ENAMEL
Developing tooth
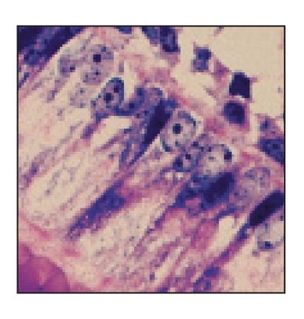
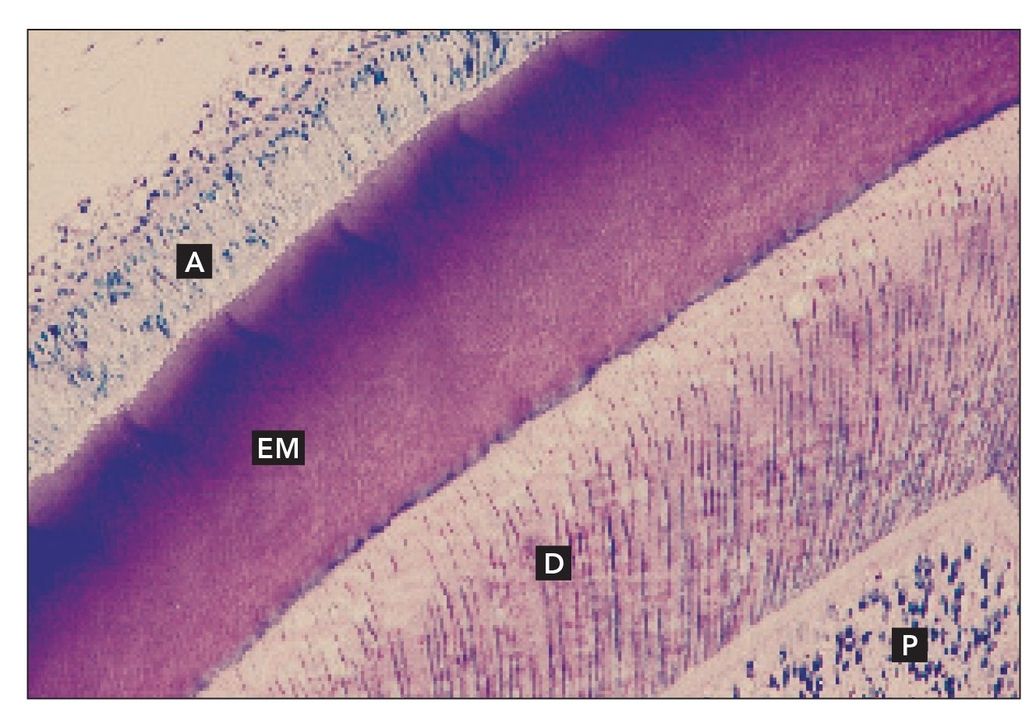
Decalcified sagittal section of a developing tooth. Ameloblasts (A) sit on the surface of the enamel matrix (EM). Dentin (D) and pulp (P) are also present (H and Lee stain; ×160).
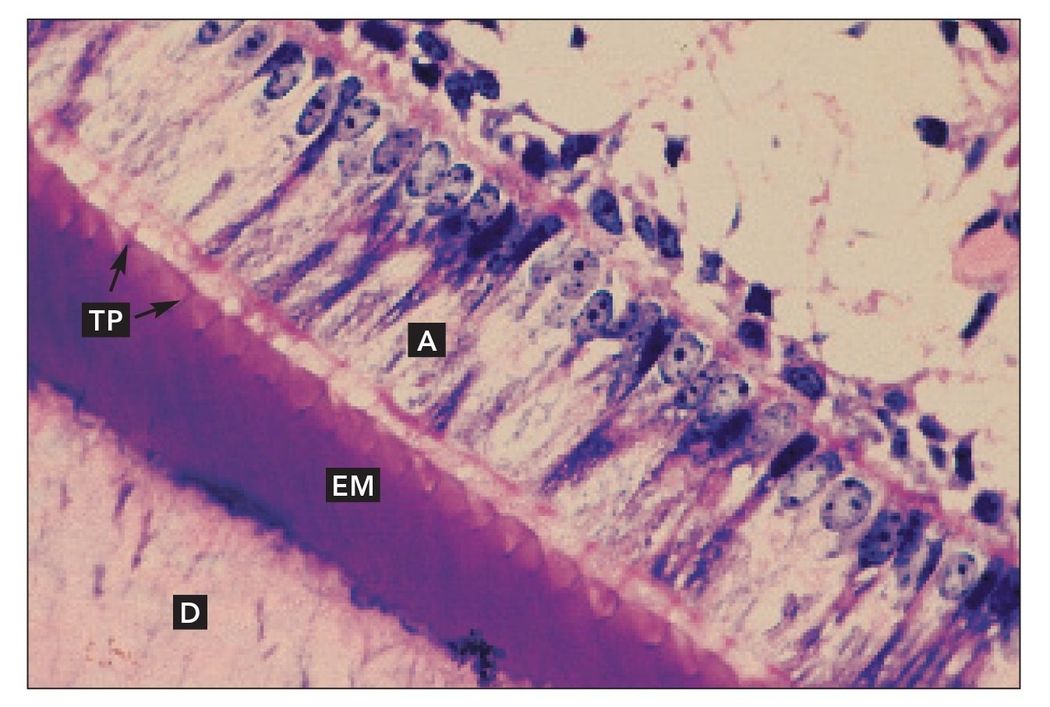
FIG 2-2
Developing tooth
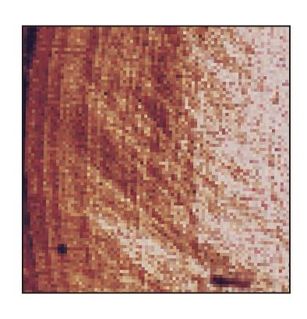
