Lateral Luxation
OBJECTIVES
1 Differentiate type of luxation injury.
2 Identify injured tissues involved.
3 Define objectives of acute treatment.
4 Estimate frequency and type of possible complications.
DESCRIPTION AND CLINICAL APPEARANCE
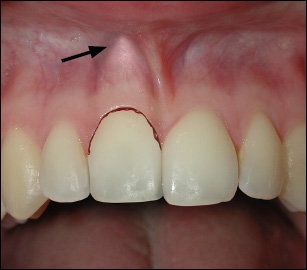
There is lateral eccentric displacement of the tooth in its socket; and it is accompanied by comminution or fracture of the alveolar bone plate (labial and/or lingual).
The crown appears displaced in its socket, usually in a palatal direction. The tooth is immobile due to its locked position in the bone, and there is a high ankylotic (metallic) percussion tone. There may or may not be bleeding from the gingival sulcus. The root apex and the displaced labial bone can be palpated in the sulcus area (arrow).
RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE
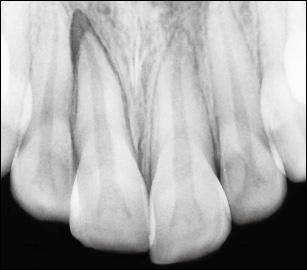
A steep (occlusal) or eccentric radiographic exposure is necessary to disclose displacement. The tooth appears displaced, with the apical or lateral part of the socket empty. A periapical exposure bisecting angle may not reveal displacement.
BIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS AND TREATMENT PRINCIPLES
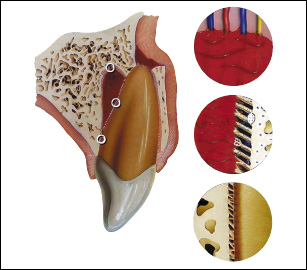
The injury is v/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


