7
Sample Patient Histories and Discussion
White Lesions
Case 1
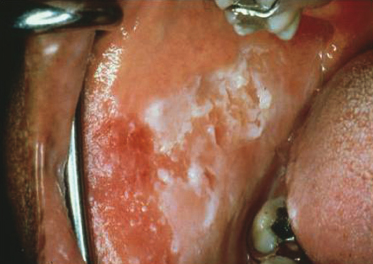
A 38-year-old woman has three children and is in the process of divorce from an abusive husband. She takes Ambien to help her sleep at night and is very concerned about the bilateral, superficial “peeling” of this roughened, ragged, and thickened plaque area of her right cheek. When the patient responded negatively to a series of questions regarding habits and application of materials to the area, a biopsy was done. What is the diagnosis?
- Candidiasis
- Leukoedema
- White sponge nevus
- Morsicatio buccarum
Case 2
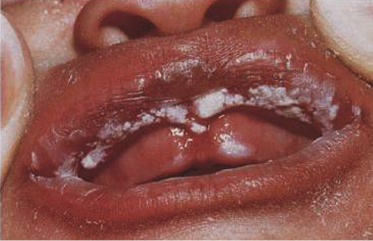
A 2-month-old bottle-fed baby has had this oral condition since shortly after birth, although she feeds well and is gaining weight normally. She lives in a rural community without access to a pediatrician. These lesions wipe away, leaving an erythematous base. What is the diagnosis?
- Candidiasis
- Diphtheria
- White sponge nevus
- Hairy leukoplakia
Case 3
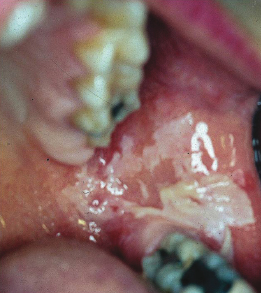
A 29-year-old schizophrenic man is living in a homeless shelter. He presents with severe pain in the lower left mandible and deep recurrent caries in tooth #18. What would not be an appropriate process to list in the differential diagnosis of this lesion?
- Chemical trauma
- Leukoedema
- Morsicatio buccarum
- Tobacco pouch keratosis
Case 4
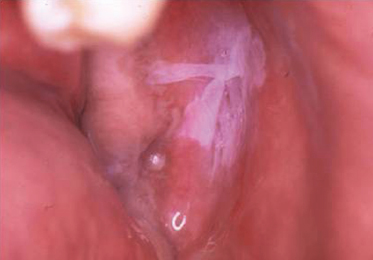
A 57-year-old widower confides to you that he believes he has halitosis. He has recently noticed that the “lining of his cheeks seems to be peeling.” The appearance combined with the history fits what most likely diagnosis?
- Leukoedema
- Lichen planus
- Chemical reaction to mouthwash
- Uremic stomatitis
Case 5
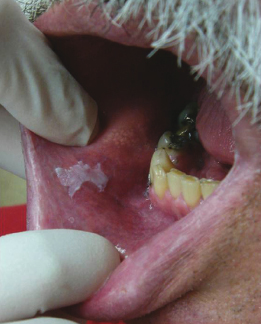
This 62-year-old man smokes one pack of cigarettes a day. This lesion was discovered on a routine new patient examination; he had not been aware of it and did not know how long it was present. Based on the information given and the clinical photograph, what is the best diagnosis for this lesion?
- Morsicatio
- Leukoplakia
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Hairy leukoplakia
Case 6
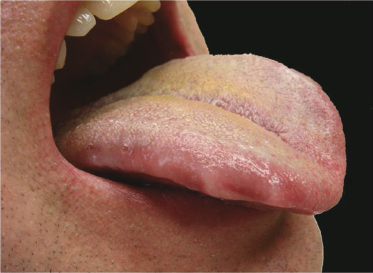
A 55-year-old woman is troubled by a burning sensation on the tip of her tongue. She is convinced that the appearance of her tongue has changed from the previous pink color. What is the white layer seen on the dorsum of this coated tongue?
- Desquamated epithelial cells and bacteria
- Cells from white sponge nevus
- Necrosis from a chemical burn
- Hyperkeratosis
Case 7
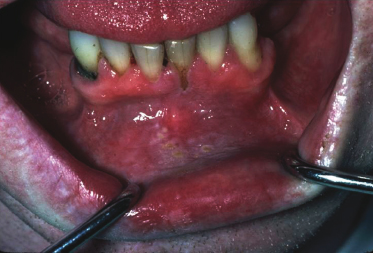
A 46-year-old man was a professional baseball player in his youth. He admits to drinking a 6-pack of beer and use of tobacco products every day. If the histology from a biopsy of this area showed only excess keratin, what would the clinical diagnosis be?
- Leukoedema
- Hyperplastic candidiasis
- Tobacco pouch keratosis
- Lichen planus
Case 8
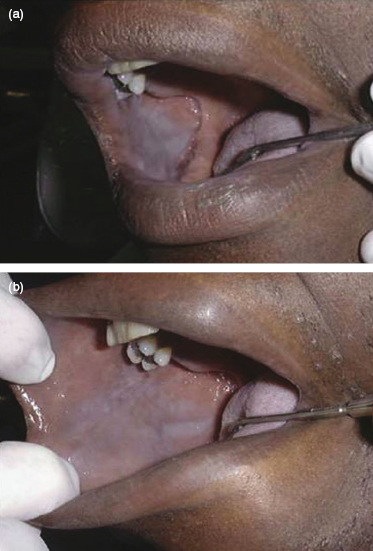
A 35-year-old man is obese and takes lisinopril for hypertension. The observed changes are bilateral and asymptomatic. What is the likely clinical diagnosis of the lesions seen in this case?
- Tobacco pouch keratosis
- Pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Nicotine stomatitis
- Leukoedema
Case 9
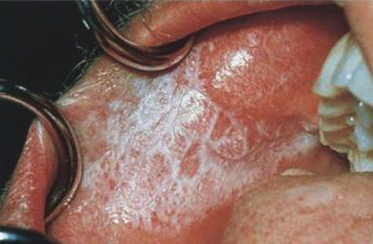
This 48-year-old man complains of roughness on the inside of both of his cheeks. He claims that this has been present for about 6 months although it is asymptomatic. The clinical photograph and history strongly suggest lichen planus; what are the lines on the buccal mucosa called?
- Wickham’s striae
- Lines of Zahn
- Lines of Retzius
- Koebner’s striae
Case 10
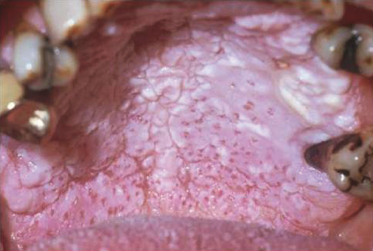
A retired 72-year-old man has smoked three packs of cigarettes a day for 30 years. He has severe periodontal disease but, on questioning, did not know about any changes in his oral tissues. What is the clinical diagnosis given to this condition?
- Leukoplakia
- Hyperkeratosis with dysplasia
- Nicotine stomatitis
- Lichen planus
Case 11
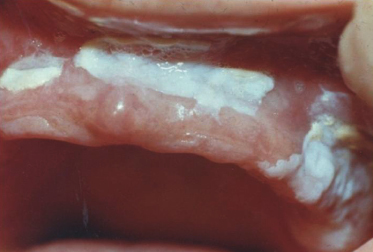
A 60-year-old woman has worn complete upper and lower dentures for 20 years. She has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and recently completed a course of antibiotics to treat bacterial pneumonia. This is an example of pseudomembranous candidiasis. What in the history is not a typical factor for the development of the disease?
- Age of 60
- History of COPD
- Denture wear
- Antibiotic use
Case 12
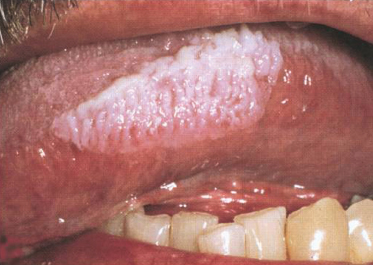
This 39-year-old man exhibits these changes bilaterally. On questioning about his social history he admits to being bisexual although he has never been tested for HIV. If you wanted to evaluate this person for hairy leukoplakia, what would be diagnostic?
- HIV testing
- Biopsy with stains for Epstein–Barr virus
- The lesions should wipe away with gauze
- Historical information about other family members with a similar condition
Red, Red-and-White, and Purpuric Lesions
Case 13-1
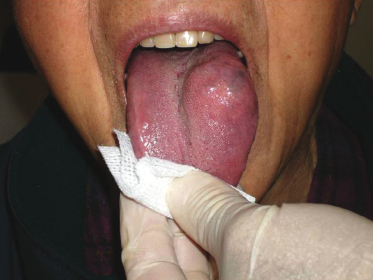
A young adult has been aware of this lesion for years and it has remained the same size. The blanchable and compressible lesion is not painful. What is the most likely provisional diagnosis of this lesion?
- Erythema migrans
- Erythematous candidiasis
- Erythroplakia
- Hemangioma
Case 13-2
A hemangioma is considered:
- Neoplastic
- Developmental
- Inflammatory
- Reactive
Case 14-1
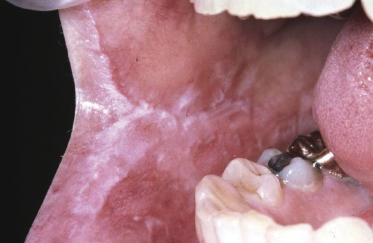
A 25-year-old woman has noticed this unilateral change for the past few months. The area is asymptomatic and cannot be wiped off. Each of the following would be a reasonable differential diagnosis for this lesion except one. Which one is the exception?
- Cinnamon allergic reaction
- Acute candidiasis
- Lupus erythematosus
- Cheek nibbling
Case 14-2
Which of the following is the most likely provisional diagnosis?
- Lichen planus
- Cinnamon allergic reaction
- Thermal burn
- White sponge nevus
Case 15-1
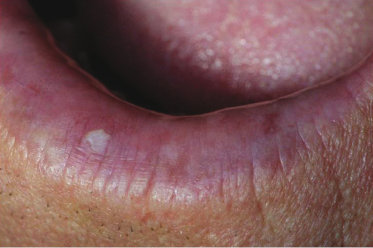
A 59-year-old man is noted to have this lower lip appearance during his routine dental cleaning appointment. None of the roughened area is removable. Based on the history and site, morphology, and color of the lesion, its provisional diagnosis is which of the following?
- Lichen planus
- Verruciform xanthoma
- Actinic cheilitis
- Candidiasis
Case 15-2
Which is true about actinic cheilitis?
- Lesion often oozes a mucous secretion.
- Actinic cheilitis is more common on the upper lip.
- Precancerous changes are reversible.
- A significant percentage of lesions are premalignant.
Case 16-1
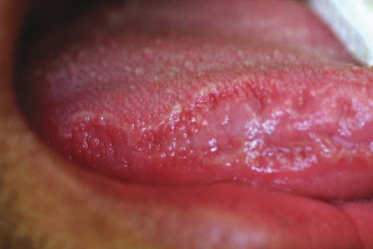
A dental student is aware of this lesion that “comes and goes.” When present, the area tends to change shape from day to day. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Traumatic erythema
- Erythema migrans
- Erythroleukoplakia
- Nicotine stomatitis
Case 16-2
Which condition is statistically associated with geographic tongue?
- Candidiasis
- Erosive lichen planus
- Psoriasis
- Fissured tongue
Case 17-1
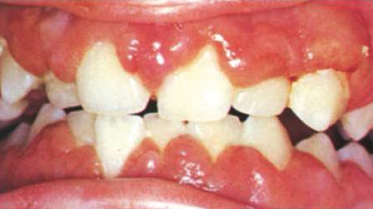
A 16-year-old girl taking phenytoin complains of fatigue, weight loss, low-grade fever, spontaneous gingival hemorrhage, and this gingival change. What part of the history is not consistent with drug-induced gingival hyperplasia?
- Anterior facial involvement
- Erythema
- Excess attached gingiva
- Spontaneous gingival hemorrhage
Case 17-2
Which is the most likely provisional diagnosis?
- Leukemia
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Scarlet fever
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Case 18-1
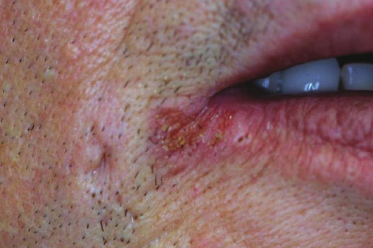
A 50-year-old man has had this chronic sore for the past year. It occasionally bleeds and is intermittently sore. What is the most likely provisional diagnosis?
- Hemangioma
- Lichen planus
- Actinic cheilitis (cheilosis)
- Angular cheilitis
Case 18-2
In addition to candidiasis, what is another cause of angular cheilitis?
- Vitamin deficiency
- Developmental defect
- Viral infection
- Protozoan infection
Case 19
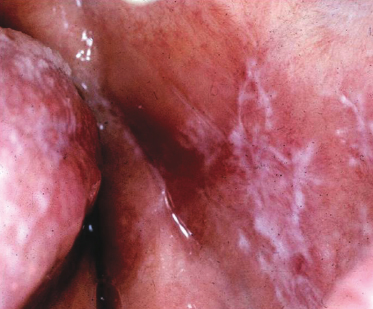
A 55-year-old woman has had asymptomatic bilateral and symmetrical lesions for the past several years. Recently, some focal pain has occurred. The areas “feel rough” to the patient when rubbed with the tip of her tongue. Once a provisional diagnosis is made based on this lesion’s site, morphology, color, and history what is the next step in management of this condition?
- Topical steroid application
- Biopsy of left and right lesions
- Cytology to rule out malignancy
- Antifungal medication
Case 20
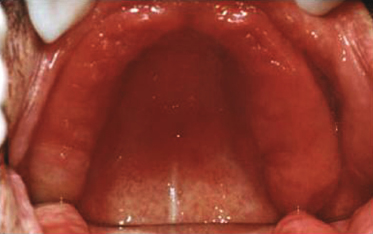
A denture patient is unaware of this lesion. What is the proper management of this condition?
- Treat both the denture and oral mucosa with antifungal agents.
- Leave the denture out at night, clean it, and rinse it in an antifungal solution.
- Use laser ablation followed by new denture construction.
- Apply antifungal cream to the affected oral soft tissues.
Acute Oral Ulcerations
Case 21
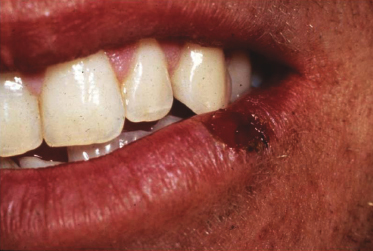
A 36-year-old woman has an asymptomatic lesion of 1 week’s duration; no other signs or symptoms were seen. Spontaneous healing occurred after 2 weeks. The patient has a history of recurrent aphthous ulcers but does not recall having lip lesions. What finding in the history suggests that this lesion is not an aphthous ulcer?
- Patient’s age
- Asymptomatic lesion
- Healed spontaneously in 2 weeks
- Site
Case 22
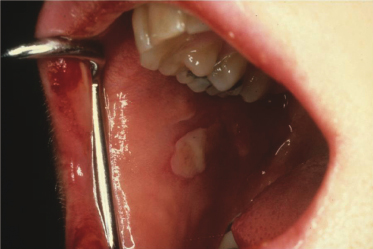
A 20-year-old woman has an acute onset of painful ragged ulcerations of the movable mucosa accompanied by fever and malaise. The patient also gives a history of “cold sores” that occur several times per year on her lip. The history of painful acute-onset ulcers of the movable mucosa favors what diagnosis?
- Erythema multiforme
- Aphthous ulcers
- Herpes simplex
- Varicella
Case 23
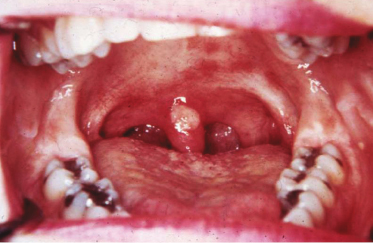
A patient has had recurrent painful bouts of oral mucosal ulcerations of greater than 1 year’s duration. Each episode of lesions resolves in approximately 10 days. Similar cutaneous lesions were seen at one time and were treated with steroids and antibiotics, resulting in resolution. What is the triad of signs and symptoms seen in Behcet’s syndrome?
- Arthritis, dermatitis, facial paralysis
- Skin lesions, fissured tongue, oral ulcers
- Oral ulceration, genital ulceration, ocular inflammation
- Blistering skin, nonpainful oral ulceration, hairy tongue
Case 24
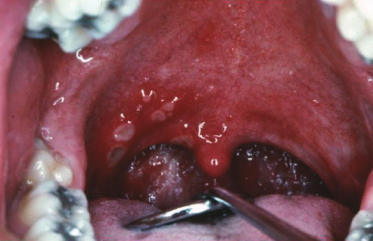
A 16-year-old boy had soft palate ulcerations derived from ruptured vesicles. The ulcers were mildly tender and accompanied by a sore throat. The lesions resolved in 1 week. No prior history of a blistering or ulcerative disease was given. What is the most likely diagnosis for these lesions?
- Herpangina
- Herpes simplex
- Recurrent aphthae
- Syphilis
Case 25
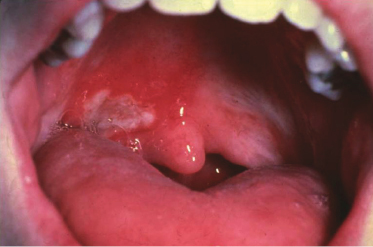
Painful, often multiple, deep ulcerations of a cyclical nature, corresponding to her menstrual cycle, began in this 16-year-old girl. No treatment has been effective. Behcet’s disease, cyclic neutropenia, Crohn’s disease, and Sweet’s syndrome all have oral lesions that can be identical to what?
