Figure 2.1.1 • Diagnodent System.
The first commercialized laser for caries detection is constituted by a flexible photoconductor with a special probe. The electric alimentation is provided by batteries, localized in the posterior part of the device. Diode and electronic instrumentation are inside (Fig. 2.1.2).
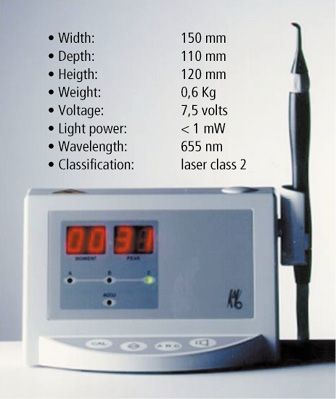
Figure 2.1.2 • The first Diagnodent, commercialized in 1998 and its characteristics.
Laser light is projected on dental surface by the flexible photoconductor and the probe. The fluorescence emitted by decayed tissues is capted by optical fibres located around the photoconductor tube. In the front, there is a display divided in two parts: on the left, the current value of measurement is indicated, on the right, the maximum value. Values are from 0 to 99.
Before using, it’s very important proceed to calibration and it is realized by a ceramic disc.
Diagnodent is provided by two different kinds of probes: one is trunk-conical for interproximal surfaces and the other one is flat for the occlusal surfaces.
Probe is located on the examined dental surface and the resulted values are directly proportionally to the gravity of the carious lesion.
The new Diagnodent is similar to a pen (Fig. 2.1.3). Batteries are located in the pen-stick and the display is on the handle. The principle is the same: on the display there are two values: one is the peak value, the other one is the real value at the moment of evaluation. At the value of 06, an acoustic signal is produced. For values between 6 to 99, frequency of acoustic signal is higher when values are progressive bigger. Two types of fibre-optic tips are available for this new device:
- a tapered tip designed for dental fissures and approximal regions
- a flat tip for smooth dental surface
When the tooth is illuminated by laser light (λ 655 nm), this light is absorbed by inorganic and organic dental substances. In caries lesions, where minerals are replaced by water, light scattering is higher than in sound tooth: during the progression of a carious process, it is shown an increase in the amount of the fluorescent light.
Every tooth is provided by its own natural fluorescence. For this reason, after calibration of the fibre-optic tip, it’s necessary measure the fluorescence of a sound spot on a smooth surface of the tooth in order to know the baseline value of that tooth. This value is subtracted from the fluorescence of the site to be measured.
False-positive could result when calculus, plaque, composite filling materials, stains, toothpastes, polishing pastes are present on dental surface or when there is an hypomineralized non carious teeth.
For this reason, it is very important point out the chronological different steps before measuring (Figg. 2.1.4, 2.1.5, 2.1.6, 2.1.7):
- calibration
- cleaning of dental surface
- determination of natural fluorescence of sound dental surface
- continuous rotary movement of the probe tip along its axis during the measuring procedure
- reading of measurements
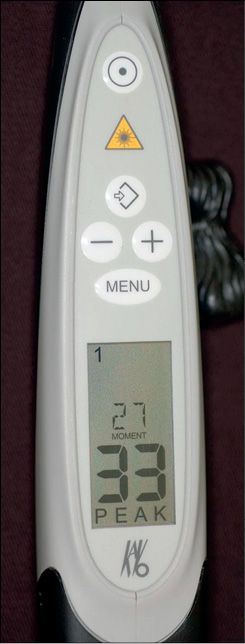
Figure 2.1.3 • The new diagnodent: Diagnodent Pen.

Figure 2.1.4 • Laser classification: laser class 1.

Figure 2.1.5 • Calibration.

Figure 2.1.6 • Calibration.
Figure 2.1.7 • Calibration.
For a correct reading, Lussi reported a guideline table 2.1.I for the clinical use of Diagnodent:
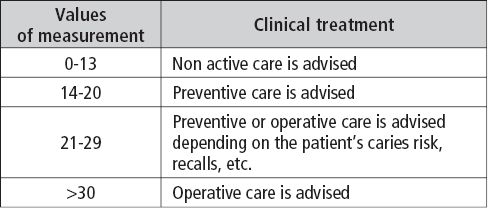
Table 2.1.I • Values of measurement of Diagnodent for a correct reading.
Because of its high sensitivity, the first laser fluorescence device was recommended as a tool in the decision-making process in relation to the diagnosis of occlusal caries as a second opinion in cases of doubt after visual inspection. In fact, the first Laser Fluorescence device was provided of tips designed for detection of only occlusal caries, therefore, direct proximal surface caries detection was impossible.
The new device was designed for occlusal and approximal surfaces. It is provided of a particular probe tip with a prismatic shape, able to penetrate into the proximal space and directs the excitation and detection light laterally to the long axis of the tip. However, there is the possibility of some interference of materials and caries when fluorescence is measured approximally. For this reason, the removal of plaque and calculus on the examined surface should be always performed before LF measurements in order to prevent possible false positive results.
According to Pitts and other Authors (38-50), the diagnosis of the activity of a dental decay is essential for a clinician to choose an appropriate management which could involve no treatment, preventive treatment or operative treatment
Diagnodent represents a very useful device to detect the presence of an incipient carious process during the diagnostic visit in order to organise a correct treatment planning, especially in Conservative Dentistry and in the Bleaching procedure.
In fact, the criteria for a therapeutic choice are depending of the diagnosis. Different studies (51-60) have shown as a correct early diagnosis is generally difficult. If we compare the percentage of correct early diagnosis when we use visual examination (20%), visual examination and the explorer (40%), x-ray examination (53%), Diagnodent (93%), we can affirm that only Diagnodent can provide a correct and early diagnosis of a carious process. (Tab. 2.1.II)
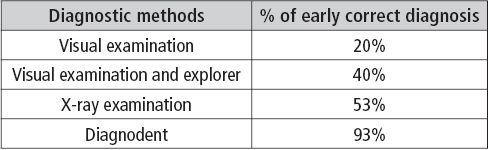
Table 2.1.II • Percentage of a correct early diagnosis, using different diagnostic methods.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


