THE NECK
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
Overview and Topographic Anatomy
GENERAL INFORMATION
The neck is the area between the base of the skull and inferior border of the mandible and the superior thoracic aperture
The anterior portion of the neck contains the major visceral structures between the head and the thorax:
• Pharynx
• Larynx
• Trachea
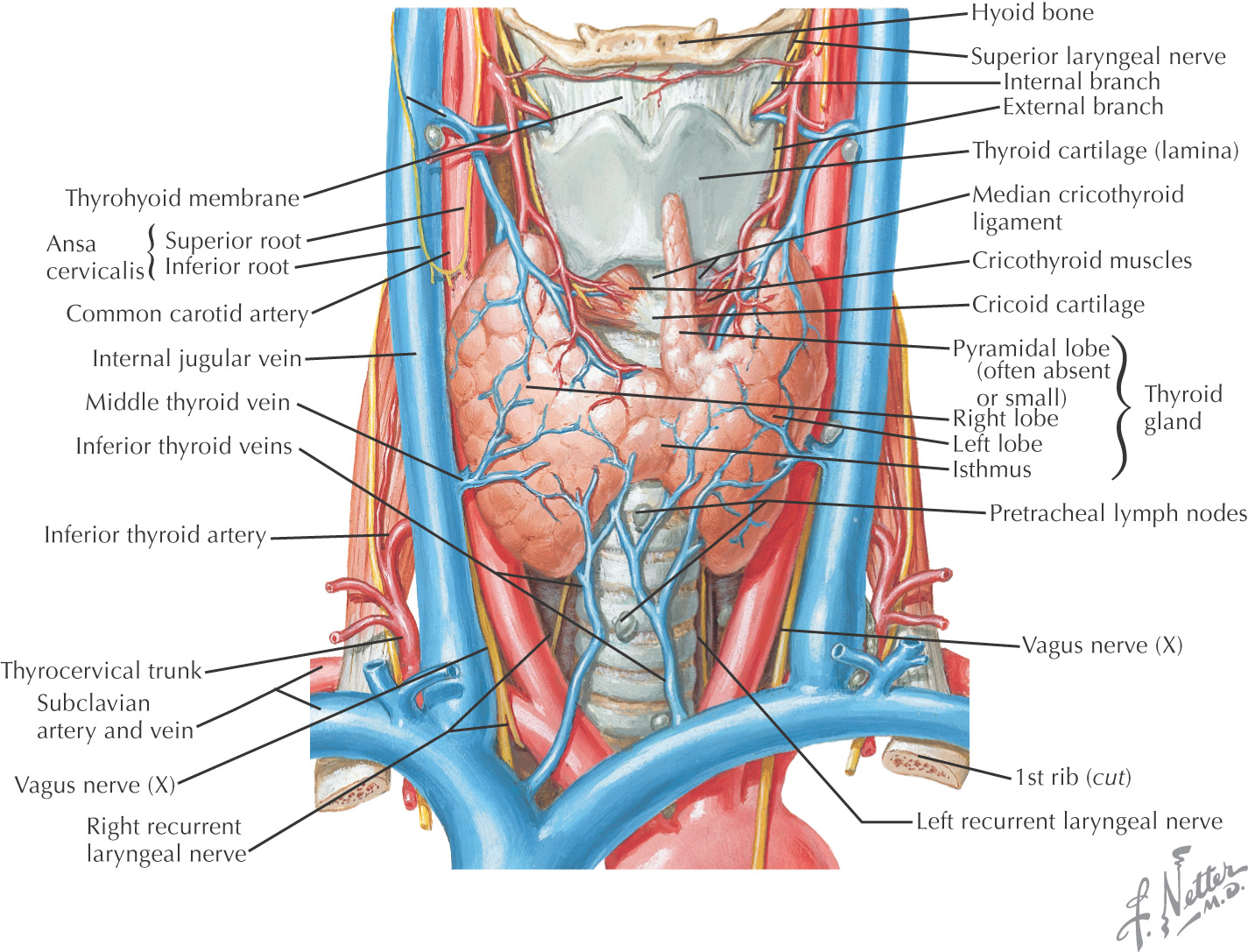
• Thyroid and parathyroid glands
For descriptive purposes, the neck is divided into 2 triangles:
Skin is the most superficial structure covering the neck
