TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is the articulation between the squamous portion of the temporal bone and the condyle of the mandible
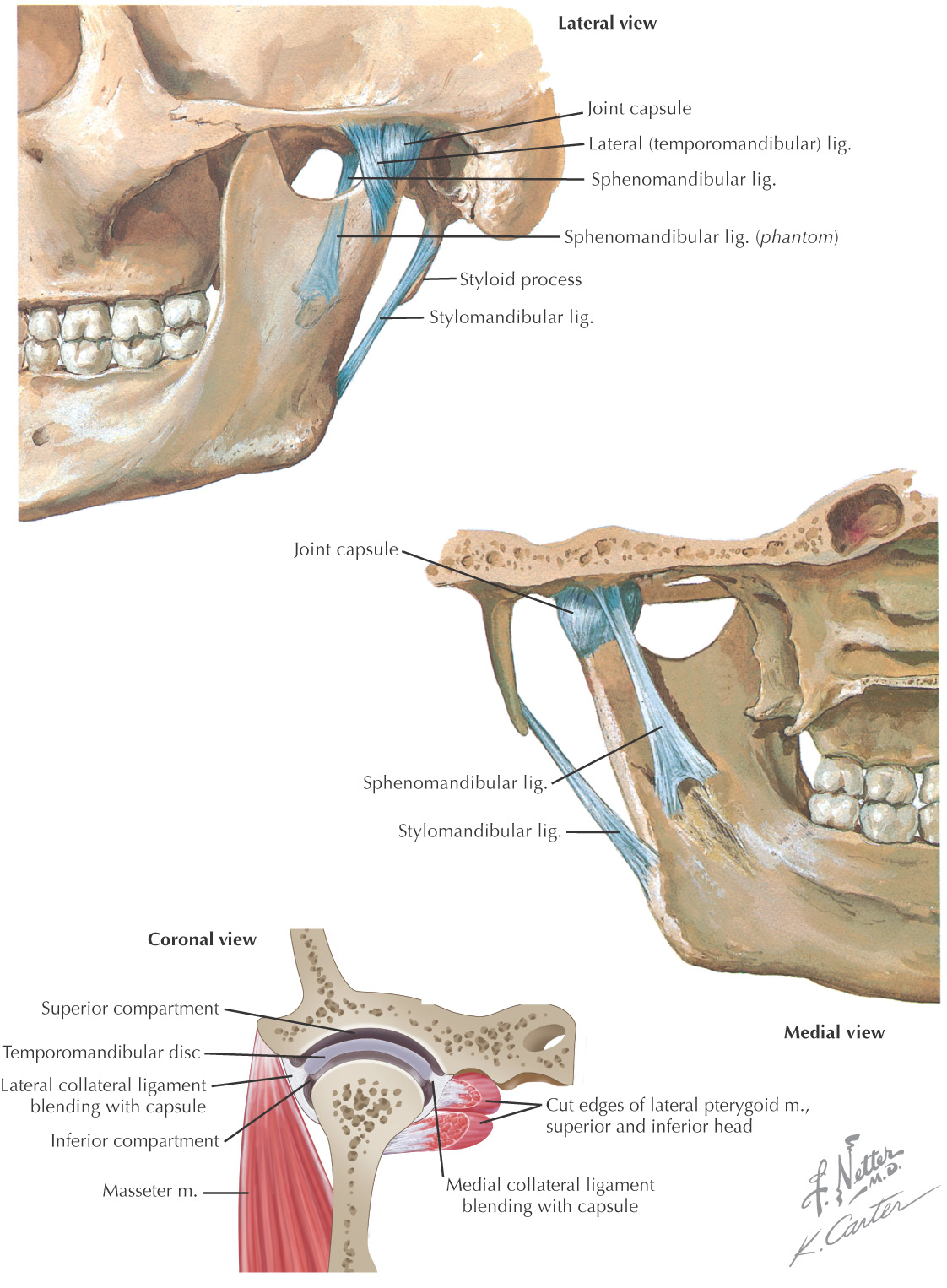
Structural Components
The TMJ comprises 2 types of synovial joints—hinge and sliding—and consists of the following:
• Squamous portion of the temporal bone
• Articular disc (contained within the TMJ)
• Ligaments (serve as boundaries)
TMJ Dysfunction
Affects approximately 25% of the population and may be severe in a small subgroup
Causes include arthritis, trauma, infection, bruxism, and disc displacement
More common in females
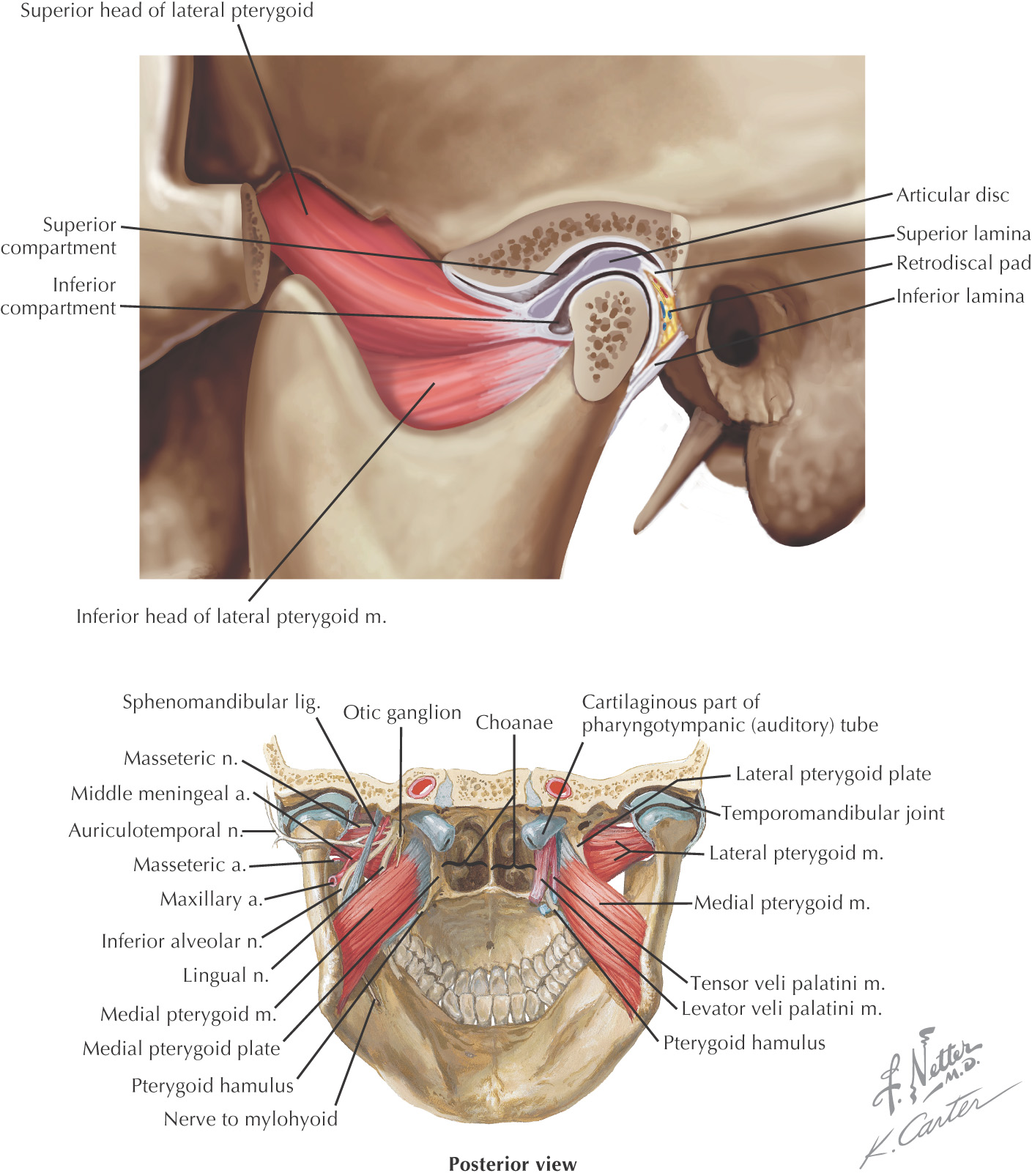
Anatomy
ANATOMIC FEATURES
Vascular Supply
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses