Fig. 5.1
Microesthetic evaluation. (a, b) Surface characteristics of teeth in a 20-year-old patient and their relationship with lips. (c, d) Surface characteristics of teeth in a 50-year-old patient and their relationship with lips
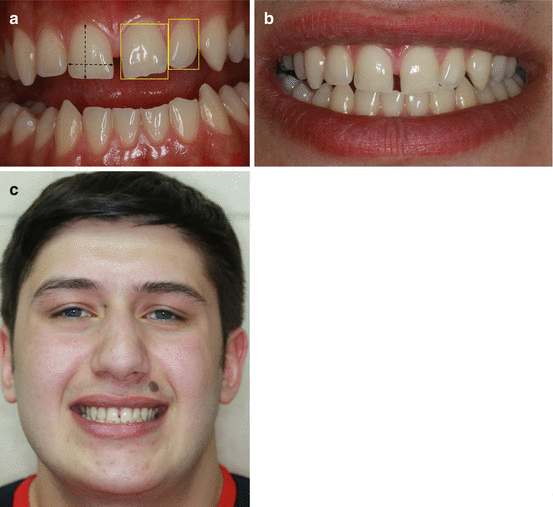
Fig. 5.2
Macroesthetic evaluation. (a) Evaluation of the tooth proportions and relationship of each tooth to other. (b) Evaluation of the harmony between teeth and surrounding structures. (c) Evaluation of the harmony between teeth and facial characteristics
Harmoniously aligned teeth with the surrounding soft tissue as well as face ensures natural and attractive smiles for a patient, and clinician should work in collaboration with the multidisciplinary team members to combine their technical and artistic skills for creating pleasant, biomimetic, and natural restorations (Fig. 5.3a, b).
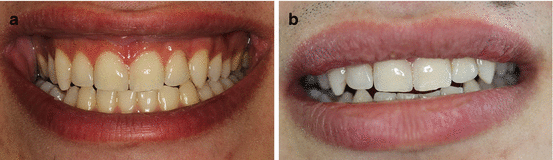

Fig. 5.3
(a) Final restorations (note harmoniously aligned teeth and gingiva), (b) harmonious relationship between the teeth and the lips
For these reasons, thorough evaluation and understanding of the various proportions, dimensions, and artistic elements are essentially important to create a balanced, harmonious, and naturally pleasant restoration. Therefore, a detailed, systematic facial, dentofacial, dentogingival, and dental analysis should be done carefully for a successful, pleasant, biomimetic, and natural esthetic outcome [3–5].
Key Note
Smile design process should be managed by multidisciplinary approaches in decision-making process for creation of an individualized patient treatment, and clinician can use a variety of smile design softwares and protocols to achieve most predictable and pleasant final results.
Currently, a variety of smile design software and protocols are available to clinicians for creating most predictable and pleasant final results. Some of these softwares are available for a fee for clinical implication (Digital Smile System, Varese, Italy; Smile Designer Pro, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Smylist Professional, Budapest, Hungary; Smiletron, Swatar, Malta), and another such as Photoshop software [8] (Adobe system, San Jose, CA, USA) and Keynote (Apple Inc., Cupertino, California, USA) can also be used for determination of the smile design (Figs. 5.4 and 5.5). As previously described, smile design process should be managed by multidisciplinary approaches in decision-making process for an individualized treatment [7]. Smile design requires a series of esthetic principle integration to the treatment procedure for creation of harmonized restorations with the patient’s facial, dentofacial, and dental compositions [9]. For clinician who uses one of the previously mentioned smile design software, it is obviously necessary to obtain both facial and dental photographs of the patient from correct angle and distance.
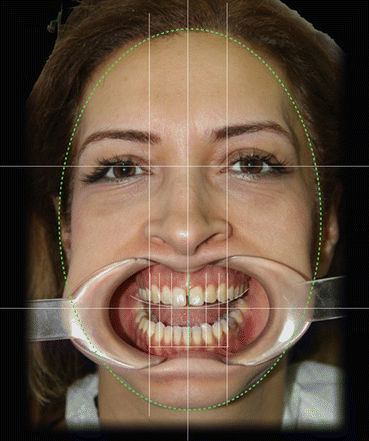
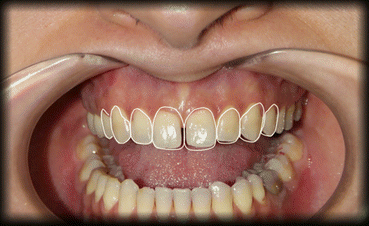

Fig. 5.4
Smile analysis of patient by using Keynote (Apple Inc., Cupertino, California, USA)

Fig. 5.5
Smile analysis: Determination of the tooth proportions using Keynote (Apple Inc., Cupertino, California, USA)
Esthetic digital smile designing protocol requires a series of full frame digital photographs as well as videos of the patient during smiling and speaking for capturing the dynamic phase [3, 7, 9]. If possible, these photographs must be in high resolution with a good lighting condition because the photoraphs are the essential part of the smile analysis of the patient and will be used later for the esthetic analysis within the main principles and guidelines. During capturing of photographs, clinician can also use a tripod which enables stable support for the camera to avoid having any blurry photos. In addition, clinician can also use these photographs for the consultation with the multidisciplinary team member of the restorative procedure for correct analysis of the patient. Posture of the patient is important for obtaining proper and standardized photographs for smile analysis. Therefore, the patient must seat or stand in front of the clinician or photographer in natural head position, and camera must be positioned to focus the head, [10, 11] (Fig. 5.6).


Fig. 5.6
Frontal photograph of the patient in natural head position
As previously stated, smile design process begins with macroesthetic level in which patient’s face and its relation with the smile is evaluated [7, 8
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