- Herpangina
- Recurrent aphthous ulcers
- Erythema multiforme
- Pemphigus vulgaris
Case 26
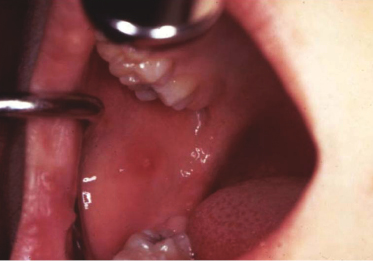
An 8-year-old girl was seen by her physician for a complaint of fever, malaise, and sore throat. During the exam this ulceration was found. The lesion was asymptomatic and thus the patient was unaware of its presence. If this lesion were an initial finding for primary varicella zoster (i.e., chicken pox) what is likely to follow?
- Painful ocular inflammation
- Gingivostomatitis
- Necrosis of the interdental papillae
- Vesicular skin lesions
Case 27
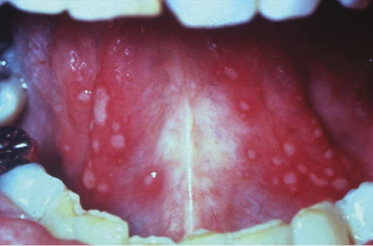
A 38-year-old woman complains of almost constant painful crops of small ulcerations of the oral mucosa not preceded by vesicles. Individual ulcers heal within 2 weeks but are almost immediately replaced by new similar-appearing lesions. She reports that she is in otherwise good health with no concurrent skin lesions. What is the likely diagnosis for these lesions?
- Herpetiform aphthae
- Herpes simplex
- Herpes zoster
- Chicken pox
Case 28
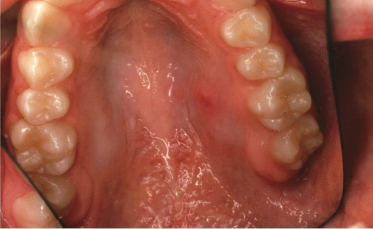
A 25-year-old man is seen because of a painful swelling on his hard palate. It has been present for about a week and the pain worsens when eating rough foods such as potato chips. Upon intraoral examination, ulceration is seen in the area of the swelling. Which would not be part of a reasonable differential diagnosis?
- Recurrent aphthous ulcer
- Necrotizing sialometaplasia
- Superficial mucocele
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
Chronic Vesiculoerosive and Ulcerative Lesions
Case 29
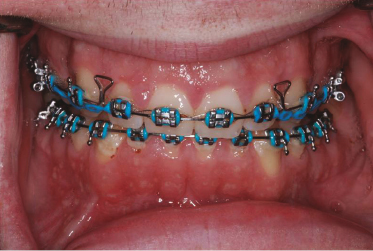
An 18-year-old boy with mandibular alveolar mucosa papules has similar lesions on the buccal mucosa and palate. His medical and social histories are noncontributory; however, on the review of systems he mentions some recent episodes of intestinal cramping and diarrhea. Although these lesions do not look ulcerative, the history should make you suspect what condition?
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
- Noma
- Erosive lichen planus
- Pyostomatitis vegetans
Case 30
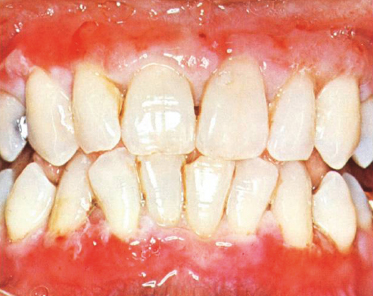
A 62-year-old woman complains that for the last 2 years she has been unable to eat spicy foods and finds it painful to perform good oral hygiene. Upon head and neck examination, it is noticed that she has conjunctival inflammation. The clinical appearance is that of desquamative gingivitis. The presence of eye involvement should make you suspect what disease?
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid
- Erosive lichen planus
- Erythema multiforme (Stevens–Johnson syndrome)
- Herpes zoster
Case 31
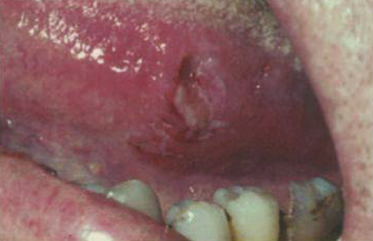
A 54-year-old man presents with an area that has been tender for 3 months. He is in good health, drinks red wine with dinner about 3 times per week, and has never used tobacco. A nonhealing ulcer on the lateral tongue should make you think of all of these choices except which one?
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Deep fungal infection
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid
- Traumatic granuloma
Case 32
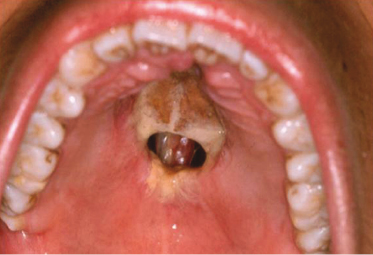
This 62-year-old man emigrated from Guatemala 10 years ago. He has no health insurance and resisted going to the hospital until he began feeling deep fatigue and episodes of epistaxis. The patient in this case eventually died of his disease despite aggressive chemotherapy. He had no other known risk factors such as diabetes mellitus, and his immune status was intact. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Behcet’s syndrome
- Midline lethal granuloma
- Tertiary syphilis
- Wegener’s granulomatosis
Case 33
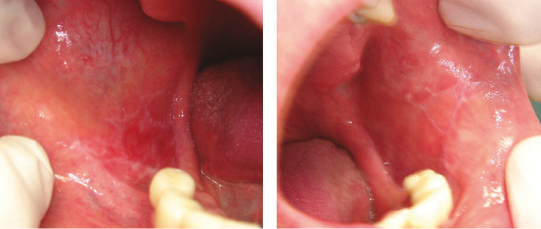
A 61-year-old man experiences tenderness of the buccal mucosa that comes and goes. He changed to a mild children’s dentifrice and stopped using mouthwash, but the lesions persisted. These lesions of lichen planus can easily be confused with a lichenoid hypersensitivity response. What clinical sign does not help to distinguish that this is lichen planus?
- Lesions are bilateral
- Lesions come and go
- White striae
- Ulceration
Case 34
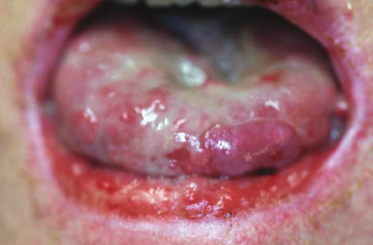
A 54-year old man has had continuous, very painful mouth sores for approximately 7 months. The only time the sores remitted was when he was given high dose methylprednisolone for a bowel condition 2 months ago. The patient has pemphigus vulgaris. What will help to confirm the disease besides histopathology?
- Presence of rheumatoid factor
- Presence of antinuclear antibodies
- Positive Nikolsky sign
- Direct and indirect immunofluorescence studies
Case 35
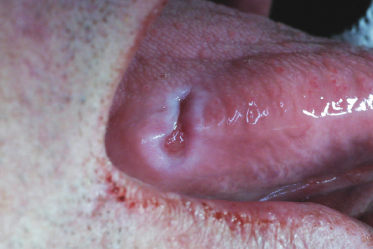
A 38-year-old man bit his tongue 4 weeks ago and is concerned because it has not healed. Since most oral ulcerations resolve in 2 weeks a biopsy was taken from this patient. When the patient returned for a follow-up visit the next week the lesion was almost completely resolved. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Traumatic ulcerative granuloma
- Deep fungal infection
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Erythema multiforme
Case 36
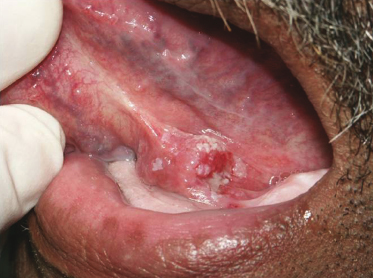
This 72-year-old edentulous man does not wear dentures. He has smoked cigarettes and used alcohol his entire adult life. He complained of a “raised” lesion on the left lateral tongue. This asymptomatic lesion was found on oral examination. The site and lack of symptoms should make what diagnosis the primary consideration in your differential diagnosis?
- Recurrent herpes
- Traumatic ulcer
- Noma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Papillary Lesions
Case 37-1
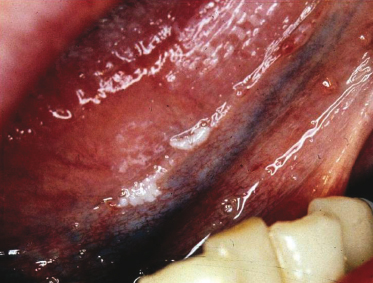
An HIV-positive male is unaware of this tongue lesion and, thus, duration is unknown. What is the most likely provisional diagnosis of this lesion?
- Verruca vulgaris
- Hairy tongue
- Squamous papilloma
- Hairy leukoplakia
Case 37-2
If a biopsy of suspected hairy leukoplakia is taken, the confirmatory microscopic features should demonstrate evidence of the following:
- Human papillomavirus
- Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)
- Human immunodeficiency virus
- Herpes simplex virus
Case 38-1
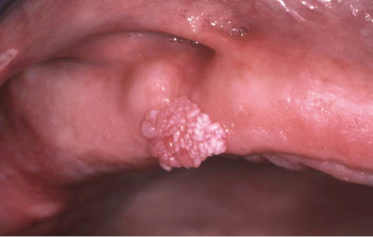
A 41-year-old man has this firm, nonpainful, pedunculated palatal lesion of 1 year’s duration. What is the least likely clinical diagnosis?
