Examination and Diagnosis
OBJECTIVES
1 Perform clinical procedures to gather necessary information about the type and extent of injury.
2 Perform radiographic examination procedures to gather necessary information about injuries to the tooth and supporting structures.
3 Perform radiographic examination procedures to detect foreign bodies embedded in lip wounds.
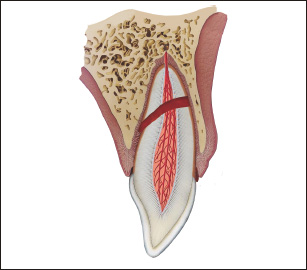
In order to arrive at a timely and accurate diagnosis and the probable extent of injury to the pulp, periodontium and associated structures, a systematic examination of the traumatized patient is essential (see also Appendices 1–3).20–22 When the patient arrives for treatment of an acute trauma, the oral region is usually heavily contaminated. The first step in the examination procedure, therefore, is to wash the patient’s face and oral cavity. If there are soft tissue wounds, a mild detergent should be used. While this is being done, it is possible to get an initial impression of the extent of injury. Thereafter, a series of questions must be asked to aid in diagnosis and treatment planning. These questions include the following.
When did the injury occur?
The answer will reveal a time factor, which is critical when considering treatment of avulsed or displaced teeth as the time factor can have a direct influence on the choice of treatment.
Where did the injury occur?
While there might be legal implications in this answer, this will also indicate the possibility of contamination of wounds.
How did the injury occur?
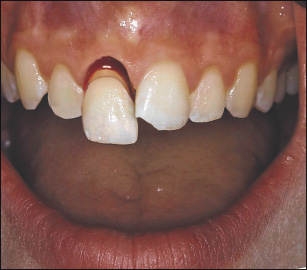
The answer to this question will indicate possible zones of injury (e.g. crown-root fractures in the premolar and molar region after impact to the chin). Any inconsistency between the wounds observed in a child and the history provided should raise suspicion of child abuse and call for the assistance of other medical specialties. Also a marked treatment delay should raise the suspicion of child abuse.
Was there a period of unconsciousness?
If so, how long? Is there headache? Amnesia? Nausea? Vomiting? These are all signs of brain concussion and require medical attention and sometimes observation at a hospital. However, this usually does not contraindicate emergency treatment of the dental injury (e.g. replantation of avulsed teeth).
Have there been previous injuries to the teeth?
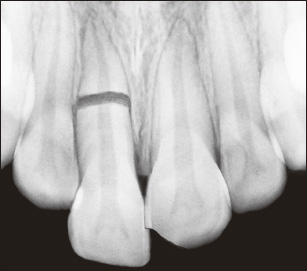
Answers to this may explain radiographic findings, such as pulp canal obliteration and incomplete root formation in a dentition with otherwise completed root development.
What measures have been taken at the place of accident or another clinic?
Teeth may have been replanted or stored in media after the accident. The patient may also have been referred from another emergency clinic and it is of importance to document what has been done at the other clinic.
Is there a change in occlusion?
An affirmative answer could imply tooth luxation, alveolar fracture, jaw fracture, or luxation or fracture of the temporomandibular joint.
Is there an increased reaction in the teeth to cold and/or heat?
A positive finding indicates exposure of dentin and need of dentinal coverage.
Medical history
Finally, a short medical history should reveal possible allergies, blood disorders, medication and other information that may influence treatmen/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