Higher magnification of Fig 2-1. Tomes’ processes (TP) extend from the ameloblasts (A), producing the enamel matrix (EM). Dentin (D) is visible in the lower left corner (×640).
FIG 2-3
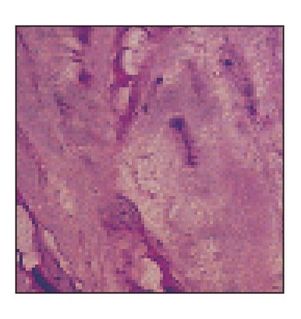
Enamel matrix
Decalcified thin section of enamel matrix at high magnification (H and Lee stain; ×640).
Reduced dental epithelium
Decalcified sagittal section of the reduced dental epithelium (RDE) over the cusp tip of an unerupted tooth. Enamel is represented by the enamel space (ES). Dentin (D) is also visible (H and E stain; ×40).
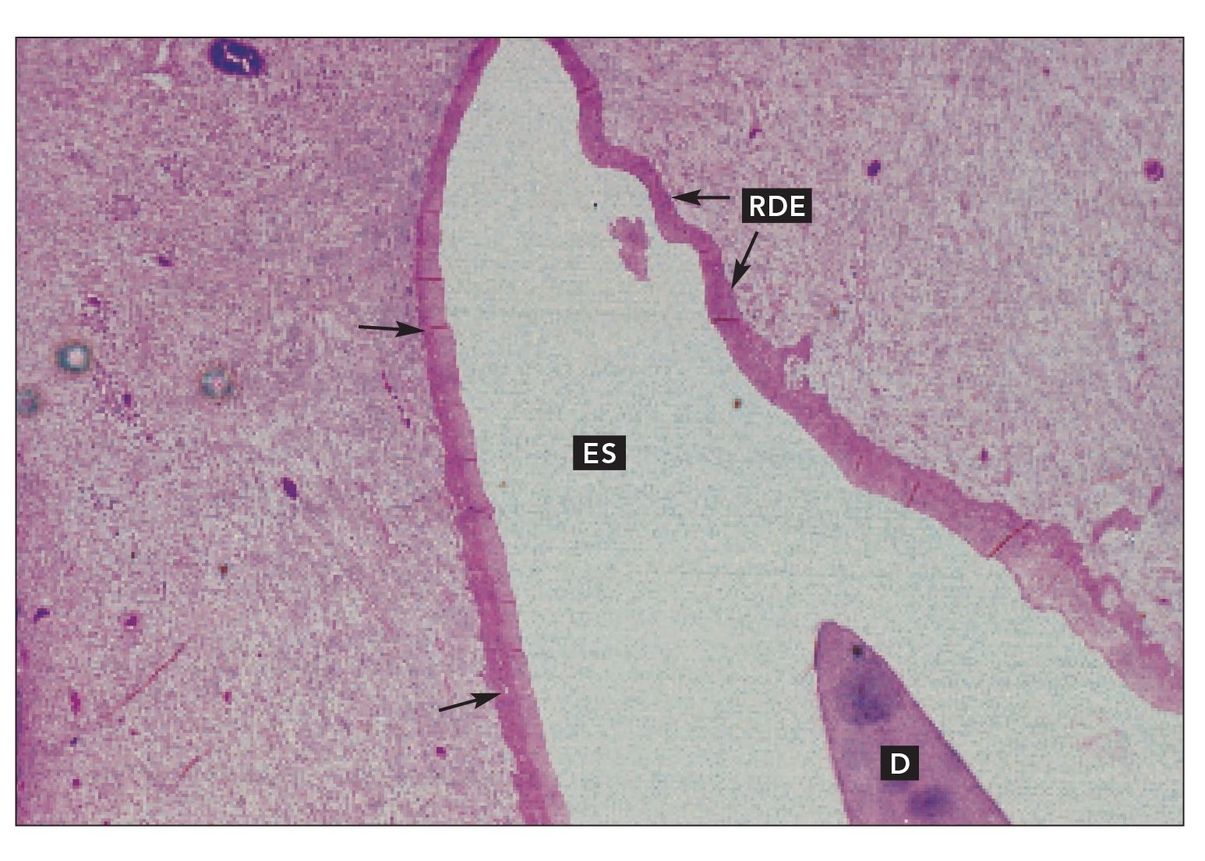
FIG 2-5
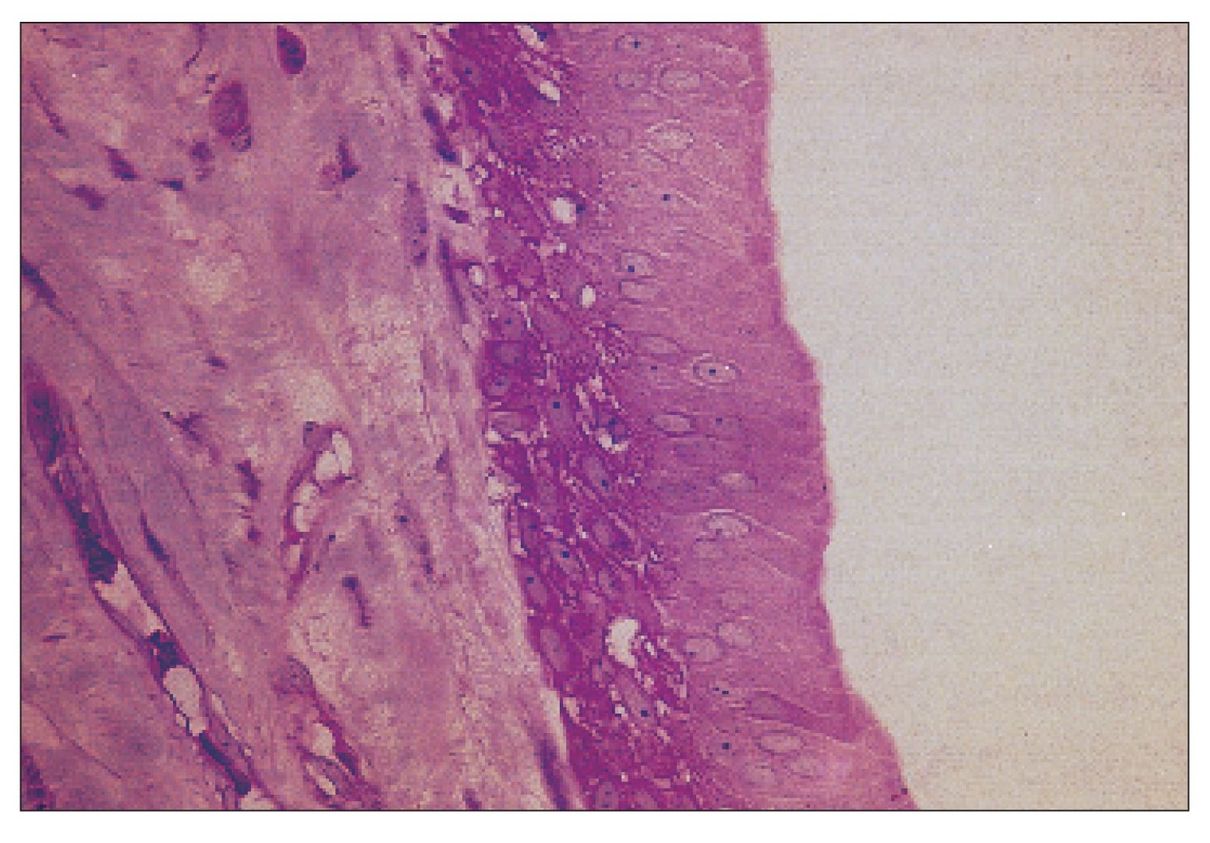
Reduced dental epithelium
Higher magnification of the reduced dental epithelium between the unlabeled arrows shown in Fig 2-4 (×400).
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


