1 Endodontics
The word endodontic comes from two Greek words meaning “inside” and “tooth.” Endodontics is the science of diagnosing and treating pulpal and periradicular disease. Endodontics is that branch of dentistry concerned with the morphology, physiology, and pathology of the human dental pulp and periradicular tissues. Its study and practice encompass the basic and clinical sciences, including the biology of the normal pulp, and the etiology, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases and injuries of the pulp and associated periradicular conditions.*
OUTLINE OF REVIEW
1.1 Pulpal Diseases
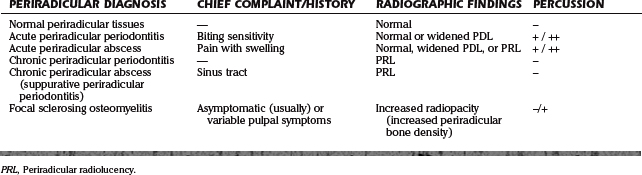
1.2 Periradicular Diseases
1.3 Endodontic Diagnosis
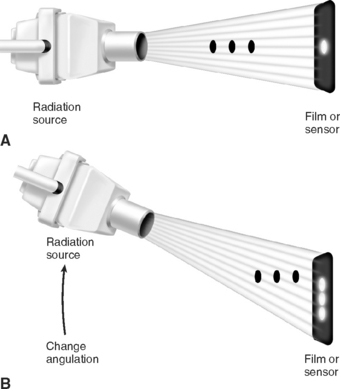
1.4 Endodontic Examination and Testing
Extraoral Exam
Intraoral Endodontic Examination
Intraoral diagnostic tests enable the practitioner to:
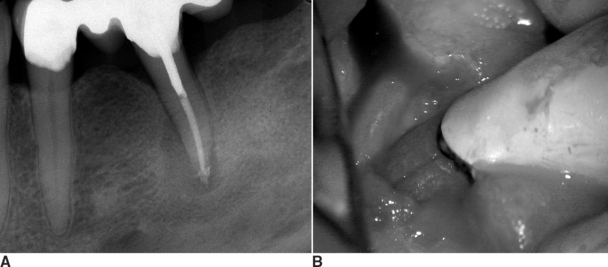
1.5 Cracked Tooth Syndrome
A strong majority are lower molars, with a slight preference for the first molar over the second.
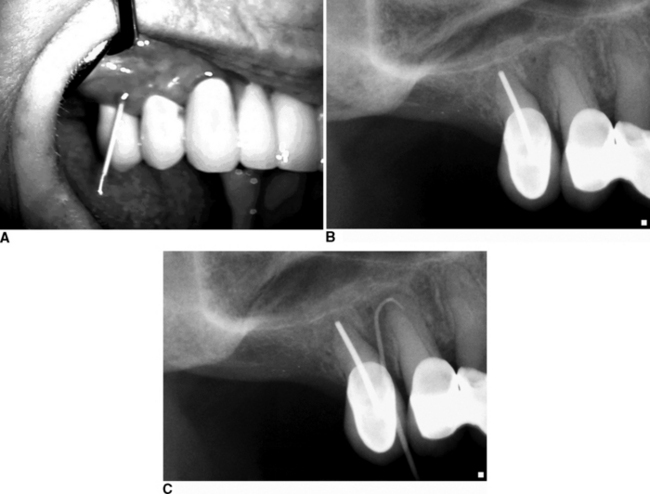
1.6 Vertical Root Fracture
Predisposing factors are a weakening of the root structure by:
1.7 Endodontic–Periodontal Relationships
OUTLINE OF REVIEW
2.1 Nonsurgical Endodontics
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses