Fig. 10.1
Showing proposed treatment and planned restorative options to the patient using smile design software. (a) Showing intraoral situation. (b) Full facial appearance of the proposed restorative options
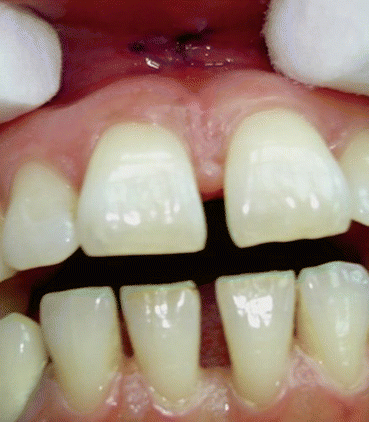
Fig. 10.2
A frenectomy case due to enlarged frenum
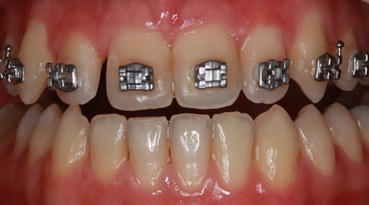
Fig. 10.3
Example of orthodontic treatment for diastema
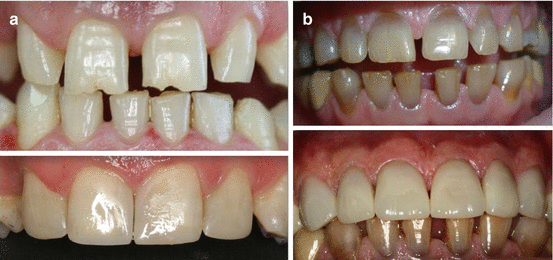
Fig. 10.4
Restorative treatment of diastema closure. (a) Diastema closure with direct composite resin. (b) Diastema closure with porcelain laminate veneers
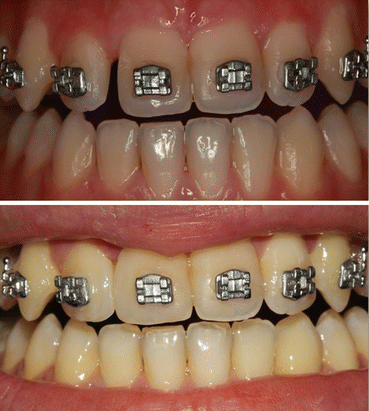
Fig. 10.5
Example of diastema closure with orthodontic-restorative combined procedures
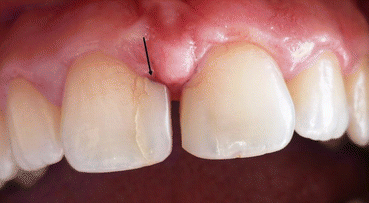
Fig. 10.6
Example of an over-countered (arrow) and did not properly finished restoration of diastema closure with composite resin
Key Note
When a multidisciplinary treatment procedure is planned between the orthodontist and restorative dentist regarding the closure of diastema, then collaboration should begin at the diagnostic phase for the correct treatment procedure and successful outcome of the case.
When a multidisciplinary treatment procedure is planned between the orthodontist and restorative dentist regarding the closure of diastema, then collaboration should begin at the diagnostic phase for the correct treatment procedure and successful outcome of the case [16]. Not in all the diastema cases but in some of them that gingival tissue can be found in asymmetric and creation of a pleasant restoration, and also natural smile cannot be overemphasized during closure of diastema [5]. Creation of an esthetically pleasant final restoration that is in harmony with the gingival structure can be accomplished by the periodontal surgery. When a disproportionate tooth form is identified and this is due to the gingival soft tissue, clinician should need to alter gingival soft tissue first by periodontal surgery (i.e., gingivectomy or gingival grafting) before initiation of any definitive restoration (Fig. 10.7) [5]. Leveling of gingival structures can be also accomplished by the orthodontic intrusion or extrusion treatments [5].
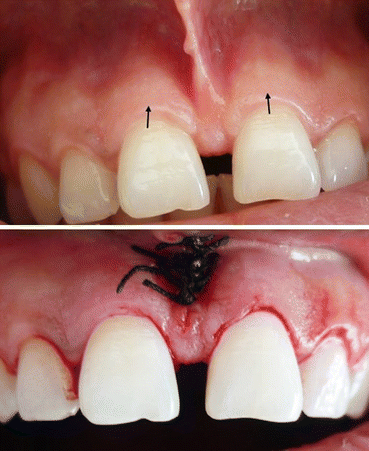

Fig. 10.7
Frenectomy and periodontal crown lengthening procedure due to short clinical crowns before initiation of definitive restoration
Both median and polydiastemas can make an esthetically unpleasant appearance for the patients, and hence, many patients seek treatment of these occurrences for esthetical reasons. As described in previous chapters, occurrence of the diastema in the childhood due to physiological development is normal characteristics, and less than 2-mm diastema can close spontaneously by the growth and eruption of the canine teeth. If they do not close spontaneously by the growth of the children, less than 2–3 mm diastema can be successfully closed by the removable appliances. For adult patient with a wider diastema more than 2 mm, fixed orthodontic appliances can be used to close diastema. Tooth size discrepancies can also cause the formation of diastema, and these situations can be successfully treated by the orthodontic, restorative, or in combination of both treatment approaches. Generally fixed-type orthodontic treatment can provide better control in crown/root angulation, overbite, and overjet [2]. In the case of missing laterals that can cause midline diastema, closing of the median space and alignment of the teeth according to dental midline can successfully be done by orthodontic treatment [2]. Thereafter, missed lateral space can be reconstructed with fixed prosthesis (Fig. 10.8) or minimal invasively by using adhesive-type bridges.
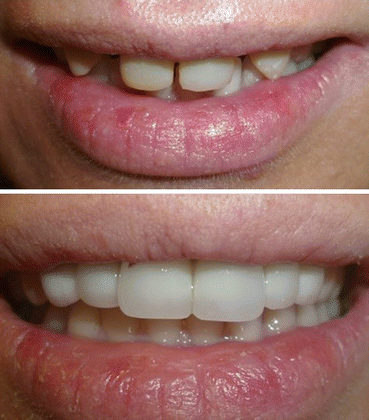

Fig. 10.8
Treatment of diastema with full ceramic fixed bridge in the case of congenitally missed laterals
Clinician can also use computer-assisted treatment planning, digital impression, and digital smile design by using computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems [16]. However, little information is available regarding the fabrication of porcelain laminate veneers, esthetic characterization, longevity of the restorations, and applicability in clinical environment due to its relatively high cost [17–19].
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


