4
Adhesion and cohesion
Figure 4.1 Adhesion and cohesion.
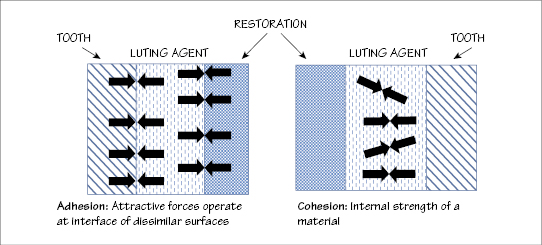
Figure 4.2 Adhesive and cohesive failures of cemented restorations.
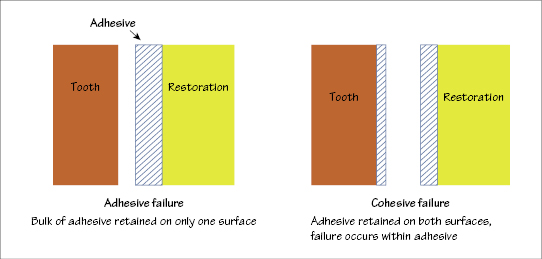
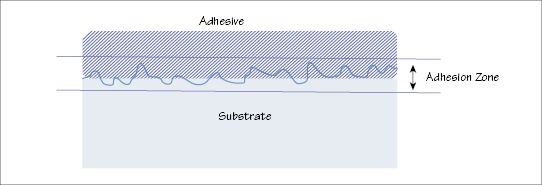
Figure 4.3 Adhesion zone between adhesive and substrate (schematic).
Box 4.1 Molecular forces determining cohesive strength of an adhesive
1 The chemical bonds within the adhesive material
2 Chemical bonds due to cross-linking of the polymer(s) within a resin-based material
3 Intermolecular interactions between the adhesive molecules
4 Mechanical bonds and interactions between the molecules in the adhesive
Table 4.1 Basic types of adhesion
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Specific | Molecular attraction between contacting surfaces |
| Mechanical | Adhesion through mechanical interlocking between adhesive and substrate surfaces |
| Effective | Bonding between adhesive and substrate due to a combination of specific and mechanical adhesion |
Table 4.2 Bond energies and bond lengths in adhesive forces
| Average bond energy (kJ/mol) |
Average bond length (nm) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Ionic bond | 600 | 0.25 |
| Covalent bond | 550 | 0.15 |
| Metallic bond | 250 | 0.40 |
| Hydrog/> |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


