28
Inorganic (acid–base reaction) cements
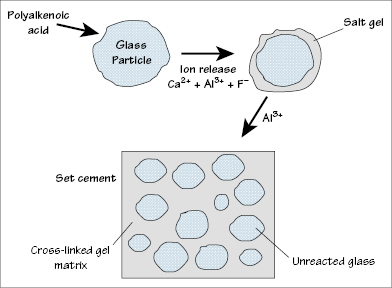
Figure 28.1 Setting reaction of glass ionomer cement (GIC).
Box 28.1 Types of permanent dental cement
Zinc phosphate
Zinc polycarboxylate
Glass ionomer
Calcium aluminate/glass ionomer
Hybrid (resin-reinforced) ionomer
Resin
Table 28.1 Approximate composition of zinc phosphate (ZNP) cement
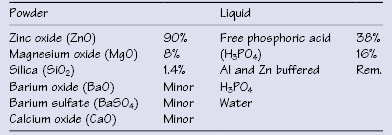
Table 28.2 Average properties of inorganic cements
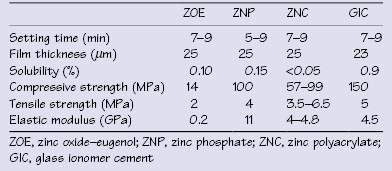
Table 28.3 Zinc polycarboxylate and GIC characteristics compared with those of zinc phosphate (ZNP) cement
| Characteristic | Zinc polycarboxylate | Glass ionomer cement |
|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | Same or slightly greater | Same or slightly less |
| Compressive strength | Lower | Greater |
| Tensile strength | Greater | Lower (GICs tend to be brittle) |
| Solubility | Lower | Greater |
| Working time | Comparable | Slightly shorter |
| Setting time | Comparable | Longer (requires initial isolation) |
| Bonding (ZNP only bonds mechanically) | Mechanical, some chemical | Mechanical and chemical |
| Biological reactions |
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