FASCIA
The neck is surrounded by 2 main layers of cervical fascia that can be further subdivided:
• Superficial layer of deep cervical fascia (investing)
• Middle layer of deep fascia (includes muscular and visceral parts such as the pretracheal)
• Deep layer of deep fascia (includes prevertebral and alar)
Superficial fascia is deep to the skin and surrounds the platysma muscle
Sensory branches to the neck are located in the superficial fascia
Deep to the superficial fascia is the investing layer of deep cervical fascia
The superficial (or investing) layer of deep cervical fascia attaches posteriorly along the midline and passes anteriorly to surround the entire neck
The superficial (or investing) layer of deep cervical fascia surrounds these muscles:
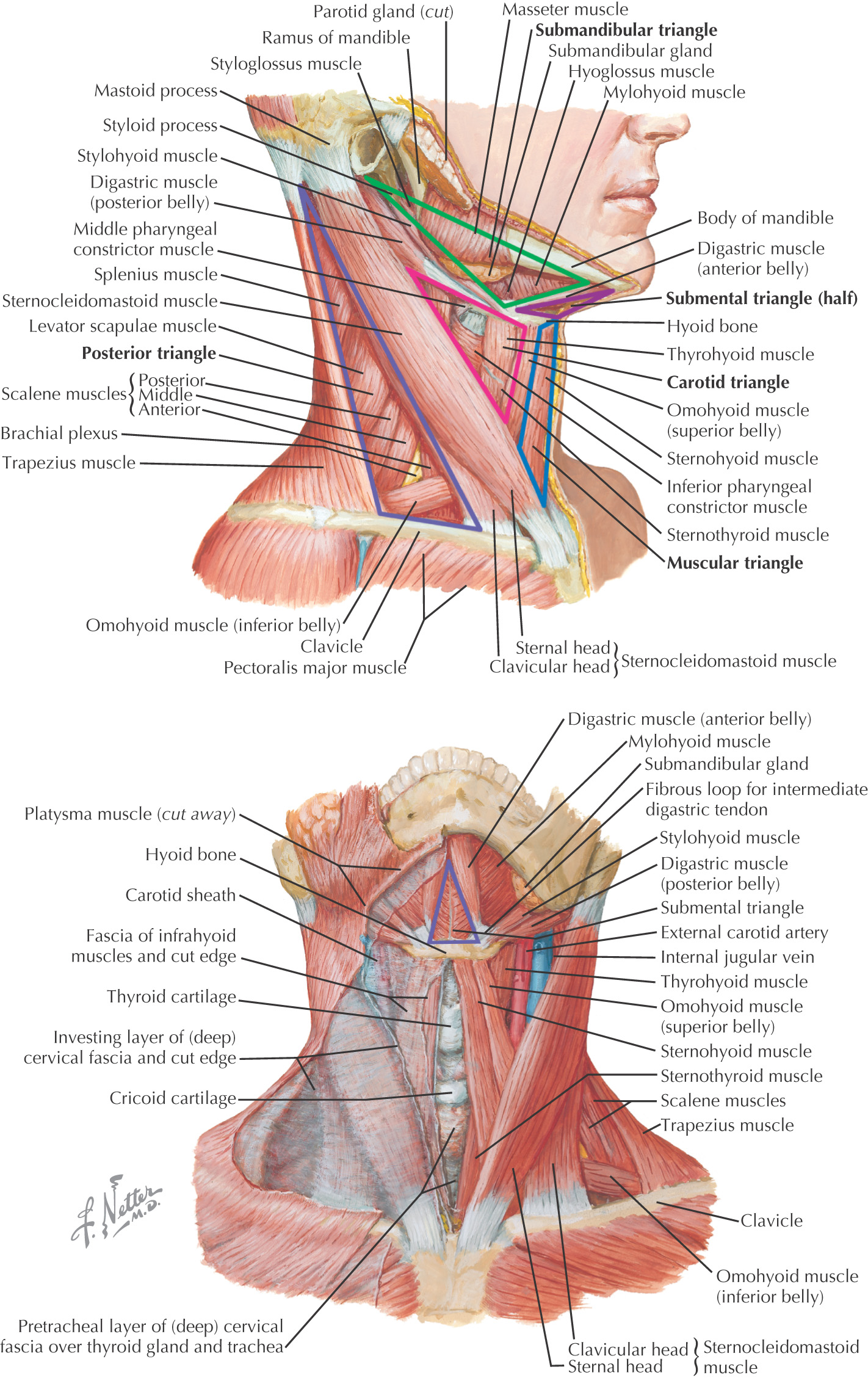
Triangles of the Neck
ANTERIOR TRIANGLE
Borders of the anterior triangle:
• Anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid
• Inferior border of the mandible
Using the hyoid as a keystone, the omohyoid and digastric muscles subdivide the anterior triangle into:
All of the triangles within the anterior triangle are paired except for the submental triangle, which spans the right and the left sides of the neck
Hyoid bone divides the anterior triangle into 2 areas: suprahyoid and infrahyoid regions
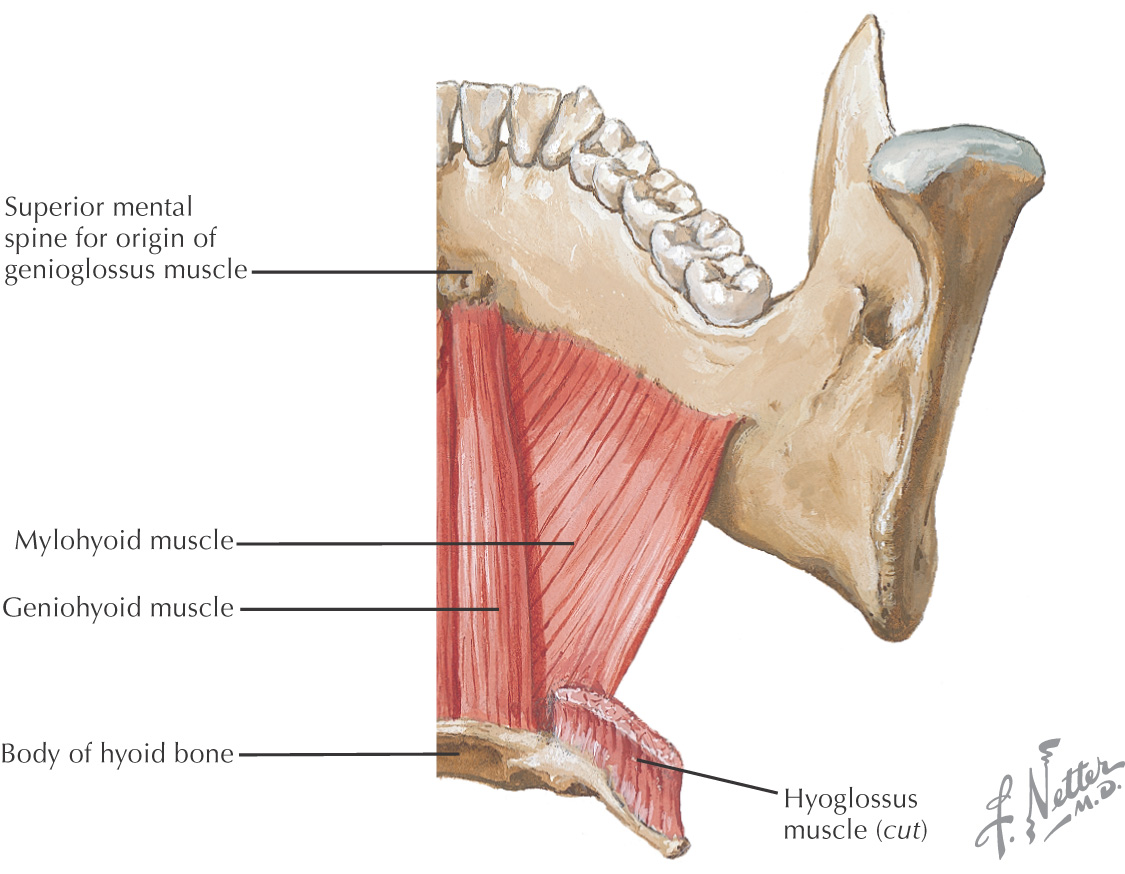
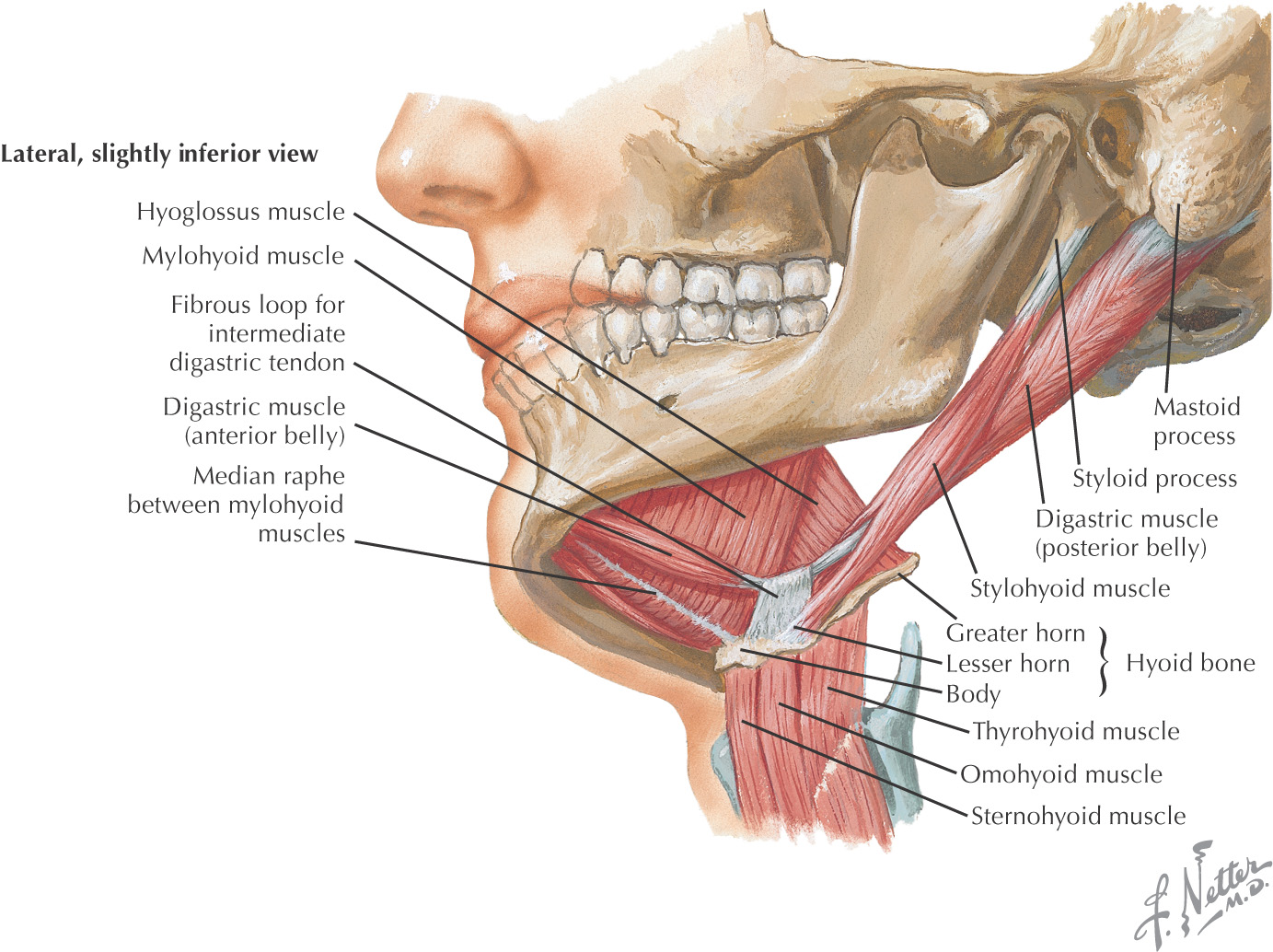
The suprahyoid region contains 4 muscles:
The infrahyoid region contains 4 muscles commonly called strap muscles:
• Omohyoid
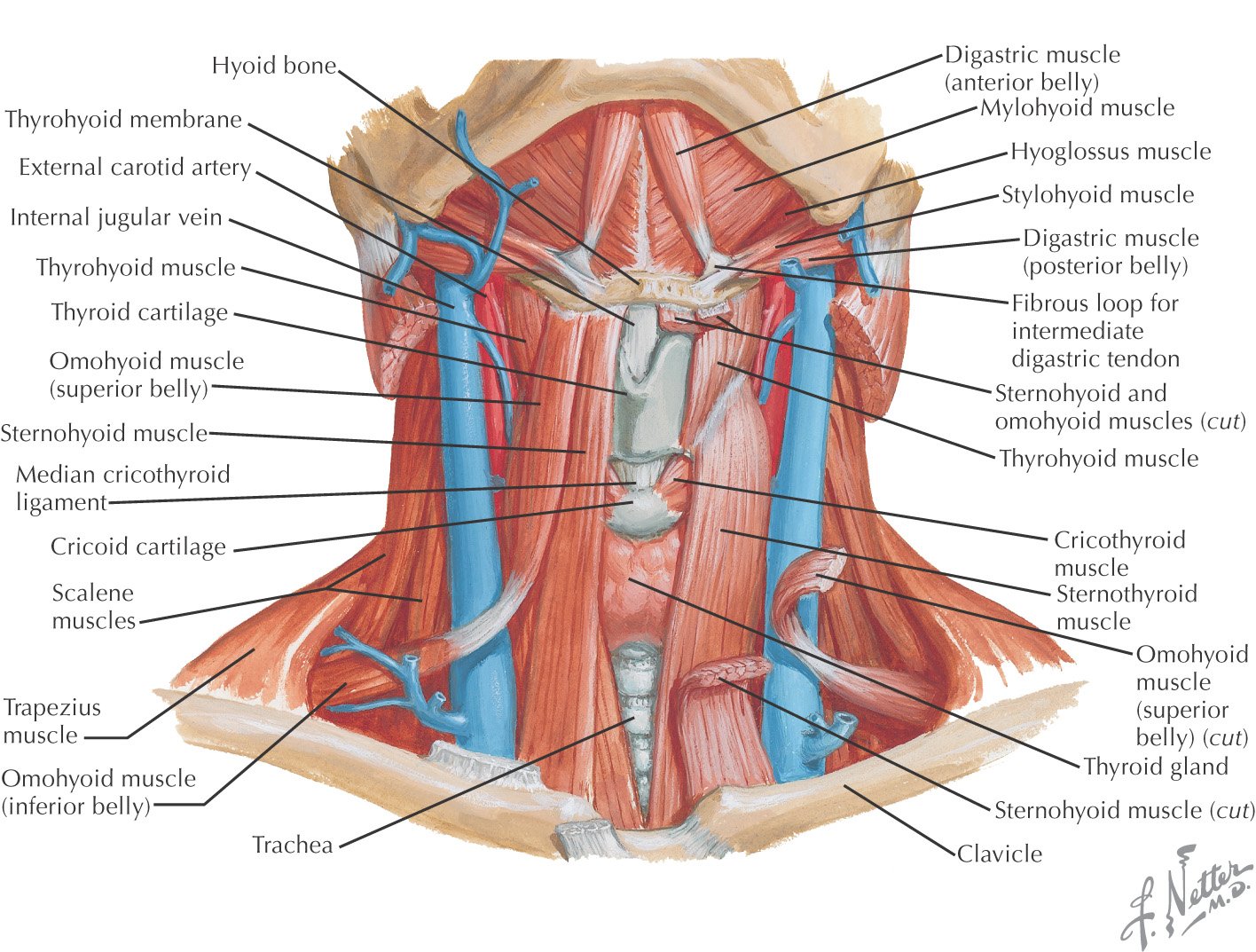
Anterior Triangle
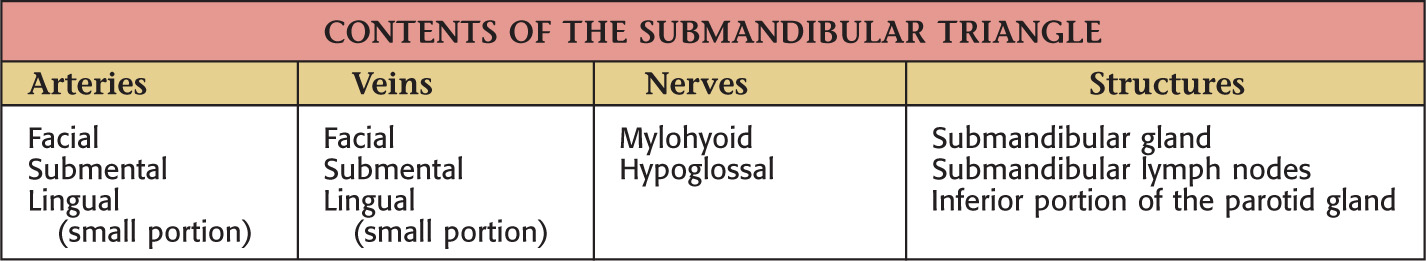
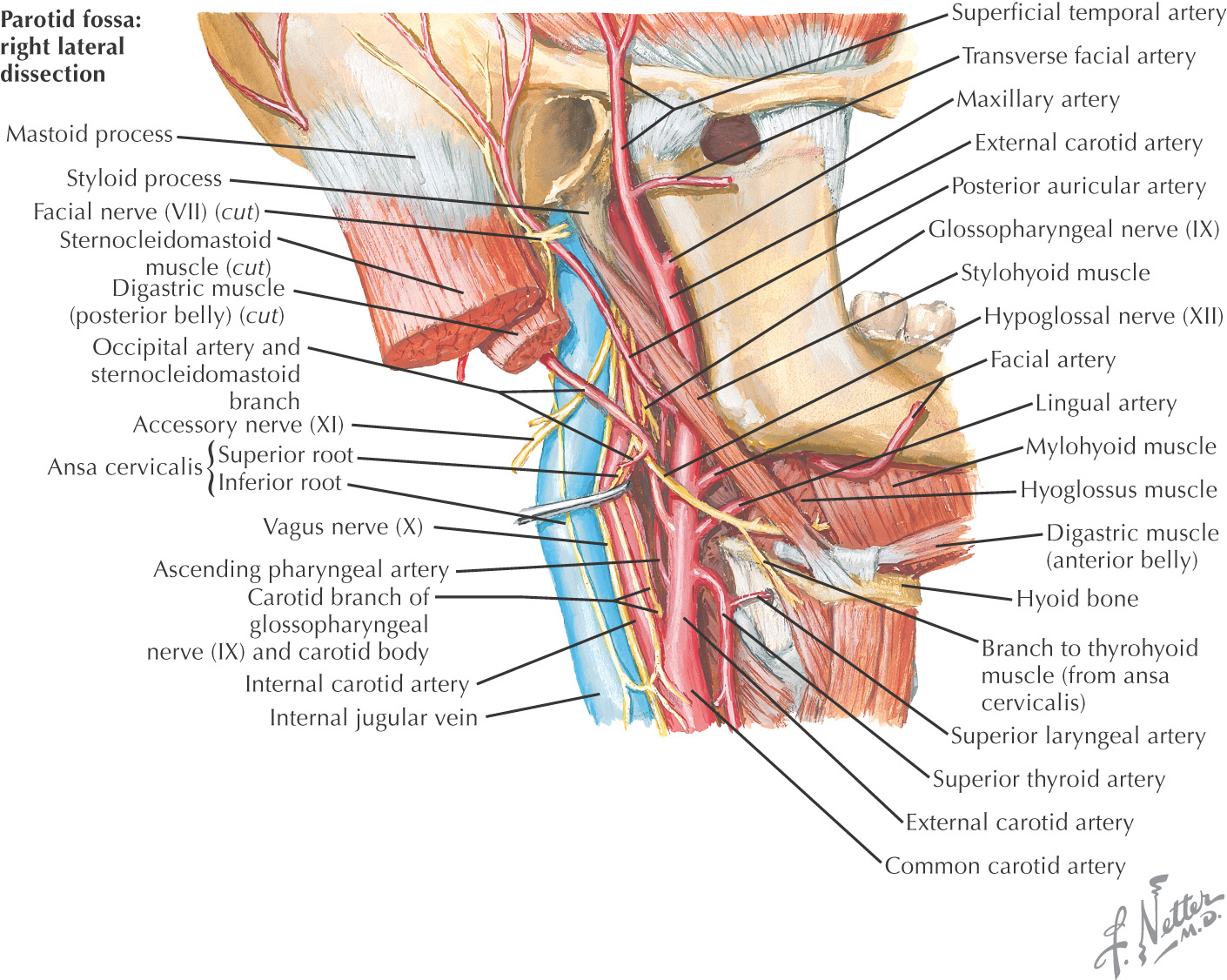
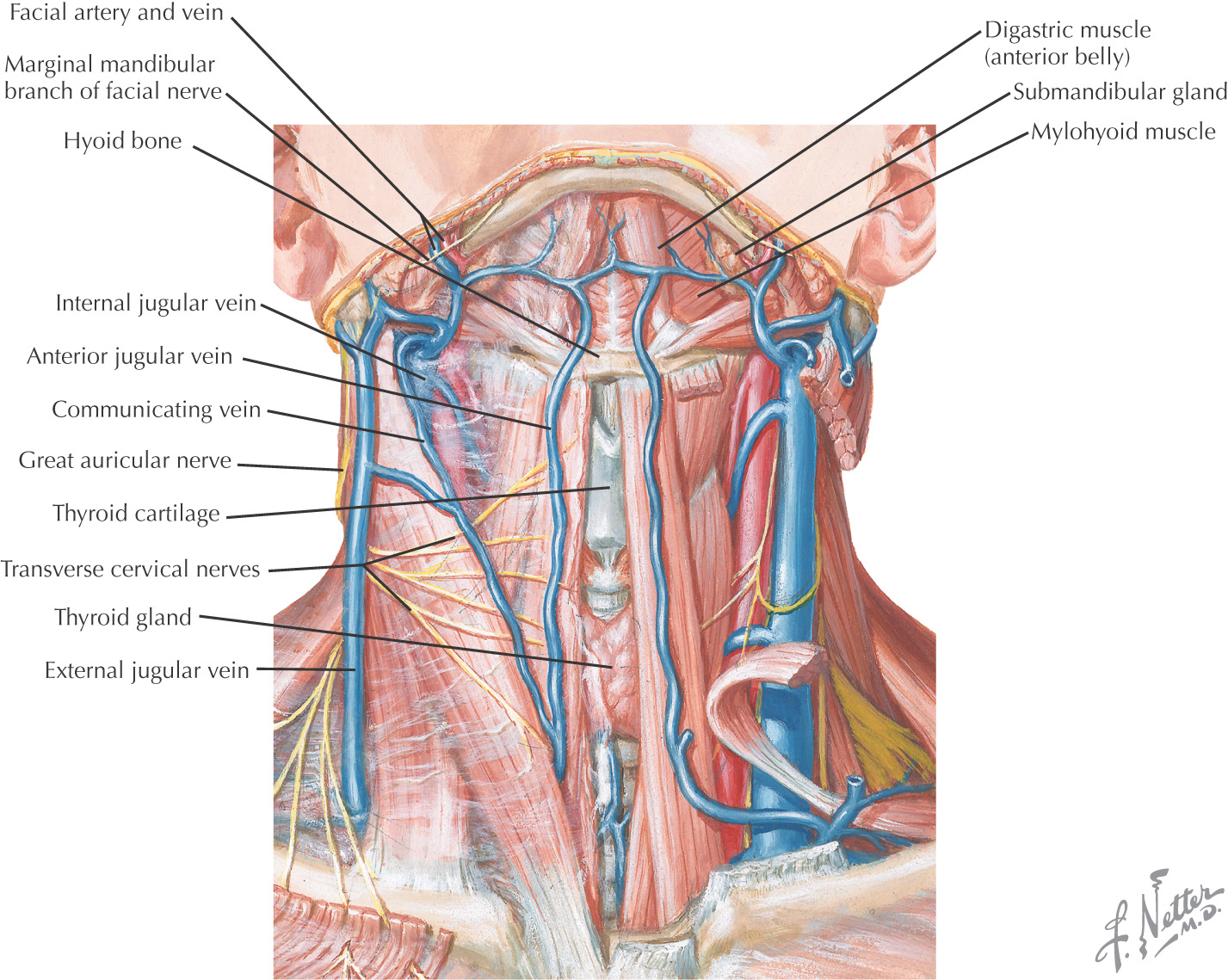
SUBMANDIBULAR TRIANGLE
Often called the digastric triangle
Borders of the submandibular triangle:
• Inferior border of the mandible
Floor of the triangle is composed of the:
Roof is made of the:
• Skin
• Superficial fascia with platysma
Submandibular triangle is paired
Lesser’s triangle is a small subdivision of the submandibular triangle, which aids in identifying the lingual artery (especially for ligation)
Boundaries of Lesser’s triangle:
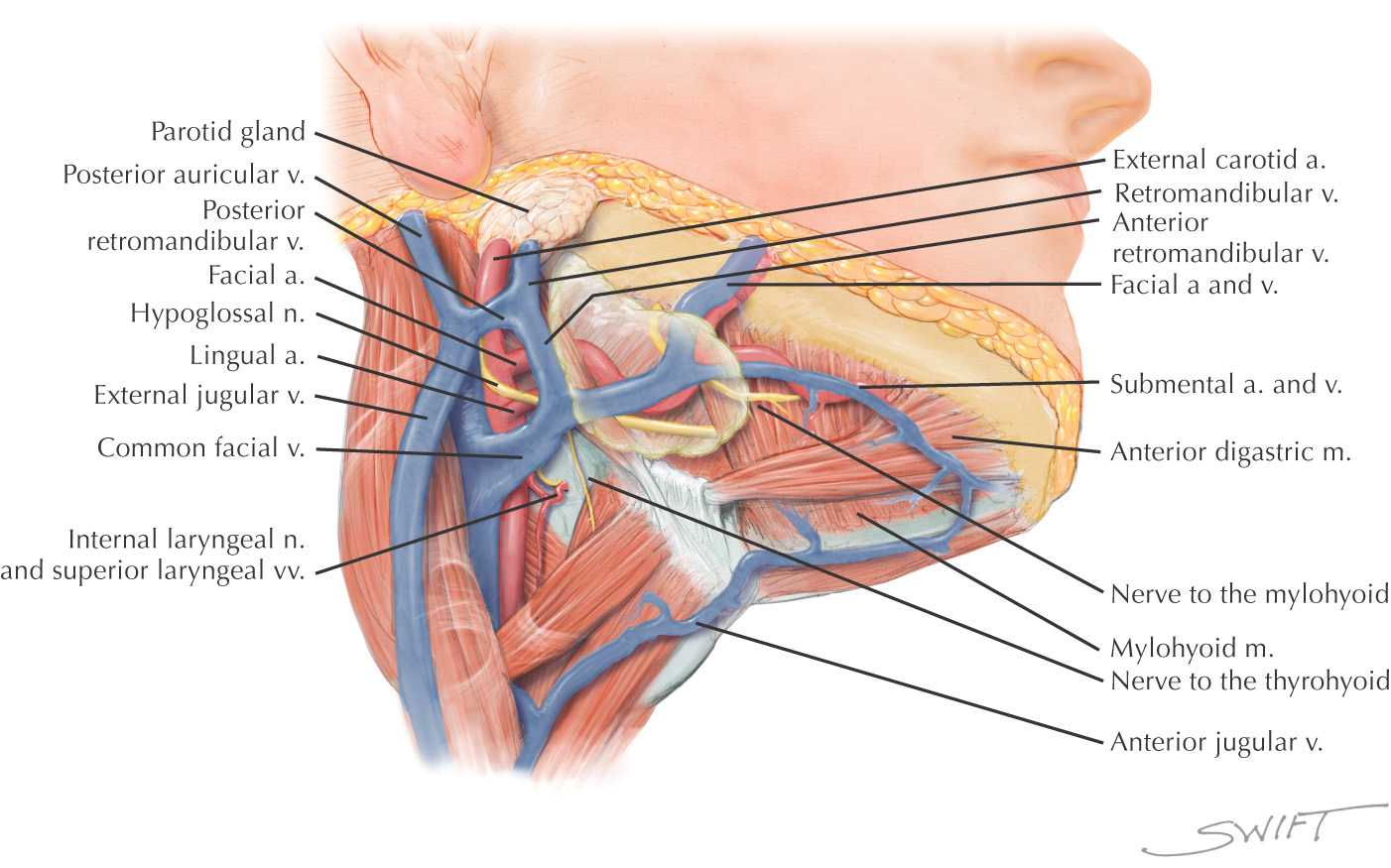
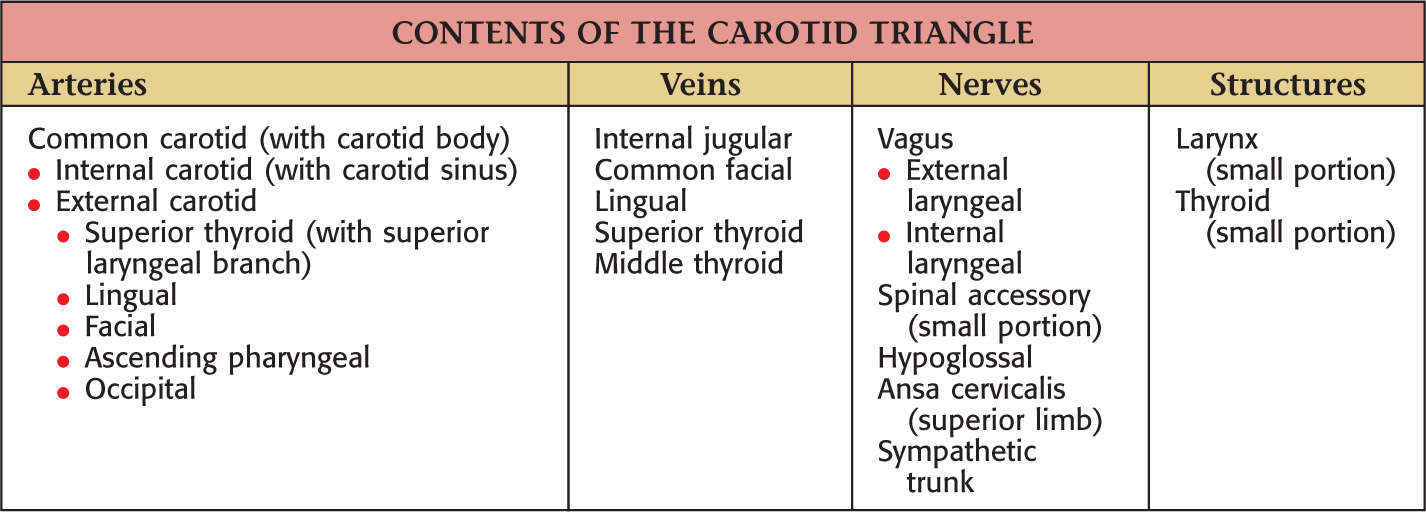
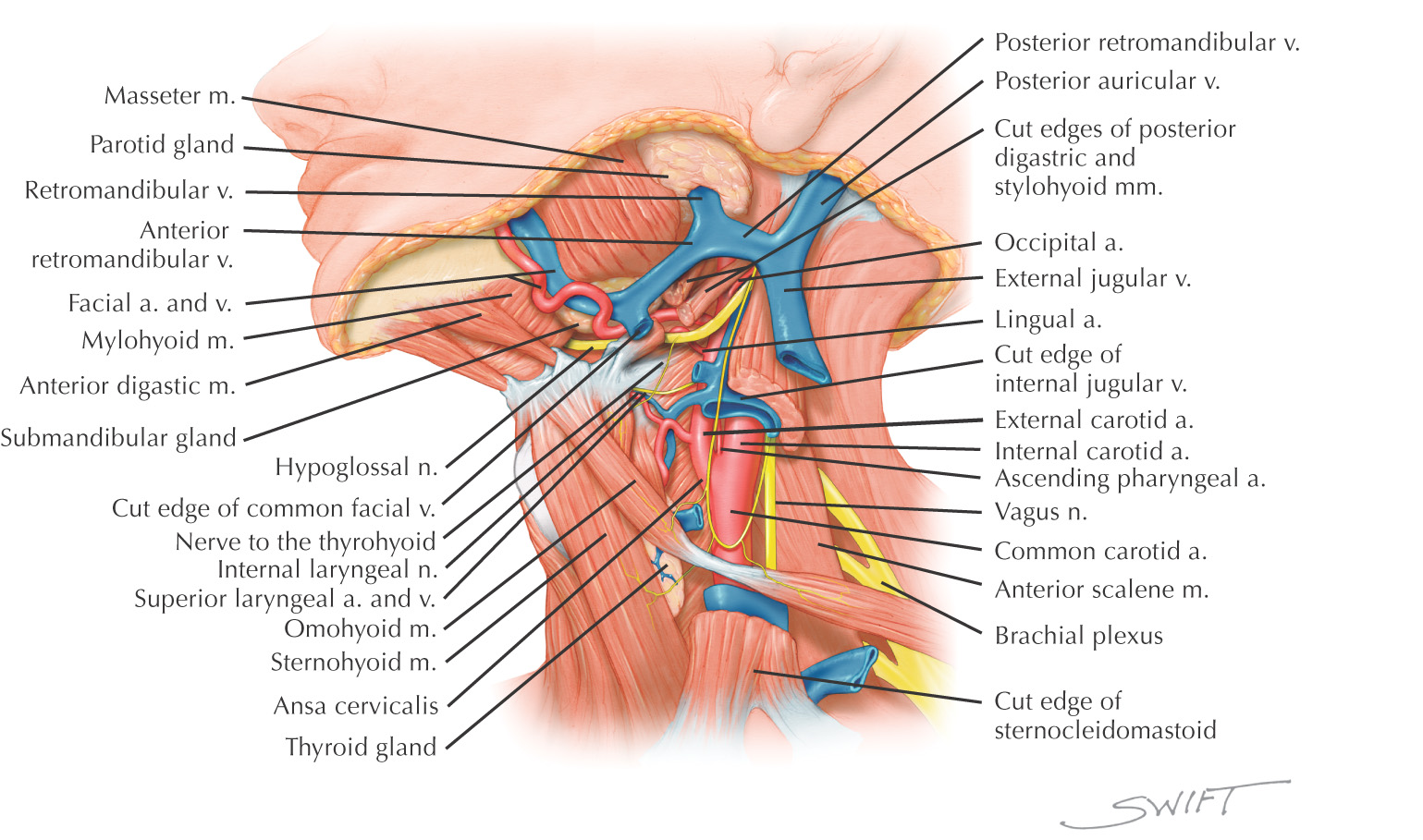
CAROTID TRIANGLE
Named because parts of all three carotid arteries are located within it
Borders of the carotid triangle:
• Anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid
Floor of the triangle is composed of the:
Roof is made of the:
• Skin
• Superficial fascia with platysma
Carotid triangle is paired
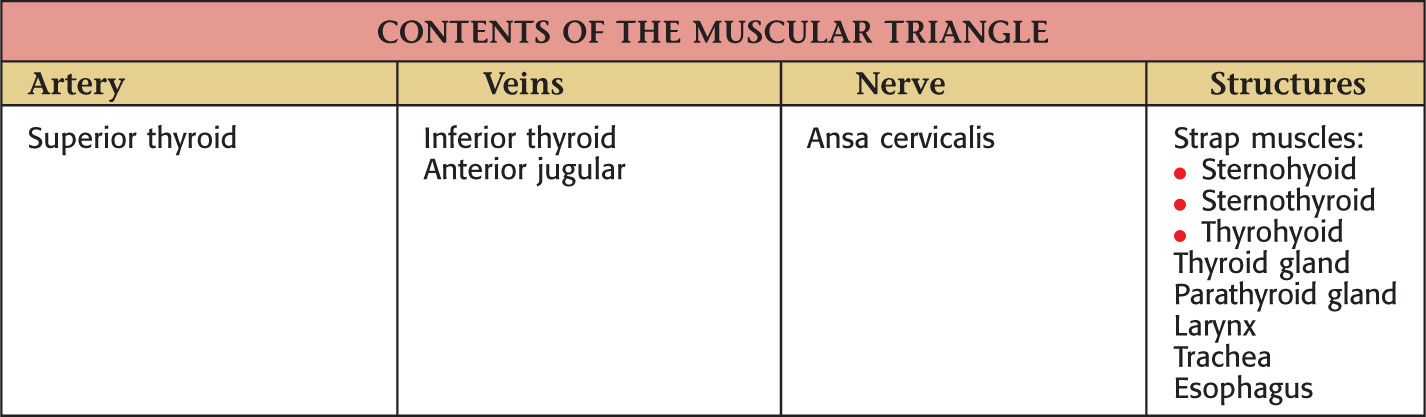
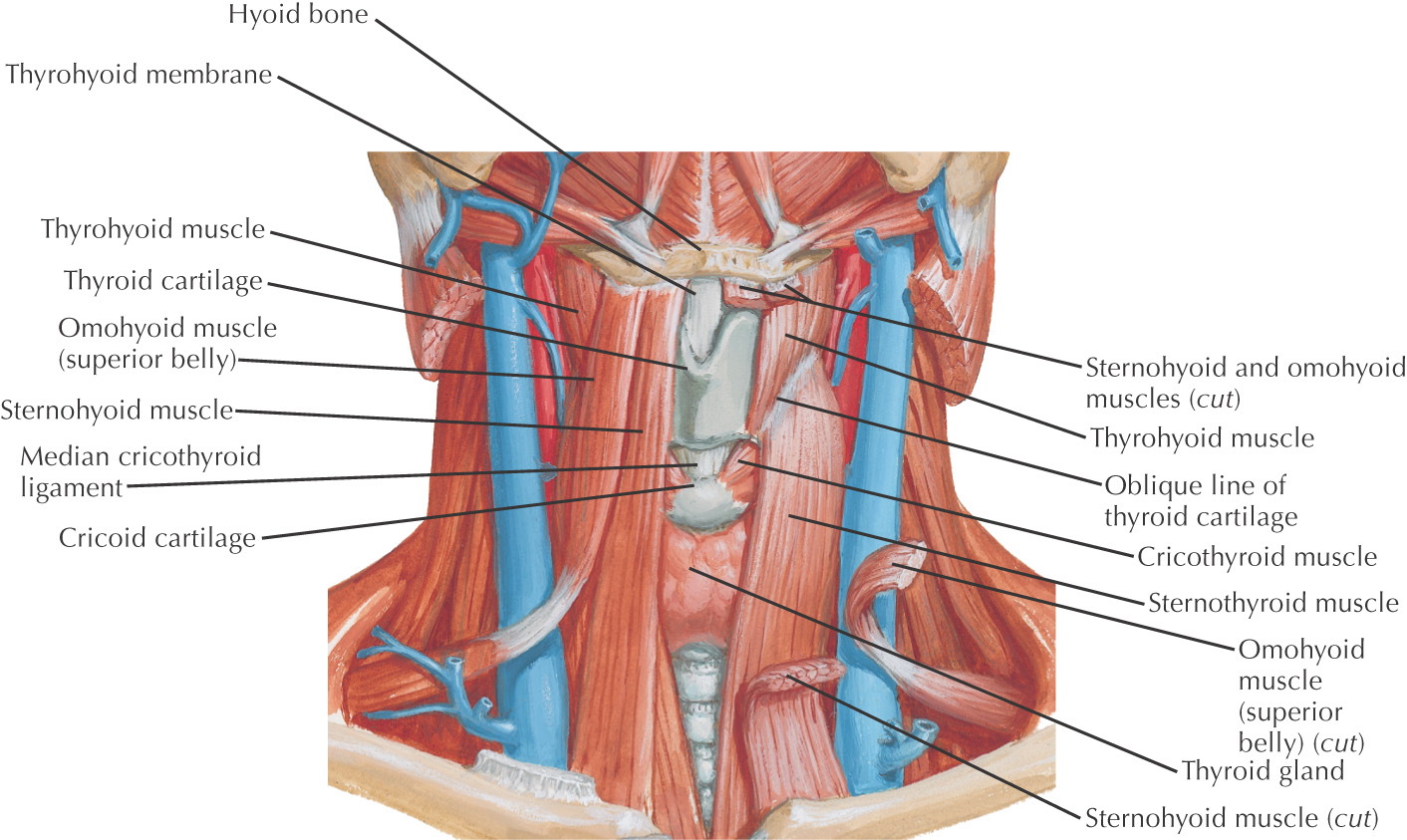
MUSCULAR TRIANGLE
