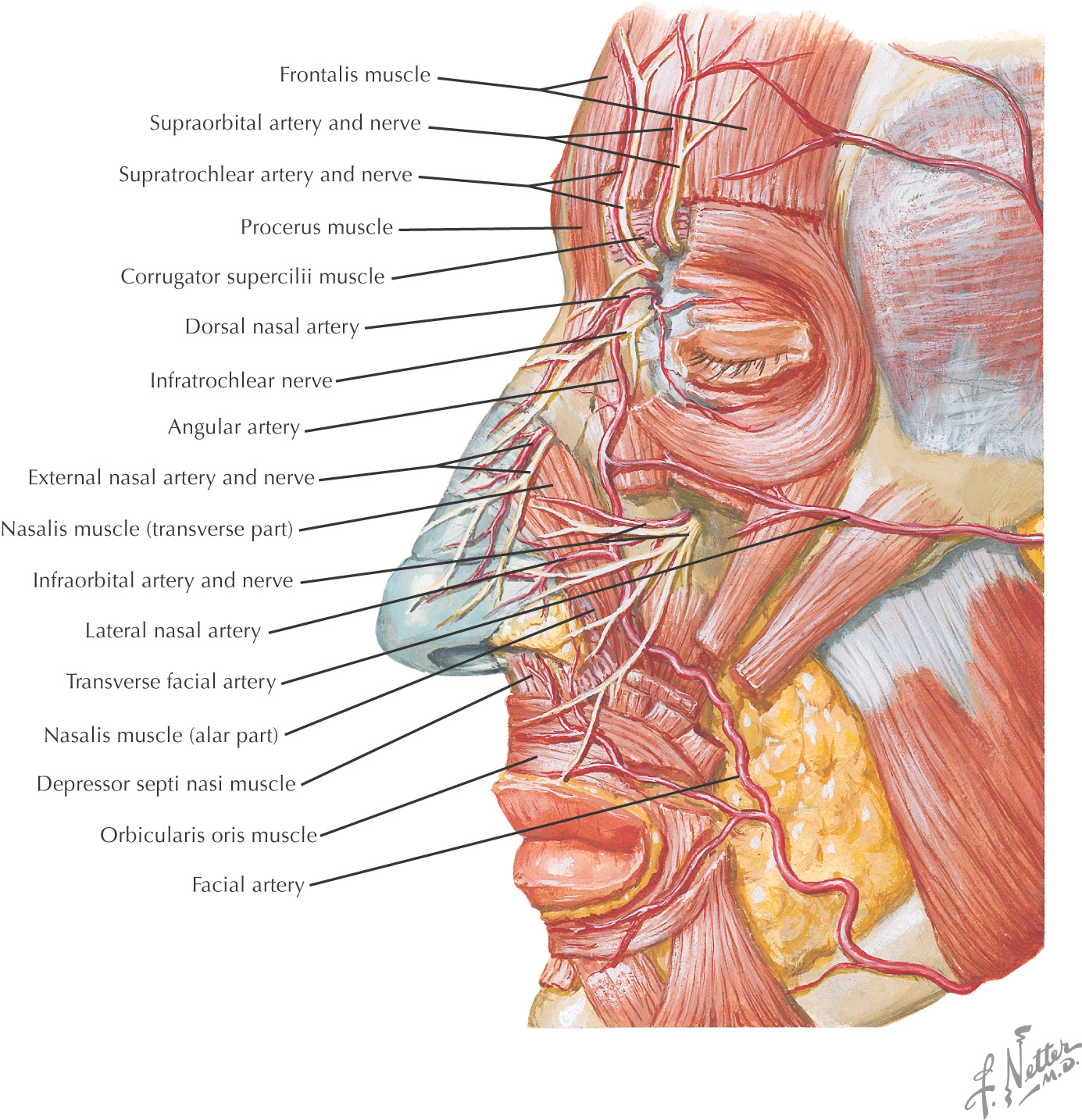
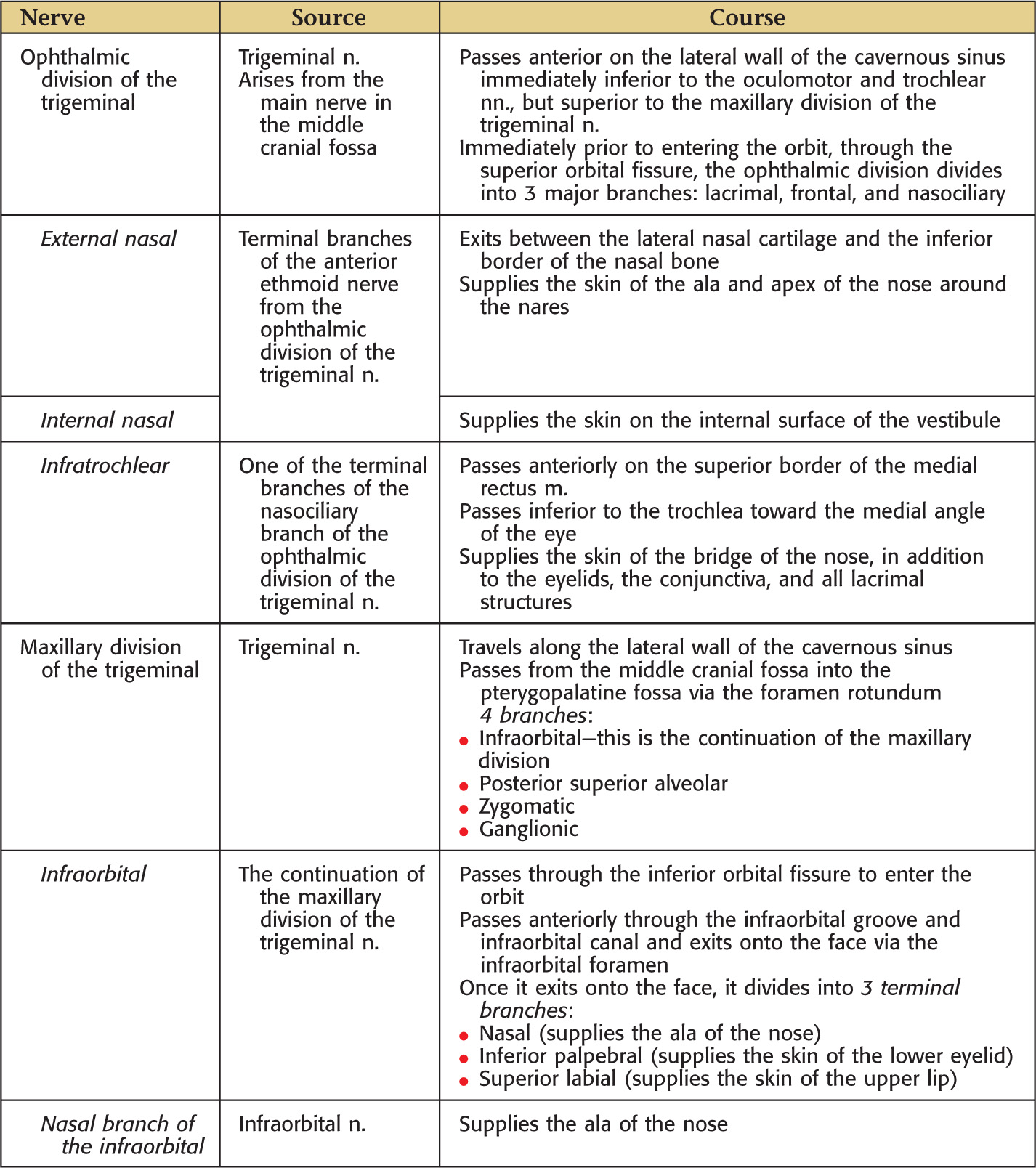
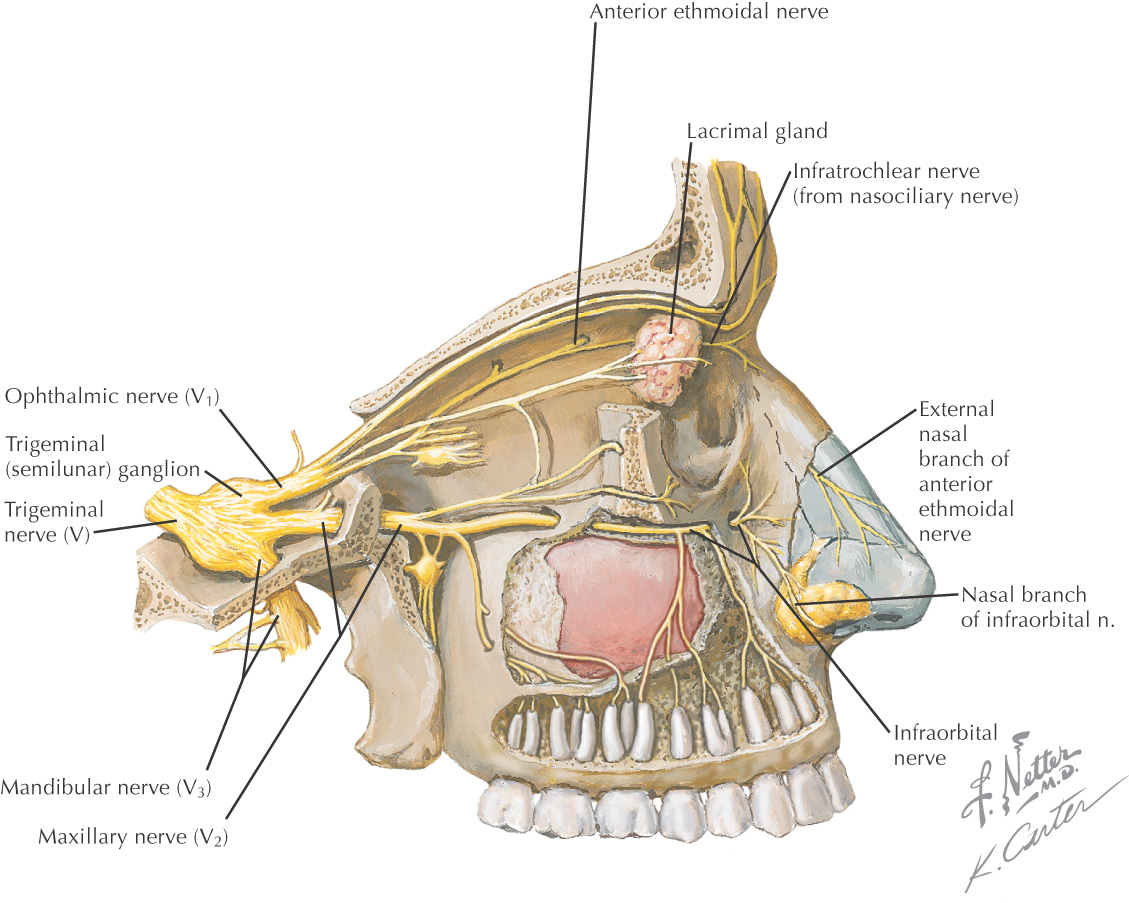
