Chapter 68 Microdebrider-assisted tonsillectomy
1 INTRODUCTION
Tonsillectomy remains one of the most common surgical procedures performed on children. In contrast to several decades ago when infectious indications were common, the reason most children undergo tonsillectomy today is to relieve upper airway obstruction. Traditional ‘extracapsular’ tonsillectomy remains a fairly morbid procedure. Children routinely require several days off from school and parents are often forced to take time off from work. Despite advances in surgical technology a significant reduction in postoperative pain following this procedure has eluded surgeons. This is evidenced by the wide array of techniques available to the surgeon. Furthermore, the rate of postoperative hemorrhage has remained fairly stable despite the technique practiced. Partial ‘intracapsular’ tonsillectomy seeks to significantly reduce postoperative pain and hemorrhage risk while effectively treating upper airway obstruction.
2 PATIENT SELECTION
The safety of intracapsular tonsillectomy in the young patient has been studied. Bent et al. found no significant difference in the rate of readmission, pain, oral intake or anal-gesic requirements in patients younger than 3 years of age who underwent partial tonsillectomy compared to a control group.1
3 OUTLINE OF PROCEDURE
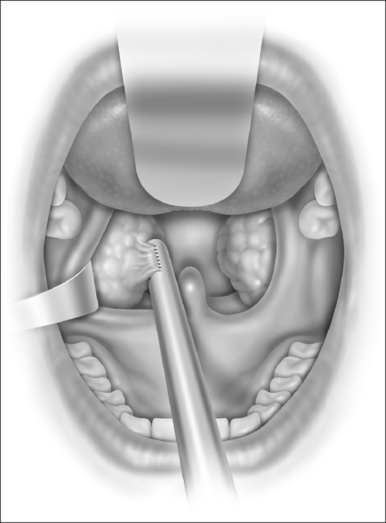
With the microdebrider set at a rate of 1500 rpm on oscillating mode, dissection of the tonsil begins at the inferior pole (Fig. 68.1). This helps prevent blood from obscuring visualization of the anterior and posterior pillars. Dissection proceeds from a lateral to medial direction until the plane of the pillars is reached. At this point it is generally helpful to further stabilize and control the anterior pillar to maximize tissue removal and minimize injury to mucosa. A Hurd elevator is particularly helpful in this circumstance as it can also help to medialize the remaining tonsil tissue, making dissection easier. Dissection is carried down to but not through the capsule of the tonsil. The use of a mirror can facilitate dissection of the superior pole. Care is taken to avoid inadvertent injury to the uvula, which can occur rapidly given the suction associated with the microdebrider. After dissection is completed, hemostasis is achieved using suction cautery with settings generally between 20 and 40 watts according to surgeon preference (Fig. 68.2). The contralateral tonsil is then dissected in an identical fashion. Once the procedure is completed the pharynx is irrigated with sterile normal saline and the mouth gag is allowed to relax. After approximately one minute the gag is reopened and hemostasis is confirmed. A suction catheter is then passed under direct vision and the stomach and hypopharynx are suctioned free of any blood or irrigation fluid that may cause post-extubation laryngospasm.The mouth gag and nasal catheters (if present) are removed and the patient is turned over to anesthesia personnel for extubation.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses