CHAPTER 9 Pharmacology
PHARMACOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES AND CONCEPTS
Understanding a pharmacological effect on a patient and possible interaction with other drugs is essential to safe dental care. Thorough medical history helps identify adverse effects and potential drug interactions with current prescription (Rx) drugs, dental drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) drugs. Dental settings are advised to have the current Physician’s Desk Reference (PDR) Index for reference information concerning drug information by brand and generic names, product categories, manufacturers.
Prescription Writing
Table 9-1 Pharmacological abbreviations for prescription writing
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| a.c. | Before meals |
| b.i.d. | Twice daily |
| h.s. | At bedtime |
| q.d. | Once per day |
| q.i.d. | 4 times per day |
| q.o.d. | Every other day |
| q6h | Every 6 hours |
| p.c. | After meals |
| p.o. | By mouth |
| p.r.n. | As needed |
| sl. | Sublingual |
| stat | Immediately |
| supp | Suppository |
| t.i.d. | 3 times per day |
| u.d. | As directed |
DRUG EFFECTS ON AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
ADRENERGICS
ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS
CHOLINERGICS
ANTICHOLINERGICS
ANXIETY AND PAIN MANAGEMENT
Antianxiety Drugs
CLINICAL STUDY
| Age | 45 YRS | SCENARIO |
| Sex |  Male Male  Female Female |
The patient is scheduled for an oral prophylaxis today. He has generalized dental biofilm and slight calculus deposits throughout, with only slight to moderate gingivitis. |
| B/P | 105/57 | |
| Chief Complaint | “I hate being here but I know that I have to keep up my mouth.” | |
| Medical History |
Analgesics
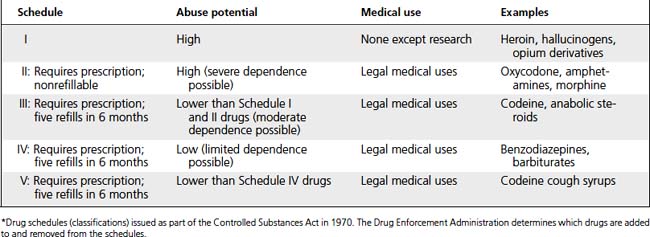
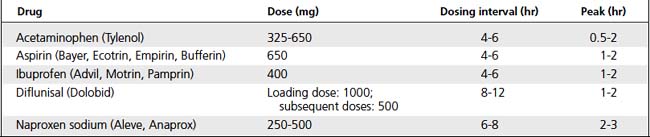
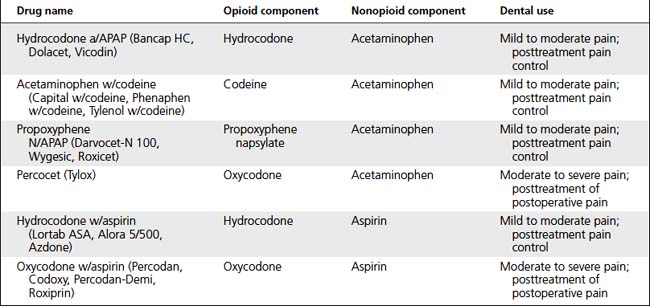
Analgesics inhibit perception of pain. Nonopioids reduce pain perception by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis; MORE effective if they are taken before onset of pain. Opioids depress pain perception in CNS by binding with opioid receptors (Tables 9-3, 9-4, and 9-5).
| Drug | Interactions |
|---|---|
| NSAIA |
ACE, Angiotensin converting enzyme; NSAIA, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agent; VA, valproic acid.
Anesthetics and Sedatives
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 •
•