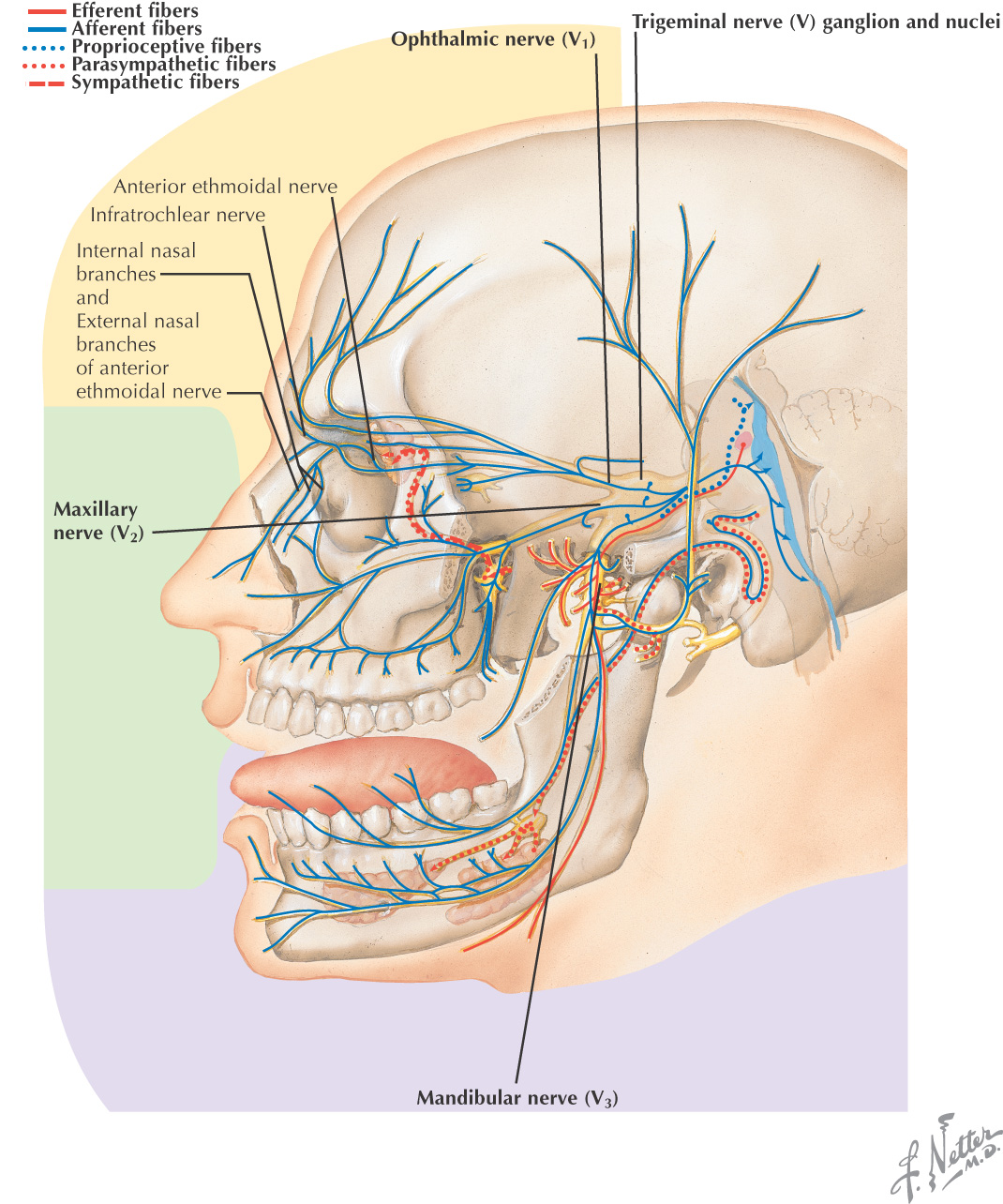
NERVE SUPPLY OF THE NOSE
The sensory supply to the nose arises from branches of the ophthalmic and maxillary divisions of the trigeminal nerve
/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses