CHAPTER 5 Radiology
FUNDAMENTAL RADIATION PHYSICS
Understanding radiation physics requires a basic knowledge of atomic structure, radiation types, properties of radiation.
A. Atomic structure: nucleus and electrons in orbiting shells of an atom function in state of equilibrium until ionization occurs (Figure 5-1):
3. Ionization:
a. Occurs when an atom loses an electron from one of its shells and becomes part of ion pair (not unlike the celebrity world with its changing pairs); this process elicits chemical changes in matter.
B. Types of radiation: particulate and electromagnetic radiation are types of ionizing radiation:
2. Electromagnetic radiation:
b. Some forms are ionizing and others are not, depending on their energy (wavelengths) (e.g., x-rays have short wavelengths and are ionizing).
c. Arranged in a spectrum according to its energies, which is demonstrated by its wavelengths and frequencies; wave concept suggests that electromagnetic radiation is much like waves or ripples of water and involves wave frequency and length.
X-Ray Machine and Components
X-ray machine has basic operable components and internal components that are important for safe operation and functioning.
A. Basic operable components: include control panel, tubehead, position-indicating device (PID):
B. Internal components: include x-ray tube, power supply, circuit, transformer:
1. X-ray tube:
2. Power supply:
a. Electricity that provides energy to unit to produce x-rays and is described by its current, amperage, voltage.
Generation of X-Rays
A. X-ray process: involves use of both cathode and anode:
1. Cathode: negative pole in x-ray tube:
B. X-ray production:
2. Types include Bremsstrahlung and characteristic radiation:
a. Bremsstrahlung radiation:
Interaction of X-Rays with Matter
A. Photoelectric effect:
Units of Radiation Measurement
Mechanisms of Radiation Injury
A. Direct theory:
B. Indirect theory:
Factors That Determine Radiation Injury
A. Total dose: amount of radiation absorbed in the tissue that determines effect.
1. Acute exposure: ionizing radiation given in shorter amount of time; results in MORE dramatic biological effects.
B. Exposure area: amount of the body exposed to radiation, also determines biological effect of radiation on the tissues.
C. Cell types: effects of radiation are determined by cell maturity and cell type:
D. Radiosensitivity: human tissue cells have different sensitivities to radiation:
1. Radiosensitive tissues and cells are highly sensitive to radiation (e.g., bone marrow, reproductive, small lymphocyte).
E. Critical organs and radiation:
1. When sensitive organs and tissues are exposed to radiation during dental irradiation, significant decrease in quality of person’s life may occur.
2. Include skin, eye lens, thyroid, bone marrow (hematopoietic):
a. Skin irradiation may lead to erythema: FIRST clinical sign of overexposure (250 rad in 14-day period).
c. Thyroid irradiation can result in increased cancer risk, particularly when radiation exposure of 6000 mrad or more occurs.
Radiation Exposure and Risks
Radiation Protection
A. Patient: patient exposure to radiation MUST BE reduced by using filtration, collimation, positioning, shielding:
1. Filtration involves filtering-out of nonproductive x-rays; inherent filtration plus added filtration equals total filtration for the machine:
2. Collimation restricts size and shape of x-ray beam (reducing film fog) and therefore restricts patient exposure (scatter exposure):
3. The PID (beam-indicating device [BID]): aiming device that is used to direct the x-ray beam:
a. Cone-shaped PID: closed, pointed, plastic device that increases scatter radiation and should NOT be used.
4. Lead aprons or lead equivalent (contains 0.25 to 0.3 mm of lead thickness) shields; aprons worn by patients to protect tissues from scatter radiation; mandated by law in many states; should be used in conjunction with thyroid collar for intraoral films (questionable use now).
B. Clinician: measures MUST be taken to protect clinician from unnecessary radiation; include proper positioning, use of monitors, attention to proper methods of taking radiographs:
1. Positioning:
2. Monitoring:
a. Involves using personnel monitoring devices and following national guidelines when measuring occupational radiation exposure; film badges that measure exposure to low doses of radiation should be worn at waist level; two types of monitoring available.
b. Maximum permissible dose (MPD): developed by National Council on Radiation Protection (NCRP):
(3) Formula represents whole-body dose equivalent of ionizing and electromagnetic radiations and is expressed in sieverts.
Digital Imaging
A. Principles:
B. Advantages:
2. Images can be displayed immediately, which is useful for intraoperative procedures such as endodontic treatment; eliminates darkroom procedures.
CLINICAL STUDY
| Age | 42 YRS | SCENARIO |
| Sex | 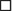 Male Male  Female Female |
The new patient’s intraoral examination reveals several suspect areas and fractured restorations on the maxillary arch. It has been at least 6 or 7 years since patient has had radiographs taken. The dental hygienist recommends a full-mouth series (FMX). However, the patient is reluctant because of what she has heard about the dangers and misuse of radiation. |
| Height | 5′4″ | |
| Weight | 170 LBS | |
| BP | 118/76 | |
| Chief Complaint | “Boy, the fillings in my upper back teeth are so sensitive! They feel like they are moving when I bite down.” | |
| Medical History |
1. What is the most probable diagnosis of the patient’s condition? Identify all possible causes for her symptoms. What other information should be gathered to determine the cause of the sensitivity?
1. Sinus infection and carious lesions are present. Sensitivity of maxillary teeth could be related to the closeness of the roots of maxillary teeth to enlarged, inflamed sinuses; such sensitivity should dissipate as sinusitis clears up. Movement of restorations is more serious in nature and is indicative of fractured restorations. Ill-fitting restorations often have marginal leakage and/or recurrent caries. Other information can be gained by asking: “What are the teeth sensitive to (e.g., temperature, pressure, sweets)?”, “How long have they been sensitive?”, and “Does anything seem to exacerbate or alleviate the discomfort?”
2. Benefit versus risk of having radiographs taken should be discussed with patient. Clinical examinations warrant FMX radiographs to confirm exact diagnosis and direction of proper treatment. Although minimal amount of radiation exposure occurs, benefit of diagnosis far outweighs risk of allowing carious lesions to continue without diagnosis and then treatment.
3. Devices on x-ray machine such as filter, collimator, lead-lined PID reduce radiation exposure to patient. Using lead apron or lead equivalent with thyroid collar and film-holding devices with fast-speed film (F-speed film is fastest) keeps patient exposure to minimum while providing excellent-quality diagnostic radiographs.
CHARACTERISTICS OF RADIATION IMAGES
Radiation images are characterized by their quantity, quality, intensity, clarity.
A. Quantity: number of x-rays that are produced; measured in amperes, milliampere-seconds, density of the radiographs.
B. Quality: energy and penetrating power of the beam; measured in kilovolts; affects image contrasts:
1. Kilovolt (kV): equal to 1000 volts and is measurement used to determine energy in a tubehead:
C. Beam intensity: affected by mA, kVp, exposure time, distance:
1. The mA affects intensity by controlling the number of electrons produced; higher the mA, MORE intense the beam.
2. The kVp controls energy of electrons traveling from the cathode to the anode; higher the kVp, MORE intense the beam.
3. Exposure time affects the intensity in the same manner as mA; increase in time = MORE intense beam.
4. Distance also affects beam intensity; as beam travels longer distance to film or tooth, becomes LESS intense:
D. Accurate image (geometric) formation: BEST produced by controlling image sharpness, magnification, distortion:
1. Sharpness (detail, definition): umbra is increased clarity or distinctness of outlines of object; penumbra is fuzziness or LACK of sharpness in image.
2. Magnification: enlargement of actual image:
RADIOGRAPHIC EXAMINATION
Intraoral Radiographic Views
Views include periapical (PA), bitewing (BW), occlusal, full-mouth series (FMX).
A. The PA view: captures from cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to root on the film; included in FMX; uses size 1 to 2 films:
B. The BW view: visualizes crowns, contacts, height of alveolar bone in relation to CEJ; included in FMX; uses size 1 to 2 films:
Intraoral Techniques
Intraoral radiography includes bisecting, paralleling, and occlusal techniques.
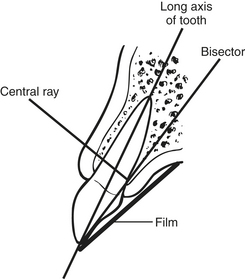
A. Bisecting (angle) technique (Figure 5-3):
1. Based on rule of isometry: two triangles are equal if they have equal angles and share common side.
2. Requires bisection of the angle, forms two equal triangles; angle formed by plane of film and plane of long axis of tooth.
C. Occlusal technique:
D. Buccal object (SLOB: Same Lingual, Opposite Buccal) rule: shows whether artifact or object is lingual or buccal; in second radiograph, if central ray is moved and object moves in same direction, then lingual, if it moves in opposite direction, buccal; used mainly in endodontics, since on PAs, roots are often superimposed on one another and require separation for proper identification so as to visualize lengths and anatomy.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 •
• 
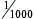 of ampere) is used.
of ampere) is used.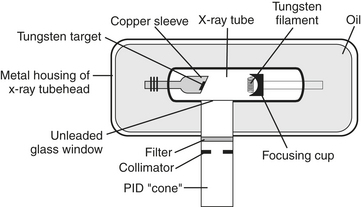
 on the CD-ROM for the ADA and FDA Guide to Patient Selection for Dental Radiographs.)
on the CD-ROM for the ADA and FDA Guide to Patient Selection for Dental Radiographs.) for WebLink to the ADA/FDA Guide to Patient Selection for Dental Radiographs, which includes the chart Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.) These guidelines will allow for ALARA concept, although each case is subject to clinical judgment.
for WebLink to the ADA/FDA Guide to Patient Selection for Dental Radiographs, which includes the chart Guidelines for Prescribing Dental Radiographs.) These guidelines will allow for ALARA concept, although each case is subject to clinical judgment.