- Verruca vulgaris
- Squamous papilloma
- Verrucous carcinoma
- Verruciform xanthoma
Case 38-2
What clinical clue is not present in the current history that could aid in a provisional diagnosis of verrucous carcinoma?
- Rapid onset
- Pain
- Smokeless tobacco habit
- Compressible
Case 39-1
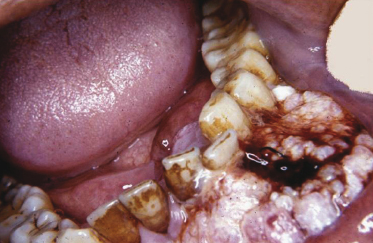
A 51-year-old man is seen in the emergency clinic with this large gingival mass of 8 months’ duration. According to the patient the nonpainful lesion has slowly increased in size. Based on the history, site, morphology, and color of the lesion its provisional diagnosis is which of the following?
- Verrucous carcinoma
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
- Giant cell fibroma
Case 39-2
What is the proper treatment for verrucous carcinoma?
- Cessation of tobacco habit followed by chemical cauterization
- Complete surgical removal
- Biopsy; antiviral treatment; then surgical removal
- Surgical removal followed by radiation therapy
Case 40
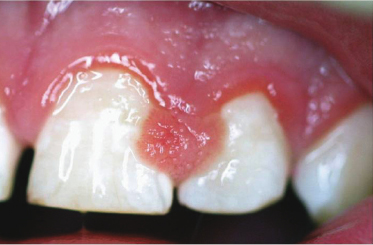
A 14-year-old boy is seen at the pediatric dentist for a fluoride treatment. The patient and his mother report that this firm lesion has been present less than a month. What is this lesion’s morphology?
- Sessile macule
- Pedunculated vesicle
- Sessile plaque
- Pedunculated papule
Case 41
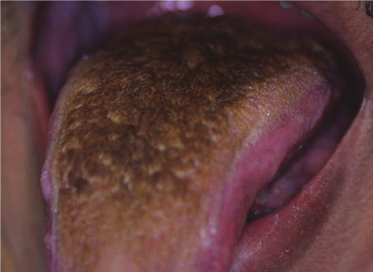
An adult patient is embarrassed by this extensive tongue lesion. Although the lesion will not wipe off, the tongue does not have a burning sensation. What abnormality causes this appearance?
- Increased spongiosis of the stratum spinosum layer
- Elongated hyperkeratotic filiform papillae
- Excess melanin deposition in the basal cell layer
- Interruption in the normal maturation sequence of the epithelium
Case 42-1
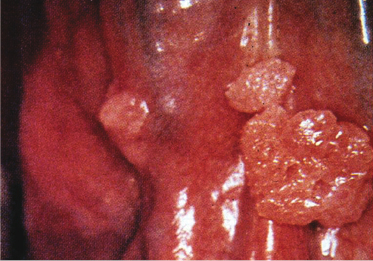
A partial denture wearer has this asymptomatic palatal lesion. What is the provisional diagnosis?
- Denture stomatitis
- Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Papilloma
Case 42-2
What disease is often associated with inflammatory papillary hyperplasia (IPH)?
- Giant cell fibroma
- Verruca vulgaris
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Candidiasis
Case 43
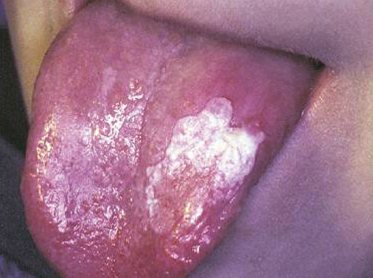
A 52-year-old cigarette smoker is aware of this nonwipeable tongue lesion. The lesion has been present for several years and is believed to have slowly enlarged. What is the diagnosis?
- Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
- Geographic tongue
- Leukoplakia
- White sponge nevus
Case 44
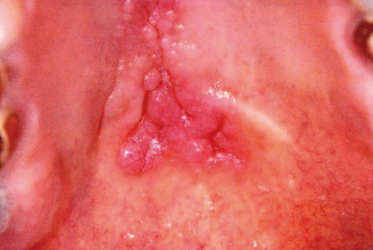
These asymptomatic ventral tongue lesions are also noted on the patient’s anterior facial gingiva. What is the likely provisional diagnosis?