Borders of the muscular triangle:
• Anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid
• Midline
Floor of the triangle is composed of the:
Roof is made of the:
• Skin
• Superficial fascia with platysma
Muscular triangle is paired
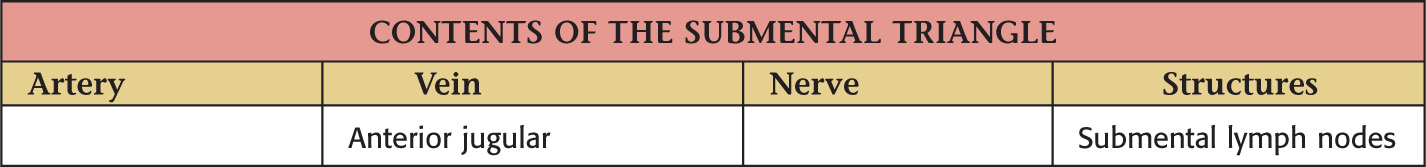
SUBMENTAL TRIANGLE
Borders of the submental triangle:
Floor of the triangle is composed of the:
Roof is made of the:
• Skin
• Superficial fascia with platysma
Submental triangle is unpaired
Posterior Triangle
GENERAL INFORMATION
Borders of the posterior triangle:
• Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid
• Middle third of the clavicle
• Anterior border of the trapezius
Located on the lateral side of the neck and spirals around the neck
Is subdivided into 2 triangles by the omohyoid:
• Omoclavicular (also called the supraclavicular triangle)
Roof of the posterior triangle includes:
• Skin
• Superficial fascia with platysma
• Superficial (investing) layer of deep cervical fascia
Floor of the posterior triangle includes*:
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


