Chapter 3
Temporary restorative materials
Certain dental cements mixed to a base or putty-like consistency can be used as temporary restorative materials, and there are other materials available that have temporary filling as their main function.
Provisional or temporary crown materials are also considered temporary restorative materials but will not be discussed in this chapter.
CAVITTM
CAVITTM (3M ESPE) is a self-cure, temporary restorative material (Figure 3.1).
Figure 3.1 CAVITTM – 3M ESPE.
Material constituents/composition
- Zinc oxide
- Calcium sulphate
- Barium sulphate
- Talc
- Ethylene bis(oxyethylene) diacetate
- Zinc sulphate
- Poly(vinyl acetate)
Properties
- Self-cure
- Packable
- Radiopaque
- Available in light curable form
Advantages
- No manipulation required
- Easy to place
Disadvantages
- Is not suitable for ‘shallow’ restorations
Indications and contraindications for use
Indications
- Temporary restorations
- Inlay and onlay temporary restorations
Contraindications
- Not indicated for use in areas less than 3–5 millimetres thick
Manipulation
Wearing personal protective equipment.
Once the tooth is prepared for restoration:
- Dispense the required amount of CAVITTM on a waxed paper pad using a sterile instrument
- Transfer to the operator with a flat plastic instrument or operators instrument of choice
- The operator will place the material into the cavity preparation
- Be prepared with a piece of gauze to wipe excess material from the blunt instrument
- Dispose of any waste material and waxed paper pad in the contaminated waste bin (Figure 3.2)
- No mixing required
Figure 3.2 Step 1 – CAVITTM – 3M ESPE dispensed.
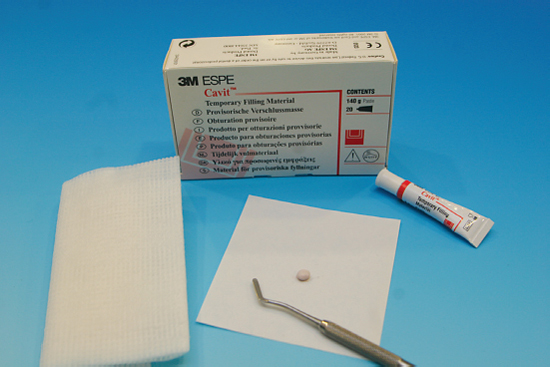
Instruments and materials used in set-up
Materials used in set-up:
- Waxed paper pad
- CAVITTM material
- Flat plastic instrument
ZINC OXIDE EUGENOL
Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE) may be used as a base, a temporary restorative material, a temporary luting agent, impression material, bite registration material, an endodontic sealer or a periodontal dressing. In this chapter, ZOE will be discussed in the/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