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Squamous papilloma
- Verruciform xanthoma
- Verrucous carcinoma
Pigmented Lesions
Case 45
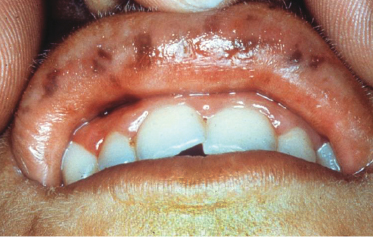
A 29-year-old man with AIDS complains of fatigue, weakness, and depression. There has been a recent onset of oral pigmentation. The patient takes a regimen of antiviral medications. Why would a person with AIDS have the described symptoms and pigmentation as in this case?
- AZT treatment
- Opportunistic infection that has destroyed the adrenal cortex
- Low lymphocyte counts
- Increased melanocytic nevi in HIV-positive populations
Case 46
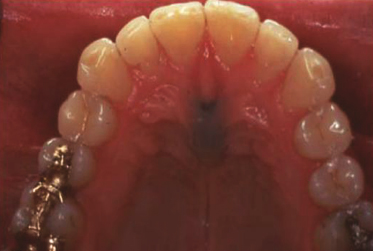
What structure in the area could form a fluid-filled cystic lesion that might appear blue?
- Incisive canal
- Mucocele
- Dentigerous cyst
- Cyst from a nonvital tooth
Case 47
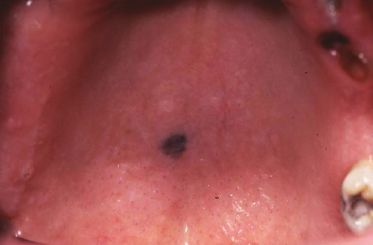
What is the best treatment for this lesion?
- Observation
- Wide excision
- Brush cytology for diagnosis
- Biopsy
Case 48
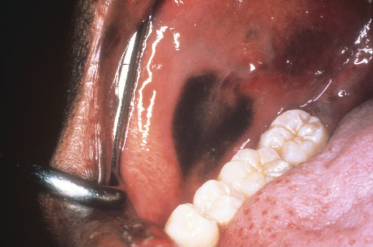
What is the likely diagnosis of this lesion given its rapid appearance following trauma?
- Melanoma
- Melanoacanthoma
- Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
- Blue nevus
Case 49
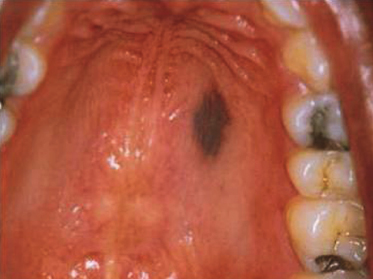
When biopsied this lesion showed increased melanin pigment in the basal layer. What is the diagnosis?
- Pigmented nevus
- Melanoma
- Amalgam tattoo
- Melanotic macule
Case 50
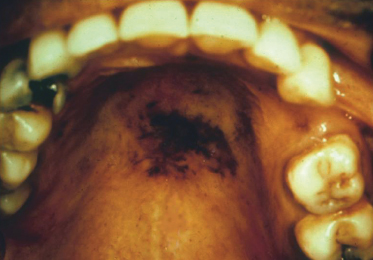
This person is being treated with an antimalarial drug that is known to cause oral pigmentation. What disease listed would be commonly treated so?
- Mucous membrane pemphigoid
- Lupus erythematosus
- Cat scratch disease
- Diabetes mellitus
Case 51
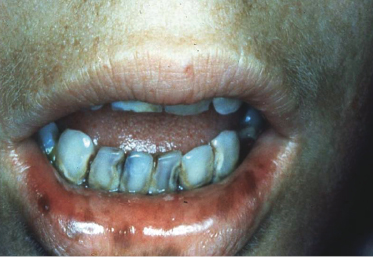
A 12-year-old boy with congenital pigmentation of the orofacial area has multiple medical problems, including hyperthyroidism and multiple bone lesions resulting in several fractures. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
- Addison’s disease
- Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy
- McCune–Albright syndrome
Case 52
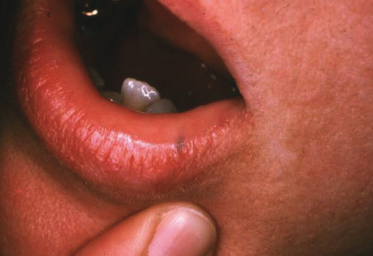
An 8-year-old boy has had this asymptomatic lesion for “a long time.” Considering the history what is the most likely diagnosis?
- Mucocele
- Foreign body
- Peutz–Jeghe/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


